Short Term Causes of the Civil War
advertisement

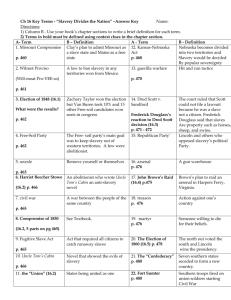
Good Morning! Turn in Guided Reading Pick up and start working on Bell Ringer #9 Social Studies Solutions 19-20 LONG TERM AND IMMEDIATE CAUSES OF THE CIVIL WAR Key Event Compromise of 1820 How does it lead to division? Admitted ______________ as a _____ state and _________ as a _____ state, drew a line to determine the future of __________, did not settle issue of ________________ Sectionalism (Slavery, Economics, Tariffs, Land, etc.) Each region of the country is only concerned about its _____ __________. ________ favors a high tariff which ______ the South’s ________, South’s economy is dependent on ___________, while the North __________ opposes it. Annexation of Texas Debate over __________ delays Texas becoming a state Wilmot Proviso Attempted to _____ slavery in territories gained from ___________war, _____ in Congress Compromise of 1850 (Stronger Fugitive Slave Law) North gets ______________ admitted as a _____ state, ________ gets as stronger ___________ ______ law but the North didn’t like it, which ___________ tensions UNCLE TOM’S CABIN Harriet Beecher Stowe--author Depicted evils of slavery to public Uncle Tom— slave Simon Legree— cruel slave owner 1852—sold over 1 million copies Importance: The undecided now favor antislavery side Angers Southerners, see it as attack on way of life KANSAS-NEBRASKA ACT: 1854—popular sovereignty passed as law in Compromise of 1850 to determine slavery (people of state vote on slavery) Rush to populate state with “voters” for each side (pro-slavery and abolitionists) Result = Bleeding Kansas: slavery and abolitionist forces resort to violence Foreshadows Civil War, shows popular sovereignty will not work A fight in the U.S. Senate: Preston Brooks v Charles Sumner—Brooks beats Sumner with a cane for his attacks on slavery in the South, foreshadows Civil War DRED SCOTT V. SANFORD 1857 Scott is a slave he is taken into free states sues for freedom based on Missouri Compromise (above line is free) Supreme Court (majority Southern) rules: Blacks are not citizens, slaves are property & you can take property anywhere Can’t ban slavery Missouri Compromise is illegal DEVELOPMENT OF REPUBLICAN PARTY Topic of slavery has come to dominate the differences in political parties By 1850—differences have peaked so that anitslavery Whigs, Democrats, and Free-Soilers: form a new anti-slavery party The Republicans: official party policy was to oppose the growth of slavery where it didn’t already exist LINCOLN-DOUGLAS DEBATES Senate Race 1858: Debate over slavery: neither man favored slavery, so how argue it? Douglas issues Freeport Doctrine— Stephen Douglas (Democrat) and Abraham Lincoln (Republican) slavery needs certain laws in order to exist, if you don’t want slavery don’t pass the laws and there will be not slavery Douglas goes on to win election, but Lincoln gains national fame JOHN BROWN’S RAID John Brown was an extreme abolitionist (no slavery) Attempted to capture Harper’s Ferry (a military arsenal in Virginia) with the intent to arm slaves to rebel He and his men were surrounded and forced to surrender Brown found guilty and then hanged—becomes a martyr for abolitionists Southerners believe Brown represents Northerners who want control of the Southern lifestyle and economy SOUTHERN SECESSION 1860 election— slavery had divided the parties: Republican Lincoln pledges to stop spread of slavery but not interfere with South Douglas got support of Northern Democrats John Breckinridge got Southern Democrats John Bell runs under Constitutional Union Party LINCOLN’S ELECTION Lincoln wins election with no southern electoral votes Southern states secede (leave) in fear of gov’t where they have no voice Lincoln says states’ don’t have right to secede, main goal is to preserve the Union SC is first, followed by 6 others Confederated States of America (CSA or South) formed before Lincoln takes office Jefferson Davis is elected Confederate President “This country will be drenched in blood…the people of the North…are not going to let the country be destroyed without a might effort to save it…” Uncle Tom’s Cabin Depicts the ________ of ________________, angers many ______________ people who now join _____-slavery side, angers ____________ because they see at as an ___________ on their way of life Kansas-Nebraska Act Rules ______________ Compromise unconstitutional, adopts idea of __________ __________ to determine slavery in the ________________, leads to ______________ ______________ (pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces fighting) Dred Scott v. Sanford Rules that __________ are not __________, slavery can’t be ______, slaves are ___________, angers _________________. Lincoln-Douglas Debates _____________ ____________ issued by Douglas states slavery needs laws to exist, don’t pass these laws and there will be no slavery, makes ________________ ____________, demonstrates __________ as a topic of tension between North and South John Brown’s Raid ___________ sees him as a __________ or hero for the cause, __________ sees Brown as the North trying to take over South, angers the _________. Election of 1860 _______________ wins with no ____________ votes, causes __ __ to ___________ from Union, South feels they have no ____________ in _____________. Review Questions 1. a. b. c. d. Which event convinced many Southerners that they had lost their voice in the national government? The Dred Scott decision The issuance of the Freeport Doctrine John Brown’s raid at Harpers’ Ferry Lincoln’s election as president 2. Which of the following was the LEAST divisive issue in the election of 1856? a. The candidacy of James Buchanan b. The Kansas-Nebraska Act c. The expansion of slavery d. Uncle Tom’s Cabin 3. Why did Kansas become a center of controversy over the issue of slavery? a. Because it extended the power of the Missouri Compromise b. Because the Kansas-Nebraska Act opened the territory to slavery and popular sovereignty c. The Know-Nothing Party disagreed with opening the territory to slavery d. All of the above 4. Why did most Free-Soilers object to slavery? a. They believed slavery was morally wrong b. They believed the South should be forced to industrialize c. They believed that white workers could not get jobs in competition w/ slaves d. The party actually had no opinion on slavery 5. What was the significance of the Dred Scott decision? a. It declared slaves were property b. It effectively repealed the Missouri Compromise c. It stated that because Scott was a slave, he had no rights in court d. All of the above 6. What was the significance of the election of 1856 for Abraham Lincoln? a. He won the election b. His debates against his opponent, Stephen Douglas afforded him national attention c. Stephen Douglas became president d. Lincoln learned nothing about running for office in the national spotlight 7. “So you’re the little lady that started this big war,” stated by Lincoln, most likely refers to whom? a. Harriet Tubman b. Harriet Beecher Stowe c. Elizabeth Cady Stanton d. Sojourner Truth Civil War Timeline Part 1 Create a timeline (events must be in order by month and year) Include 2 major facts about each event— should include significance of event! Give your timeline a title Include at least 6 pictures total! This is the 1st part of the timeline, you will complete the 2nd half later this week. Quiz Grade John Brown’s Raid Kansas-Nebraska Act Compromise of 1850 Election of 1860 Dred Scott v. Sanford Compromise of 1820 Uncle Tom’s Cabin Lincoln-Douglas Debates TITLE: (Example of how to construct your timeline below) Event 1 Date Event 2 Date Event 3 Date Event 4 Date 1. Important Fact 1. Important Fact 1. Important Fact 1. Important Fact 2. Important Fact 2. Important Fact 2. Important Fact 2. Important Fact