“American high schools are obsolete
advertisement
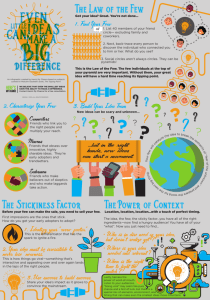
America’s Emerging Education System – and the Perkins Act Connection By Hans Meeder Key Points for Discussion • • • • What’s coming and how soon? How did we get here? What’s happening now? How can I play a part? The Tipping Point The Three Rules 1. The Law of the Few 2. The Stickiness Factor 3. The Power of Context 3 The Innovation and Adoption Cycle The Law of the Few: Connectors, Mavens, & Salesmen The Rules of The Tipping Point Making an idea or attitude or product tip can be done through the influence of special kinds of people. That’s the Law of the Few. It can be done by changing the content of communication, by making a message so memorable that it sticks in someone’s mind and compels them to action. That is the Stickiness Factor. But we need to remember that small changes in context can be just as important in tipping epidemics (Ch. 4). The 1st High School Tipping Point 1892. The Committee of Ten 1906. National Society for the Promotion of Industrial Education (Charles Prosser) 1917. The Smith-Hughes Act (salaries for vocational teachers and teacher preparation) 1918. “Cardinal Principles of Secondary Education” 1959. Conant report “The American High School Today” --- the triumph of “differentiation” Miscalculations in the 20th Century High School Model Belief in fixed intelligence and low expectations, racial and ethnic prejudices Belief in a static economy and slowchanging workforce demands See “Left Back, A Century of Battles Over School Reform” by Diane Ravitch, 2000 Moving toward the Next Tipping Point for American High Schools Tipping Point Factors 2001. States Career Clusters Initiative 2002. College and Career Transitions Initiative 2004. American Diploma Project…”Ready or Not” 2003-2004. Department of Education High School Regional and National Summits 2005. National Governors Association, High School Summit “American high schools are obsolete…” “American high schools are obsolete. By obsolete, I mean that our high schools, even when they are working exactly as designed, cannot teach our kids what they need to know today. Training the workforce of tomorrow with high schools of today is like trying to teach kids about today’s computers on a 50-year-old mainframe. It’s the wrong tool for the times.” -- Bill Gates, Founder and Chairman, Microsoft Corp. What Are the Results? What happens to entering 9th graders four years later… 37% 29% Graduate from High School Not College-Ready Dropout of High School 34% Greene & Winters 2005 Graduate from High School College-Ready The Silent Epidemic The Silent Epidemic Perspectives of High School Dropouts A Report by Civic Enterprises, LLC John M. Bridgeland, John J. DiIulio, Jr., Karen Burke Morison Dropouts Did Not Feel Motivated Or Inspired To Work Hard Did you feel motivated and inspired to work hard in high school? Was not motivated 69% / inspired Was motivated/ inspired 27% Not sure 4% Source: The Silent Epidemic, 2006 30 Tipping Point Factor: “The World is Flat, A Brief History of the 21st Century” by Thomas L. Friedman Globalization • Version 1.0. 1492 (Columbus) - 1800. – Key factors-- muscle, horsepower, windpower, steampower – Agent of change -- Countries and governments • Version 2.0. 1800 to 2000 – slowed by Great Depression and World Wars I and II – key factors: falling transportation costs, and later, by falling telecommunications costs – telegraph, telephones, the PC, satellites, fiber-optic cable, and early version of the Internet. Source: The World is Flat, A brief History of the 21st Century by Thomas L. Friedman Globalization • Version 3.0. 2000 to present – Key factors-- power for individuals to collaborate and compete globally. Software, applications, global fiber-optic network – Agent of change -- Individuals, much more diverse --- non-Western, non-white Source: The World is Flat, A brief History of the 21st Century by Thomas L. Friedman Friedman’s Ten Flattening Forces • Fall of the Berlin Wall • Netscape IPO • Work flow software • Open-sourcing • Outsourcing Friedman’s Ten Flattening Forces • Fall of the Berlin Wall • Netscape IPO • Work flow software • Open-sourcing • Outsourcing •Offshoring • Supply-chaining • Insourcing •In-forming •Wireless “Hey, we are roughing it out here! Only 45 minutes of IM-ing a night, you hear me?!” Tipping Point Factor: The College AND Work Readiness Agenda Downloadable copy available: www.acteonline.org Tipping Point Factor, The Perkins Act of 2006 KEY THEMES: • CTE Programs of Study • State and Local Accountability for Program Improvement • Tech Prep Accountability and Flexibility • Economic and Personal Competitiveness Perkins “CTE Programs of Study” • Builds on Tech Prep, career clusters, career pathways, career academies • State develops in consultation with locals • Each local district and college must offer the required courses of at least one Program of Study… – (many states will require that Programs of Study become the rule vs. the exception) Tipping Point Factor: State Career Initiatives Montana Career Fields and Clusters Model Human Services & Resources Environmental & Agricultural Systems Business & Management Agriculture, Food, & Natural Resources Law, Public Safety and Security Marketing, Sales, and Services Government and Public Administration Human Services Business, Management, and Administration Education and Training Hospitality and Tourism Foundation Knowledge and Skills •Interpersonal Relationships •Information Literacy •Problem Solving •Critical Thinking •Teamwork Communication & Information Systems Finance Industrial, Manufacturing, & Engineering Systems Manufacturing Arts, A/V Technology and Communications Transportation, Distribution & Logistics Information Technology Architecture and Construction Health Sciences Health Science Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics English English I English II English III English IV Academic Transfer Advanced Placement Early Entry Math Pre Algebra Algebra I Geometry Algebra I Algebra II Algebra II Trigonometry Pre-Calculus Calculus Academic Transfer Advanced Placement Early Entry Earth Science Biology Biology I Chemistry I Chemistry I Physics Anatomy/Physiology Academic Transfer Advanced Placement Early Entry American History Geography American History Geography World History Academic Transfer Advanced Placement Early Entry Career Cluster Exploration Input Technologies/ Keyboarding Other Career Exploration Advanced Computer Applications Cisco I,II, III, IV Computer Applications Computer Graphics Computer Programming Desktop American History Economics Government/Civics Modern Problems Psychology/Sociology Electronics I, II, III Interactive Media and Web Design Intro to Information Technology Multimedia Introduction Network Systems Art/Music/Theatre PE/Health/Wellness World Languages Speech/Communications Art/Music/Theatre PE/Health/Wellness World Languages Speech/Communications Art/Music/Theatre PE/Health/Wellness World Languages Speech/Communications Academic Transfer Advanced Placement Early Entry FBLA Cooperative Education Service Learning Skills USA Career Days Internships Career Interviews Job Shadowing Career Research Website Development/ Maintenance for Community Organizations Mentorship Part-time Employment Animation Business Technology Adv/Business Tech Commercial Art I, II Computer Repair Graphic Design Develop Web Pages Yearbook Staff Participate with School Multimedia/Video Projects Volunteering Electronic Tools for College and Career Planning to… •Help Students Create Individualized Plans AND •Build awareness of the full spectrum of post-secondary education and training opportunities Tipping Point Factor: Policies that Recognize Integrated Academics • 10 Interdisciplinary courses that meet state requirements for academic course taking. • Carefully merged academic and career-oriented content. • Meet Geometry standards: Computer-aided drafting/geometry; and Construction geometry. • Meet Life Science standards: Agri-biology; medical science; nutritional and food science. • Meet Economics standards: Business economics; consumer economics. – Source: Kentucky State Department of Education, www.education.ky.gov/KDE/default.htm Tipping Point Factor: Increasing recognition in the general education community Tipping Point Factor: State Initiatives • California. 2005. S.B., $20 million in new CTE funding, 2007. $32 million in new CTE funding proposed. Governor’s CTE Summit. • South Carolina, 2005. Legislature approves Education and Economic Development Act. – Offers academic standards within “career majors” for every student. – Every student will create an individual plan for graduation and beyond. Tipping Point Factor: State Initiatives • Washington State, 2006. State legislature recognizes CTE as part of collection of evidence for alternative form of WASL assessment. • Florida, 2006. State legislature approves “A++” Plan. – High school students will select an area of interest as part of their personalized education and career plan. – Students will earn four credits in a major area of interest. Tipping Point Factor: Schools That are Getting It Done Polytech High School Woodside, Delaware High Tech High, San Diego, California Granger High School Granger, Washington “si puede” – “It can be done” Why Link High School Redesign to Career Cluster/Pathway Strategies? • In a new global context, America’s preparation system must be highly effective and efficient, reaching ALL students with high quality. • Today’s workplace demands cross-cutting skills and adaptability – flexible career preparation is usually preferable to narrow job training. • Helps change the perception of old “voc-ed” – attracting more students, including those who consider themselves “college-bound.” Why Link High School Redesign to Career Cluster/Pathway Strategies? • Opportunity to master academic content by applying it to real-world contexts – 21st Century Skills • Stronger personal motivation for students to complete high school and work toward college attainment with a personalize plan. “I got you the iPod that I promised you, and for your convenience, I’ve welded it to the lawn mower.” Creating a New Hybrid of CTE with College Readiness Expectations Heterosis/Hybrid Vigor: “the possibility to obtain a ‘better’ individual by combining the virtues of its parents” What Do We Want for Our Students and Schools? • Rigor – Where we believe in the ability of students to learn at high levels and make every effort to get them there • Relevance – Where we engage students in their passion for learning and life • Relationships – Where every youth knows he or she matters to someone Which One are You? • Connectors People with a special gift of bringing the world together – SOCIAL GLUE – SPREAD MESSAGE • Mavens They accumulate knowledge and have the social skills to start word-of-mouth epidemics – DATA BANKS – PROVIDE THE MESSAGE • Salesmen, They persuade us • The Message – Stickiness • The Context - Policy “Few will have the greatness to bend history itself; but each of us can work to change a small portion of events, and in the total of all those acts will be written the history of this generation.” -- Robert F. Kennedy For more information about presentations and state and local consulting services, contact: Email: Hans@MeederConsulting.com Web: www.MeederConsulting.com What is the Impact in the Colorado Classroom?