Cellular Respiration & Lung Capacity Worksheet
advertisement

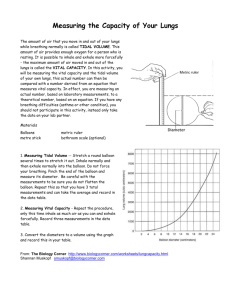
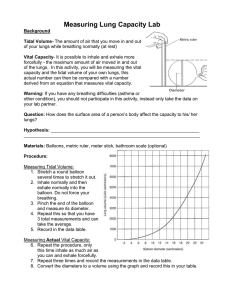
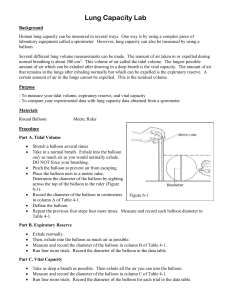
Name: ____________________________ Cellular respiration Before you collect the materials to begin the practical activity you need to answer the following questions and show me. This will help you to revise the material we covered last week. 1. In plant cells the chloroplasts use light energy to convert _____________ and __________ into __________ and ___________. This is how a plant creates its own food. 2. In animal and plant cells the mitochondria are responsible for converting ________ and _________ into ____________ and _________. This is how the cell creates energy. 3. When we breathe in we inhale _________ and when we breathe out we exhale ______________. Practical Investigation Measuring Lung Capacity Introduction: The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is called TIDAL VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume of your own lungs. If you have any breathing difficulties (asthma or other condition), you should not participate in this activity, instead only take the data on your lab partner. Name: ____________________________ Investigation: The aim of today’s investigation is for you to find out how gender (Male vs. Female) and height affect a person’s lung capacity. Materials: - Balloons - Metric ruler - Tape measure Name: ____________________________ Method: The steps you need to take... 1. Measuring your height. Use one of the tape measures to record you height. My height is __________ centimetres. 2. Measuring Tidal Volume: - blow up a round balloon several times to stretch it out. - Inhale normally and then exhale normally into the balloon. Do not force your breathing. - Pinch the end of the balloon and measure its diameter. - Repeat this so that you have 3 total measurements and can take the average and record in the data table. 3. Measuring Vital Capacity Repeat the procedure above, only this time inhale as much air as you can and exhale forcefully. Record three measurements in the data table. 4. Convert the diameters to a volume using the graph on the second page and record this in your table. 5. Once you have recorded your results come and show me so I can record each class member’s results to share with the rest of the class. Results: Record your results in this table. Tidal Volume Balloon Volume diameter 1 2 3 Average Vital Capacity Balloon Volume diameter Name: ____________________________ Writing Your Report: You must write up a report for this investigation. You can do this in your book or on your netbook. - You MUST include the following sections and answer the questions; 1. Aim What was the aim of your investigation? What were we trying to find out? 2. Hypothesis How did you expect gender and height to affect lung capacity? Why? 3. Materials What materials did you use? 4. Method What steps did you take to carry out your investigation? Why did you have to stretch out the balloon first? Why did you measure your tidal volume and vital capacity 3 times? 5. Results What results did you obtain from the investigation? What was your average tidal volume and vital capacity? What was the average vital capacity for boys? And girls? Did tall people or shorter people have the highest vital capacity? 6. Conclusion How did gender and height affect lung capacity? Why do you think this happened? When you have finished your report you need to hand it in or email it to mrspencer9@yahoo.com.au