Guide for writing a project proposal

King Saud University
College of Computer and Information Sciences
Information Technology Department
GUIDE FOR WRITING A SYSTE M
DESIGN DOCUMENT
DOCUMEN T PREPARED FOR
CAP312: SW ENG INEERI N G PROJECTS- PAR T 3
Version: 2
Date: Oct 2011
Prepared by: Maha Alyahya and Sarah Alkhudair.
Edited by: Nourah AL-Rossais
Guide for writing a System Design Document
INTRODUCTION
"The System Design Document, SDD, shows how the software system will be structured to satisfy the requirements identified in the software requirements specification. It is a translation of requirements into a description of the software structure, software components, interfaces, and data necessary for the implementation phase.
In essence, the SDD becomes a detailed blueprint for the implementation activity. In a complete SDD, each requirement must be traceable to one or more design entities."
[1]
STYLE CONVENTIONS
FORMAT
The SDD document should be typed. All text, Figures and Tables should appear on only one side of each sheet of paper. All pages other than the cover sheet should have page numbers that begin with “1” on the first page after the title page, and should continue through the last page of the reference page, but not the appendices.
The right-hand margin should be 1.5 cm and the upper and lower margins 2 - 2.5 cm. The left-hand margin must be 4 cm on each page of the document because of the binding. The margin instructions should be followed in the appendices as well.
The font size in the text should be in 12, in subsections 12 and in the main headings 14. The main headings are to be written in capitals and placed at the beginning of a new page. All headings are to be in bold letters. Leave two empty lines under the main heading, two empty lines above the subsection and one empty line under it. The headings should not have more than three numbers. A line spacing of 1.5 should be used in the text, 1 on the title page and in the abstract. The font to be used is Times New Roman. The page number is placed in the lower right corner.
The text should not be indented and both margins on the page should be justified. When a paragraph continues on the next page, at least two lines of the paragraph should be left on the upper or lower end of the page. The paragraphs are separated from each other and from the headings with one empty line. A new chapter is started on a new page. One empty line is needed to separate two paragraphs.
TEXT
The text of the report should be written in complete sentences. The style should be formal.
Formal style means to avoid slang, clichés, abbreviations that are common in spoken
English or advertising. It is convention that formal reports are written in the third person.
FIGURES AND TABLES
Page 2
Guide for writing a System Design Document
All Figures and Tables should have a number and a caption
. If a figure or table is extracted from a source, the source should be cited in the references.
SDD REPORT CONTENTS
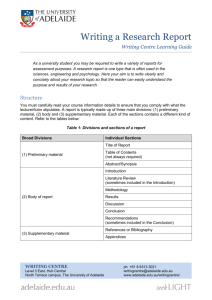
A template for the project SDD report is attached. A project SDD should include the following components:
Page 3
Guide for writing a System Design Document
TITLE PAGE
The title page should include:
University, College, and Department centered
University logo on right hand side
Project logo just above the title
Project title: The title should be a stand-alone statement that can fully describe the project by summarizing the main idea of the project. The title is supremely important. A successful title will attract readers while an unsuccessful one will discourage readers. Compose trial versions of the title as early as you can.
Student names in alphabetical order, along with the IDs.
Supervisor name
Year and semester in HIjrii and Gregorian
Page 4
Guide for writing a System Design Document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A table of contents should list each of the main sections of the SRS report, and the beginning page numbers for each section.
Page 5
Guide for writing a System Design Document
INTRODUCTION
[2]
The introduction should provide an overview of the entire SDD as follow:
Describe the purpose of this document
Describe the scope."Identify the software products to be produced by name; explain what the proposed software will do (and not do, if necessary). Major inputs, processing functionality, and outputs are described without regard to implementation detail."[3]
Describe this document's intended audience.(Skills required and assumptions)
Identify the system/product using any applicable names and/or version numbers.
Provide a complete list of all the applicable, referenced and any other pertinent documents such as: o
Related and/or companion documents o o o
Prerequisite documents
Documents which provide background and/or context for this document
Documents that result from this document (e.g. a test plan or a development plan)
"If you used any other types of documents to arrive at this design, list them here."[3]
Define any important terms, acronyms, or abbreviations.
Summarize (or give an abstract for) the contents of this document. " describe what the rest of the SDD contains and explain how the SDD is organized.
Constraints - Briefly describe any restrictions, limitations or constraints that impact the design or implementation."[3]
Page 6
Guide for writing a System Design Document
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
“
This section deals with a summary of the overall system design aspects, by giving a brief functional description with key concepts: Provide a top-level description of the system and its major external interfaces to aid the reader in understanding what the software is to accomplish. Reference appropriate graphics, illustrations, tables, etc., to show functions.
”[4]
Page 7
Guide for writing a System Design Document
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
"
This section should provide a high-level overview of how the functionality and responsibilities of the system were partitioned and then assigned to subsystems or components. Don't go into too much detail about the individual components themselves
(there is a subsequent section for detailed component descriptions). The main purpose here is to gain a general understanding of how and why the system was decomposed, and how the individual parts work together to provide the desired functionality.
At the top-most level, describe the major responsibilities that the software must undertake and the various roles that the system (or portions of the system) must play. Describe how the system was broken down into its components/subsystems (identifying each top-level component/subsystem and the roles/responsibilities assigned to it). Describe how the higher-level components collaborate with each other in order to achieve the required results. Don't forget to provide some sort of rationale for choosing this particular decomposition of the system (perhaps discussing other proposed decompositions and why they were rejected).
If there are any diagrams, models, flowcharts or documented scenarios, they may be included here. Diagrams that describe a particular component or subsystem should be included within the particular subsection that describes that component or subsystem"[2]
SUBSYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
"If a particular component is one which merits a more detailed discussion than what was presented in the System Architecture section, provide that more detailed discussion in a subsection of the System Architecture section. If necessary, describe how the component was further divided into subcomponents, and the relationships and interactions between the subcomponents.
In a similar fashion, Proceed to go into as many levels/subsections of discussion as needed in order for the reader to gain a high-level understanding of the entire system or subsystem."[2]
Page 8
Guide for writing a System Design Document
DETAILED SYSTEM DESIGN
"Most components described in the System Architecture section will require a more detailed discussion. Other lower-level components and subcomponents may need to be described as well. Each subsection of this section will refer to or contain a detailed description of a system software component.(i.e. the following will be written for each component in your system). Provide a detailed description of this software component (or a reference to such a description). Complex diagrams showing the details of component structure, behavior, or information/control flow may be included in the subsection .The discussion provided should cover the following software component attributes:
Classification
The component kind , such as a subsystem, module, class, package, function, file, etc.
Definition
The specific purpose and semantic meaning of the component.
Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities and/or behavior of this component. What does this component accomplish? What roles does it play? What kinds of services does it provide to its clients?
Constraints
Any relevant assumptions, limitations, or constraints for this component. This should include constraints on timing, storage, or component state, and might include rules for interacting with this component (encompassing preconditions, postconditions, invariants, other constraints on input or output values and local or global values, data formats and data access, synchronization, exceptions, etc.)
Composition
A description of the use and meaning of the subcomponents that are a part of this component.
Uses/Interactions
A description of this components collaborations with other components. What other components is this entity used by? What other components does this entity use (this would include any side-effects this entity might have on other parts of the system)?
This concerns the method of interaction as well as the interaction itself. Objectoriented designs should include a description of any known or anticipated subclasses, superclasses, and metaclasses.
Resources
A description of any and all resources that are managed, affected, or needed by this entity. Resources are entities external to the design such as memory, processors, printers, databases, or a software library. This should include a discussion of any possible race conditions and/or deadlock situations, and how they might be resolved.
Processing
A description of precisely how this components goes about performing the duties necessary to fulfill its responsibilities. This should encompass a description of any algorithms used; changes of state; relevant time or space complexity; concurrency; methods of creation, initialization, and cleanup; and handling of exceptional conditions."[2]
Pseudocode
A complete and concise pseudocode for this component.
Page 9
Guide for writing a System Design Document
DATA DESIGN
This section should cover the following:
GLOBAL DATA STRUCTURES
"Describe any data structures that are a major part of this system. This should include major data structures that are passed between components. That is, it is not restricted to truly global data structures."[3]
FUNCTIONAL
"List all functions and function parameters shown in the structural decomposition diagrams. For functions, give function input and output names in the description.
Refer the reader to the decomposition diagrams."[3]
DATABASE DESIGN
"List and describe database(s), tables, fields, and entity relationships, schema, query language, key and indices, data management functions."[4]
Page 10
Guide for writing a System Design Document
USER INTERFACE DESIGN
In this section provide the following:
USER INTERFACE DESIGN OVERVIEW
"Provide a high-level description of the user interface for this system. Describe any systems requirements (e.g., performance or usability) associated with all of the user interfaces."[5]
USER INTERFACE NAVIGATION HIERARCHY
"Provide and describe a diagram of the navigation hierarchy that illustrates how a user moves through the user interface."[5]
USER FUNCTION (OR USE CASES
)
INTERFACES
"Accurately and comprehensively document each user function or use case that requires an interface individually in a corresponding subsection. Label each subsection appropriately and title each subsection descriptively to indicate the function or use case being documented.
FUNCTION X (OR USE CASE X)
1.
Provide a description, and if appropriate, an image of each screen, report, or other user interface within this function or use case.
2.
Provide a Screen/Other User Interface Fields Table that includes descriptive information for each field that appears on the screen or other user interface.
In addition, if the data is selected from a pick list, include the list of possible values or their description. If the content of a field is derived from client side calculations using other fields or values, then specify the algorithm for the calculation in a descriptive footnote to the table. If the content of a field is derived from server side calculations or lookups, then specify the source of that calculation (e.g., the class or stored procedure where the calculation occurs).
3.
Also, specify the error messages to be displayed when the input does not meet requirements for the field, and provide image screens for them."[5]
Page 11
Guide for writing a System Design Document
REFERENCES
Always give complete citations for material on other sources. A proper reference involves two components: the citation in the text and the complete bibliographic entry in the
References section.
Use the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) style for referencing. For more information see http://wwwlib.murdoch.edu.au/find/citation/ieee.html
Page 12
Guide for writing a System Design Document
APPENDICES
An appendix is included at the end of the report. It contains information referred to in the report that's too large to fit in the body of the report. Provide any appendices you have in this section.
Appendices include the material needed for the report but which is unnecessary to include in the text itself (sample agreement form with client, graphs, and interview forms). The appendices must be referred to in the text and they must have all the necessary information needed for interpretation. Appendices are situated at the end of the thesis and numbered consecutively. The written form for reference to appendices within the text is: Appendix 1,
Appendix 2, etc. In the References it is: APPENDIX 1, APPENDIX 2, etc.
REFERENCES FOR THIS GUIDE
[1] IEEE (1998) IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Design Descriptions. IEEE Std
1016-1998, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc
[2] Bradford D. Appleton," A Software Design Specification Template", 1994-1997.
[3] CMSC 421 Staff, "System Design Document Template", Spring 2003.
[4]"System Design Document Template", New Mexico Department of Information
Technology, August 14, 2007.
[5] " System Design Description", TEXAS PROJECT DELIVERY FRAMEWORK, Version 1.2, 14
JAN 2008.
Page 13