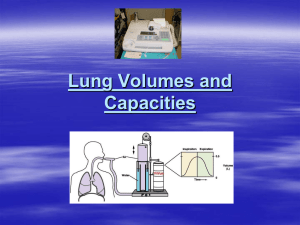
1- Total lung capacity
advertisement

المحاضرة السادسة 1- Total lung capacity: = tidal volume + inspriatory reserve volume + expiratory reserve volume + residual volume ( 6 liters) 2- Normal Capacity (Functional Residual Capacity): This is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expriation. It comprises the expiratory reserve volume + the residual volume (2-3 liters). 3- The Inspiration Capacity: It is the volume of air taken by maximal inspiration at the end of a normal expiration, it equals the tidal volume + the inspiratory reserve. 4- The vital capacity: It is the volume of air exhaled by a maximal expiration after a maximal inspiration (i.e. tidal volume + inspiratory reserve V. + expiratory reserve. V.) 5 liters. Dead Space: The Dead Space CO 2 in alveolar CO 2 in Expired Tidal air CO 2 in Alveolar Factors Affecting Vital Capacity (V.C.) : 1) Condition of respiratory muscles 2) Posture 3) Elasticity of the lung 4) Expansion and recoil of the thoracic cage 5) Volume of blood in pulmonary circulation 6) Resistance to Air Flow in Respimwry passages Orthopnoea : This is difficulty in respiration when lying down but not when standing or sitting. It occurs in left sided heart failure. It is due to decreased V.C. caused by : . 1. Pressure of viscera on the diaphragm when lying down 2. Increase and stagnation of blood in pulmonary circulation due to the left heart failure, 3. After cardiac surgery Composition of inspired, expired and alveolar air Gas Oxygen % Inspired air % Expired air % Alveolar air 20.94 16.3 14.6 CO2 N2 Water vapor 0.03 79.03 0.50 4.0 79.7 6.2 5.2 79.7 6.2 Partial pressure and tension of gases in inspired air, expired air and alveolar air: Gas Inspired air O2 159 m.m. Hg 0.15 3.85 597 760 CO2 H2O N2 Summation Expired air Alveolar air 120 104 27 47 566 760 40 47 569 760 m.m. Hg