Persuasion key ring - EAL Nexus
advertisement

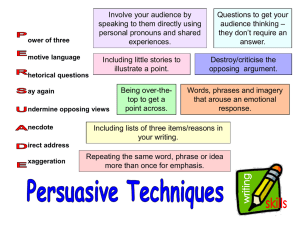
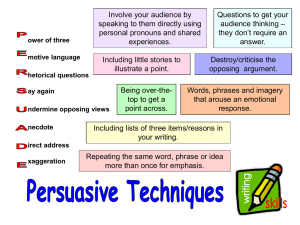
This project and its actions were made possible due to co-financing by the European Fund for the Integration of Third-Country Nationals EAL Nexus resource Persuasive writing (adverts and leaflets) Persuasion key ring Subject: English Age groups: 8–11, 12–14, 15–16, 17–18 Topic: Non-fiction writing Licence information | This resource is free to use for educational purposes. Source | This resource was originally developed by Charlotte Hurley and has been adapted by EAL Nexus. ©British Council 2014 Persuasion Persuasion Purpose: To promote a particular view or product Examples of forms: • • • • • • Adverts Spam Junk mail Catalogue Pamphlet Poster/flier • • • • • Book blurb Travel brochure Political manifesto Letter to editor Newspaper or magazine article Persuasion graphic organiser Persuasion Words and phrases to collect for writing • Informal, personal language – particularly for adverts • Emotive adjectives, words and phrases • Opinions presented as facts • Imperative verbs • Exaggeration • Rhyme and alliteration • Boastful language • Cause and effect phrases Persuasive argument writing frame (one side) Beginning – opening paragraph that introduces the issue and the writer’s point of view Middle – a series of paragraphs that begin with topic sentences followed by points that support the viewpoint. These are backed up by elaboration and examples. Ending – summary of argument Persuasive writing frame (advert or leaflet) Beginning – a paragraph that hooks and engages the reader. Often uses rhetorical questions Middle – series of paragraphs that persuade the reader to do, buy or think what the writer has set out to ‘sell’. Start with a topic then elaborate, including using ‘expert’ evidence Ending – sums up the reasons why the product should be ‘bought’ Persuasive argument (one side) key ingredients Persuade that … Writer’s point of view clearly stated in introduction and conclusion Modal verbs, e.g. could, would, might Words like Furthermore, In addition Words like: if, then, because, when … Persuasive devices: statistics and facts, emotive language, exaggeration, rhetorical questions, adjectives, ‘expert’ comment. Persuasive writing key ingredients (advert or leaflet) Persuade that … Often start with rhetorical question(s) Topic sentences start each paragraph to introduce the benefits of item ‘sold’ Devices like slogans, word play, rhyme, alliteration, repetition, exaggeration, emotive language. Different fonts, sizes and colours to grab reader’s attention Persuasion Persuasion