Chapter 3 Time Value of Money Part 2
advertisement

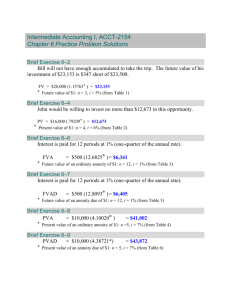
Chapter 3 Time Value of Money Part 2 Learning Objectives Explain and Illustrate an Annuity Determine Future Value of an Annuity Determine Present Value of an Annuity Present Value of Annuity Stream Adjust formulas for Annuity Due Distinguish between different loan types Build an Amortization Schedule Calculate Waiting Time and Interest Rates for an Annuity Future Value of Stream of Payments Different Amounts at Different Times Use FV formula over and over Add up each value for Future Value Note money can only be “added” at same point in time Is there a short-cut? Sometimes…yes Annuity Stream Same amount at same interval Future Value of Multiple Cash Flow Same Amount each time and same time interval between each cash flow Shortcut – Annuity Stream Evaluation Visualize with time line – page 47 Future Value of Multiple Cash Flow Three methods again for finding FV Formula or Equation Method Calculator Method Spreadsheet Method Example 3.1 Scholarship for Lisa $1,500 annual payment into scholarship fund Earns 7% interest over 18 years FV is approximately $51,000 Present Value of Annuity Stream A similar shortcut for present value Three methods but basic same equation Ordinary Annuity versus Annuity Due Need to visualize the difference between an annuity at the start of the period versus and annuity at the end of a period Start of Period – Annuity Due Example rent payment End of Period – Ordinary Annuity Example car payment Original Formulas for Ordinary Annuity Adjustment for Annuity Due – multiply by (1+r) Perpetuities Never Ending Annuity Stream How can you handle an infinite number of payments? Formula reduces to: Amortization Schedule Typical consumer loans make equal payments every period What is the balance (principal) at the end of any month if some of the payment is for interest and some for principal reduction? Amortization Schedule shows each payments application to interest expense and principal reduction Three Payment Methods All loans contain a repayment of the original amount (principal) and cost of borrowed money (interest) Types of repayment Interest and Principal at Maturity Interest as you go, Principal at Maturity Interest and Principal as you go Why the difference in interest? Table 3.1 Amortization Schedule How to build an amortization schedule Step One – Determine the payment for each period given number of periods (n), interest rate (r), and the present value (PV). Step Two – Determine each periods required interest payment Outstanding Balance x Interest rate = Interest expense Step Three – Determine principal reduction Payment – Interest expense = Principal Reduction Step Four – Determine remaining principal Beginning of Period Principal – Principal reduction = End of Period Principal Step Five – Repeat Steps Two through Four, n-1 times Waiting Time Same shortcut for Waiting Time, find n with an annuity stream Finding Interest Rates with Annuities Interest Rate with Annuities Can not isolate interest rate variable Must use an iterative process Try one interest rate and see if it works… Try another interest rate and see if it works… Try another interest rate and see if it works… Keep going until you find the correct interest rate. OR Use a calculator or spreadsheet and let it do the iterative process Homework Problem 9 – Lease versus Buy with TVM Problem 15 – Future Value Problem 17 – Present Value Problem 20 – Payments Problem 25 – Amortization Schedule