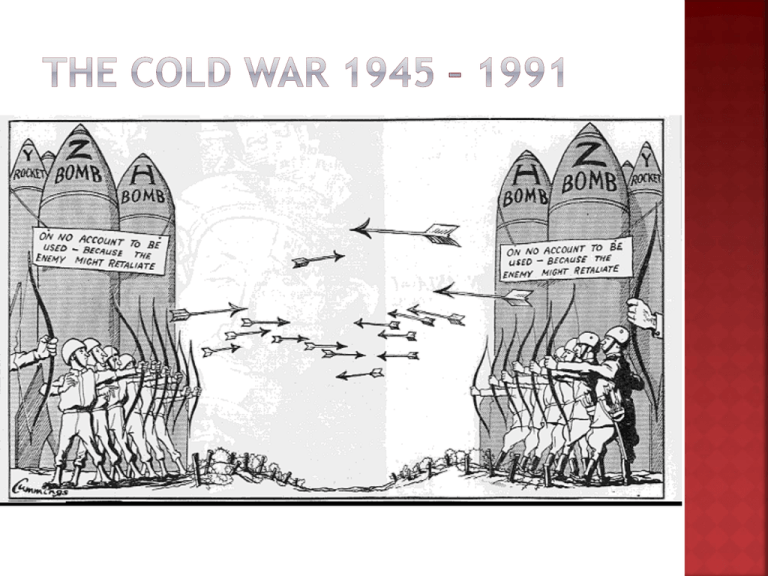
THE COLD WAR 1945 – 1991
advertisement
Potsdam Conference Yalta Conference Misunderstanding Different USSR takes Eastern Europe – worries US US in Western Europe – worries USSR Truman and Stalin Stalin a victim of Germany – NEVER AGAIN Truman – no appeasement – hard stance Arms Ideologies Race USSR scared of A Bomb – want their own Both feared an attack from one another USA wanted…. Soviets were a threat to their way of life. Self determination Access to raw materials and new markets Rebuild European Governments Reunite Germany USSR wanted… Thought they had won WWII. Want spoils of war Encourage Communism in Europe No free elections – Stalin breaks promise Rebuild its economy by using Eastern Europe Control Eastern Europe to balance US’s influence Keep Germany Divided TRUMAN INFORMS STALIN OF THE ATOMIC BOMB – MISTRUST At Potsdam, as elsewhere, the secret of the atomic bomb was kept closely guarded. We did not extend the very small circle of Americans who knew about it. Churchill naturally knew about the atomic bomb project from its very beginning, because it had involved the pooling of British and American technical skill. On July 24 I casually mentioned to Stalin that we had a new weapon of unusual destructive force. The Russian Premier showed no special interest. All he said was that he was glad to hear it and hoped we would make “good use of it against the Japanese.” Source: Memoirs of Harry S. Truman: Volume I, Year of Decisions (New York: Doubleday, 1955), p. 416. STALIN’S REACTION TO THE ATOMIC BOMB Stalin said tersely: “Roosevelt clearly felt no need to put us in the picture. He could have done it at Yalta. He could simply have told me the atom bomb was going through its experimental states. We were supposed to be allies.” It was noticeable that, even though Stalin was annoyed, he spoke calmly. He continued: “No doubt Washington and London are hoping we won’t be able to develop the bomb ourselves for some time. And meanwhile, using America’s monopoly, in fact America’s and Britain’s, they want to force us to accept their plans on questions affecting Europe and the world. Well, that’s not going to happen!” and now, for once, he cursed in ripe language. A broad grin appeared on the face of my good friend Gusev. Source: Andrei Gromyko, Memories, Translated by Harold Shukman (London: Century Hutchinson, Ltd., 1989), pp. 108–109. Who does Billy Joel blame for starting the Cold War Based on the song, is Joel for or against the Cold War. WHO STARTED THE COLD WAR??? “Containment” Truman Doctrine Berlin Airlift Stalin installs Communist Governments in Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungry, Romania, Poland From Stettin in the Balkans, to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lies the ancient capitals of Central and Eastern Europe. -- Sir Winston Churchill, 1946 Winston Churchill Strong alliance between USA and GB Henry Wallace – Secretary of Commerce USSR has the right – “Getting tough never brought anything real and lasting for the schoolyard bullies or world powers. The tougher we get, the tougher the Russians will get” List the pros and cons of each plan Who would you have supported? Explain Why did “Containment” win out? How will this affect America in the future? Reasoning Communist influence in Turkey and Greece Cant support themselves Britain cant do it either Financial aid “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation” $400 million in aide to Turkey and Greece Berlin Blockade Berlin Airlift NATO Warsaw Pact Include….. Brief summary (including key dates) Key causes Major effects on cold war Major arguments in defense of U.S. and Soviet actions (Cause and Effect) “European Recovery Program” Provide aid to ALL countries Not against any country or doctrine, but against hunger, poverty, desperation, and chaos. 12.2 Billion in aid to Western Europe USSR refuses Western Europe Helped 1948 – US, GB, and France merge their parts of Germany together USSR blocks access to Berlin. The U.S. began a massive airlift of supplies that lasted almost a year. (7,000 tons a day) Stalin eventually stops this East Germany is created NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION (NATO) 1949 United States Luxemburg Belgium Netherlands Britain Norway Canada Portugal Denmark 1952: Greece & France Iceland Italy Turkey 1955: West Germany 1983: Spain WARSAW PACT (1955) } U. S. S. R. } East Germany } Albania } Hungary } Bulgaria } Poland } Czechoslovakia } Rumania Russia detonated its first atom bomb in 1949. Truman ordered construction of the hydrogen bomb. How, if at all, do you think communication problems and ideological prejudice contributed to the cold war? Why were the Berlin blockade and resulting airlift such dramatic and important events in the cold war? Evaluate Truman’s actions during the early parts of the Cold War