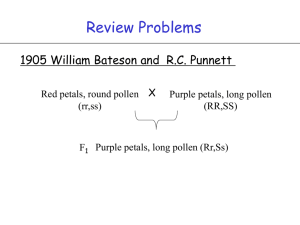
Chapter 3 - Independent assortment of genes
advertisement

Review Mendel’s “rules of the game” 1) Genes occur in pairs - Genetic characteristics are controlled by genes that exist in pairs called alleles. 2) Dominance/Recessiveness- When two unlike alleles responsible for a single character are present in a single individual, one is dominant (expressed) to the other which is said to be recessive (silent). 3) Segregation- during formation of the gametes, the paired alleles separate or segregate randomly. Question Yellow seeded plants in the F2 are predicted to have either GG or Gg genotypes. Is there a way to distinguish the genotype? Test Cross The organism of dominant phenotype but unknown genotype is crossed to a homozygous recessive individual. Test Cross o + ? Gg GG X o Possible sperm cells gg G Possible egg cells g g g Gg Gg gg gg If the offspring show 1:1 ratio of dominant:recessive phenotypes, the parent in question must have been heterozygous (Gg). Test Cross o + ? Gg GG X Possible sperm cells o gg G Possible egg cells G g g Gg Gg Gg Gg If the offspring show only the dominant phenotype, the parent in question must have been a homozygous dominant (GG) individual. Discovering genes via Mutant analysis • Generating mutants – Chemical mutagenesis (EMS) – base transition, point mutation – Radiation – deletions – Transposons/ T-DNA tags – insertion/deletions (indels) Forward Genetics - from phenotype to gene ID the phenotype ID the physiological, developmental, molecular differences ID the gene (DNA sequence) And observing segregation ratios • Planned crosses and Punnett squares, • Pedigree analysis – Mutant or polymorphism analysis • Autosomal dominant/recessive • Sex-linked genes If A represents a gene that displays autosomal dominant/recessive inheritance. The genotype of I-1 must be: a. b. c. d. AA Aa Aa Insufficient datatototell tell Insufficient data 1 2 3 R r If the DNA seen on gel 1 is from a pea plant heterozygous for “R” If the DNA seen on gel 1 is from a pea plant heterozygous for “R” and most likely likely from from a and“r” “r”atatthe theSBE1 SBE1locus, locus,the theDNA DNAin inlane gel 22 isis most apea peaplant plant a. a. b.b. c.c. d.d. Homozygous for the “R” allele Homozygous for the “R” allele Homozygous allele Homozygousfor forthe the“r” “r” allele Unable Unableto tomake makefunctional functionalstarch starchbranching branchingenzyme enzyme11 That Thatisismaking makingtwice twicethe thenormal normalamount amountof ofstarch starch branching branchingenzyme enzyme11 Reverse Genetics - from gene to phenotype • ID a gene • Mutate, knockout, over-express the gene • Analyze the morphological, physiology, developmental effects (the phenotype). Independent Assortment Chapter 3 Dihybrid cross - crosses between individuals that differ in two traits. Mendel’s dihybrid crosses P1 cross P1 cross X X yellow, round green, wrinkled green, round yellow, wrinkled F1 yellow, round Self-pollination of the F1 X F1 yellow, round yellow, round 9/16 yellow, round F2 3/16 yellow, wrinkled 3/16 green, round 1/16 green, wrinkled X yellow (Gg), round (Ww) yellow (Gg), round (Ww) o + GW o GW Gw gW gw F2 GGWW GGWw GgWW GgWw GGWw GGww GgWw Ggww GgWW GgWw ggWW ggWw GgWw Ggww ggWw ggww Gw gW gw G e n e r a t i o n Mendel’s dihybrid ratio 9:3:3:1 Mendel’s Second Principle of Inheritance Independent Assortment - during gamete formation, segregating pairs of unit factors assort independently of each other. But, what if X yellow (Gg), round (Ww) yellow (Gg), round (Ww) X yellow (Gg), round (Ww) yellow (Gg), round (Ww) o + GW o GW GW gw gw F2 GGWW GGWW GgWw GgWw GGWW GGWW GgWw GgWw GgWw ggww ggww GgWw ggww ggww GW gw GgWw gw GgWw G e n e r a t i o n Phenotypic Ratio X yellow (Gg), round (Ww) yellow (Gg), round (Ww) Expected F2 9 Yellow, round 3 Yellow, wrinkle 3 green, round 1 green, wrinkle 0 Yellow, wrinkle 0 green, round 4 green, wrinkle Resulting F2 12 Yellow, round Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Meiosis (the prelude to sexual reproduction) For sexual reproduction to occur, chromosomes must be duplicated and divided between the gametes. Meiosis I Meiosis II Independent Assortment - during gamete formation, segregating pairs of chromosomes (not genes) assort independently of each other. Mitosis takes takes place place in in Mitosis a. a. b. b. c. c. d. d. e. e. Haploid cells cells only only Haploid Diploid cells cells only only Diploid Haploid or Haploid ordiploid diploidcells cells Bacterial cells cells Bacterial None of of the the above above None Meiosis takes place in a. b. c. d. e. Haploid cells only Diploid Diploid cells cells only only Haploid or diploid cells Somatic cells None of the above Polygenic Traits (Quantitative trait loci, QTLs) Observation: Wheat kernel color is a continuum from white dark red Experiment 1 o + X o P1 F1 - all light red Experiment 2 X o + F1 o F2 1 6 15 20 15 6 1 Frequency Diagram Wheat Kernel Color 3 loci (polygenic), 6 different alleles Dark red white F2 seed color # of dominant alleles 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Continuous variation is determined by two or more genes. These are polygenic or quantitative traits. Cytoplasmic Segregation (Non-Mendelian Genetics) • Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) • Mitochondrial DNA (mt DNA) Cytoplasmic Segregation Test Cross ? • Reciprocal crosses – Who’s the pollen donor? humandisease diseaseassociated associatedwith withdysfunction dysfunctionof ofmitochondria, mitochondria, AAhuman whichresults resultsfrom fromaamutation mutationininaasingle singleautosomal autosomalgene genelocus locusinin which nuclearDNA, DNA,isismost mostlikely likelyto: to: nuclear Beinherited inheritedfrom fromthe themother, mother,because becausemitochondria mitochondriaare are a.a. Be notinherited inheritedfrom fromthe thefather father not Showheteroplasmy heteroplasmy(ainmix the progeny of mutant affected b.b. Show of WT and individuals, depending on chance eventsindividuals, during meiosis mitochondria) in the progeny of affected c. depending Show a non-Mendelian inheritance pattern, because the on chance events during meiosis number of mitochondriainheritance varies from cell tobecause cell c. Show a non-Mendelian pattern, the d. number Show a of Mendelian inheritance pattern mitochondria varies from cell to cell e. Show None aofMendelian the above inheritance pattern d. e. None of the above