PowerPoint - SASD Teacher Websites

WWII
The Rise of Hitler
Bell Work
• YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK TODAY!
• What comes to mind when you think of WWII?
• Try to come up with 10
Please write this definition into your notes.
• Totalitarian State: government in which a one-party dictatorship regulates every aspect of citizens’ lives.
• Components: a) There is only one political party to choose from b) The state controls the economy c) Police and spies are used to enforce the will of the state d) The media is censored and controlled by the government e) Schools and the media are used to indoctrinate and mobilize citizens f) Unquestioning obedience to a single leader
Title:
How did Hitler gain control of Germany and build a totalitarian state?
The story of how Hitler came to power and what he did once he had it, is one of the most powerful stories in history. As we learn this story, we will treat it like a novel – charting his rise to power, the climax of his control over the German people in the Kristallnacht, and the falling action following this event.
• Directions
• First we will look at conditions in Germany at the end of WWI
• Then, we will popcorn through
p. 762-765 and use the graphic organizer to answer our central question.
Germany after WWI
• After WWI, the Kaiser abdicated his throne and the
German government was placed in the hands of the
Weimar Republic, a democratically elected body with a constitution BUT it is filled with weak leaders who constantly fight each other. the German economy is experiencing debt and inflation due to the terms in the
Treaty of Versailles which the Weimar Republic was forced to sign after WWI. Adding insult to injury, the terms of the treaty also forced the Germans to accept all blame for WWI. The German people are angry with the Weimar Republic for signing the Treaty of
Versailles and the people want to find another
Bismarck who will restore Germany to her former greatness
Bell Work
• YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK
• Can you solve the riddle????
• You grasp my handle and give me a push. I rotate and roll, doing my job. You put pressure on me and I cause division.
Then you can enjoy the fruits of my labor, while I lie, cast aside, feeling cheesy and red of face.
• What am I?
Directions
• Continue with the story map
• What is the Author’s Theme?
• Assignment: please write this response on the back of your story map.
• Answer our title question in no less than one paragraph
• Include – What lesson can be learned by studying Hitler’s rise to power? In other words, how can you apply the author’s theme to your life?
• Hand in when finished = MAY-K it!
Propaganda
Bell Work
• Please pick up a Propaganda Notes Sheet from the front table
• Then please sign out an ipad from the cart and go to Mrs. V’s
Website http://teachers.sheboygan.k12.wi.us/lvandeven/
• Then go to the Western Civ Resources page and scroll to the bottom
• Open the Propaganda Class Examples file
How would you define this?
• What is propaganda?
10 Propaganda Techniques
1.
Name calling
2.
Glittering generalities
3.
Euphemisms
4.
Transfer
5.
Testimonial
6.
Plain folks
7.
Bandwagon
8.
Fear
9.
Bad logic
10.
Unwarranted extrapolation
These techniques encourage you:
To follow non-rational, emotional drives
To NOT question the information presented
To use a “we” v. “them” mentality
Name Calling
• Links a person, or idea, to a negative symbol to get the audience to reject the person
• The most obvious type of name calling involves bad names.
Example:
• Fascist
• Pig
• Yuppie
• Bum
• Queer
• Terrorist
Glittering Generalities
• Name Calling in reverse
• "Associating something with a 'virtue word' and creating acceptance and approval without examination of the evidence."
• Vague, broad statements that will connect with your beliefs and values but they don’t really say anything of substance.
• Example:
• Think of peace, freedom, justice, family values, etc.
• “I stand for the American Dream.”
Euphemisms
• Attempts to pacify the audience in order to make an unpleasant reality more palatable. This is accomplished by using words that are bland and euphemistic.
• Example:
• Collateral damage
• Final solution
• War Department -> Department of Defense etc.
Transfer
• "Carries the respect and authority of something respected to something else to make it accepted. Also works with something that is disrespected."
• This is an effort to transfer your approval of something you respect to another something that the propagandist wants you to approve of.
• Example:
• Using a flag as a background for photographs helps.
• “I know the president, my opponent spends time with dictators” etc.
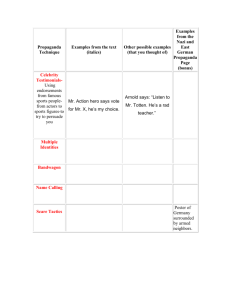
Testimonial
• ”Having some respected or hated person say that a given idea/program/product is good or bad.”
• Example:
• Pop celebrities telling you who to vote for.
• Remember that testimonials aren't worth much, particularly if the endorser is not an authority in the field.
• Michael Jordan wants you to buy Nike shoes
Plain Folks
• "The method by which a speaker attempts to convince the audience that their ideas are good because they are 'of the people,' the 'plain folks.'"
• The person speaking wants to look like the "everyman.”
• Careful choice of clothing, vocabulary, and mannerisms is necessary to make the identity connection.
• Example:
• Wearing flannel and jeans in Iowa when you really wear expensive suits
Bandwagon
• “Everyone else is doing it, and so should you."
• Few of us want to be left behind
• Example:
• Rent a stadium and fill it with people, make sure the media is there to see all of it
• Use symbols, colors, music, movement, all the dramatic arts.
• Addresses specific groups held together by common ties of nationality, religion, race, sex, vocation.
Fear
• Disaster will result if they do not follow a particular course of action
• Example:
• "The streets of our country are in turmoil. The universities are filled with students rebelling and rioting. Communists are seeking to destroy our country. Russia is threatening us with her might, and the Republic is in danger. Yes - danger from within and without. We need law and order! Without it our nation cannot survive." - Adolf Hitler, 1932
Bad Logic
• Drawing bad conclusions by forcing together facts that don’t necessarily go together
• Example:
• Premise 1: All Christians believe in God.
• Premise 2: All Muslims believe in God.
• Conclusion: All Christians are Muslims.
or
• Premise 1: Hillary Clinton supports gun-control legislation.
• Premise 2: All fascist regimes of the twentieth century have passed gun-control legislation.
• Conclusion: Hillary Clinton is a fascist.
Unwarranted Extrapolation
• Making predictions about the future on the basis of a few small facts.
• Usually used to give a basis to a fear-appeal
• Example:
• “If you allow women to vote, men will lose all of their jobs and be forced to stay at home while their wives go to work and our society will crumble!”
What are the techniques used in this modern example of propaganda?
Try out your analytical skills on
Nazi propaganda
• Open the file Nazi Propaganda
• For each item answer the following: (questions on your note sheet)
1.
What does it want the viewer to believe or do?
2.
What techniques are used by the item?
3.
Is this an effective example of propaganda?
A 1932 election poster
Opponents were using bright flashy colors in their posters
'The seed of peace, not dragon's teeth' cartoon of
Hitler, from the magazine
Kladderadatsch, 22 March
1936
'One People, One Nation,
One Leader!' poster of
Hitler, 1938
The poster for the 'Eternal
Jews' exhibition, 1937
On your own…
• Using the ipad click on the Nazi Propaganda Website link on
Mrs. V’s website
• Look through the database and choose 2 images and answer the following questions (questions on your note sheet) regarding those images
1.
Title of piece.
2.
What does it want the viewer to believe or do?
3.
What techniques are used by the item?
4.
Is this an effective example of propaganda?
• You will be asked to share one of your items and your analysis of it tomorrow with the rest of the class
Nuremberg research project
Your Challenge
• In groups of 3 or less, you will choose to research of the following 8 possible Nazi Leaders
• Then create a PowerPoint which you will share with the class
Counts
• 4 Charges
1.
The first was Conspiracy to Wage Aggressive War.
2.
The second charge was Crimes Against Peace, including the violation of treaties and other agreements.
3.
The third count was War Crimes, such as the use of slave labor and the unfair treatment of prisoners of war.
4.
The fourth count was Crimes Against Humanity, which involved the events in concentration and death camps, as well as other vicious attacks on civilians.