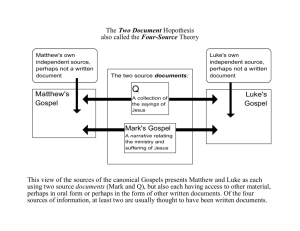
3. CANON (continued)
advertisement

Chapter 1 1. Tacitus 2. Suetonius 3. Pliny the Younger 4. Josephus 1. COVENANT (a.k.a. “Testament”) A. Definition: the open-ended contract of love between God and human beings. B. Hebrew Scripture ▪ Central focus of Hebrew Scripture = God’s love for the Jewish people ▪ Fill in the worksheet to recall the major events in Hebrew Scripture ▪ HW assignment 1. COVENANT (continued) C. New Testament ▪ Jesus IS the new testament ▪ God’s promise of love for all humanity 2. INSPIRATION Definition: The guidance given by the Holy Spirit to the human authors of Sacred Scripture so they wrote what God wanted written for our benefit. Human authors of Scripture use their unique talents and insights to address a particular audience ▪ Different authors highlight different theological themes 3. CANON A. Definition: The official list of the inspired books of the Bible. B. Number of Books in the Catholic canon ▪ Hebrew Scripture = 46 ▪ New Testament = 27 ▪ TOTAL = 73 3. CANON (continued) C. Criteria for inclusion in the canon ▪ 1. Apostolic Origin ▪ Writings were inspired by apostolic witnesses ▪ 2. Widespread Acceptance ▪ Writings were circulated and well-received by various parts of the church 3. CANON (continued) C. Criteria for inclusion in the canon (continued) ▪ 3. Conformity to the Rule of Faith ▪ Writings reflect the truth about Jesus and his teachings ▪ Consistent with one another 3. CANON (continued) D. New Testament Canon Background ▪ 27 books ▪ Written over the course of 50 years ▪ 50 C.E. – 100 C.E. ▪ Written in Greek ▪ Written by many different authors ▪ Contains many different types of writing ▪ Gospels , personal letters, homilies/sermons, symbolic writings 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon ▪ 1. Gospel = Good News ▪ Jesus himself is the Gospel of God’s love and salvation for all humanity ▪ Preaching about Jesus is also the Gospel ▪ 4 written versions of the Gospel 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ Gospels (4) ▪ The only books of the NT that narrate Jesus’ life, preaching, works, death, and Resurrection. ▪ Evangelist – a person who proclaims the Good News of Jesus Christ. “The four Evangelists” refers to the authors of the 4 Gospels: Matthew, Mark, Luke, & John. 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ 2. Acts of the Apostles (1) ▪ Narrates the spread of the Gospel after Jesus’ Resurrection ▪ Written by same author as Luke’s Gospel “Luke volume 2” ▪ Focus on Peter & Paul 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ 3. Pauline Epistles (13) ▪ Letters written to support and educate Christian communities or individuals ▪ Some written by Paul himself, some written by his disciples ▪ Examples: 1&2 Corinthians, Romans, Galatians 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ 4. Hebrews (1) ▪ Called a letter, but more like a sermon/homily 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ 5. Catholic Epistles (7) ▪ “catholic” = universal ▪ Letters written for all believers/the entire church ▪ Examples: James, 1 & 2 Peter, Jude 3. CANON (continued) E. Parts of the New Testament Canon (continued) ▪ 6. Revelation (1) ▪ Highly symbolic work ▪ Apocalyptic style ▪ Written to encourage persecuted Christians 3. CANON (continued) Create a graphic organizer or outline of the New Testament canon. For each of the 6 sections include: The section title A brief description (think: bullet point) of the section A drawing that illustrates a characteristic or the content of the section A list of the books in that section (in the order they appear in the NT) Stage 1- Jesus –Life , Death, Resurrection Stage 2 -Oral Tradition Stage 3-Writing the Gospels Summary of each stage in notes Timeline of 3 stages Label each of the 3 stages on the timeline and color-code each stage “0” 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Agree or Disagree? Scripture means whatever we personally think it means. Some things in Scripture aren’t true. 1. Catholic Perspective The Bible should be read both prayerfully and critically. ▪ Looking at the literary and historical context of the Scripture texts 2. Key Questions: What religious, social, cultural, and historical realities influenced the Scripture writer? For whom was the text being written? How might the author have adapted his material to help this particular audience understand the message? What literary device is used? How should we interpret the passage in light of that device? Example: Luke 3:7-9 3. 2 Senses of Scripture 1. Literal Sense ▪ What does the text actually mean? 2. Spiritual Sense ▪ What does the text mean for believers? Example: Matthew 15:10-11 1. Source Criticism Tries to determine what source(s) the writer used to compose his work 2. The Synoptic Gospels “synoptic” = seen together Synoptic Gospels = Matthew, Mark, & Luke ♥ = encyclopedia ☼= article ◘ = website ∞ = interview Student 1 ♥♥♥♥ ♥♥♥♥ ♥♥♥♥ Student 2 ☼☼♥♥ ☼♥♥☼ ◘♥◘◘ Student 3 ∞∞∞ ♥ ☼☼♥♥ ∞∞☼♥ How many sources did each student use? How many total sources are there? What do all 3 have in common? What is common to 2 out of the 3? What is unique about any student’s work? 3. The Four Source Theory Mark was written first Luke & Matthew used Mark as a source (♥) Luke & Matthew also used “Q” as a source (☼) Luke & Matthew each had their own unique source ▪ Special Luke – “L” (◘) ▪ Special Matthew – “M” (∞) Draw a diagram to illustrate the 4 source theory. Include: Mark, Matthew, Luke, Q, M, L Take into account: - Mark was the first Gospel written - Matthew and Luke used Mark - Matthew and Luke used the “Q” source - Matthew used a unique source “M” - Luke used a unique source “L” 4. The Q Source From the German word “quelle” which means “source” Lost source that contained many of Jesus’ sayings