Dred Scott
advertisement

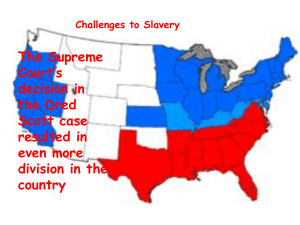
Section 3 - Slavery Dominates Politics Find Out: • Why the Republican Party was formed • The effects of the Dred Scott case • The Lincoln-Douglas Debates • The impact of John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry THE FREE-SOILERS • • • • Another party that emerged in the mid-19th century was the FreeSoilers They were northerners who opposed slavery in the territories Free-Soilers objections to slavery were based on economics not moral objection to slavery They believed slavery drove down wages for white workers “Soil” REPUBLICANS EMERGE AS LEADING PARTY 1. What political party was created from problems caused by the Kansas-Nebraska Act? • • Republicans won all but 3 presidential elections from 1860-1932 In 1854, opponents of slavery in the territories formed a new political party, the Republican Party As the party grew it took on Free-Soilers, some anti-slavery Democrats and Whigs, and KnowNothings The Republican Party Forms • Grew from split in the Whig Party over the Kansas-Nebraska Act • Southern whigs were destroyed • Northern whigs joined with other opponents of slavery and formed the Republican Party • Ran John C. Frémont for President in 1856 2. Why did the Whig party split? Because the Kansas-Nebraska Act proposed to open new territories to slavery, there was no room for compromise in the Whig Party since Northerners opposed it and Southerners supported it. 3. What was the key to the Republican Party gaining strength in the North? “Bleeding Kansas” was blamed on the Democrats since they supported the Kansas-Nebraska Act • • • • • • 4. Who ran for President in the election of 1856? Democrats nominate James Buchanan from Pennsylvania Buchanan was minister to Great Britain and out of the country since 1853 Said little about slavery and claimed his goal was to maintain the Union John C. Frémont ran in the North for the Republicans-not on Southern ballot Former President Millard Fillmore ran in South Buchanan won but Frèmont won 11 states for Dred Scott Sues for Freedom 5. The split in the country was made worse by the Supreme Court decision in the case of Dred Scott who had been a slave in Missouri. His owner took him to live in territories where slavery was illegal and then returned to Missouri. After his owner's death, Scott sued for his freedom. His case, Dred Scott V. Sandford, reached the Supreme Courts. 6.What did Chief Justice Roger B. Taney rule in 1857 on the Dred Scott Case? • • • • • First, he said Scott was not a citizen and could not sue in U.S. courts He said Scott was bound by Missouri’s slave code because he lived in Missouri and his time in free territory did not matter He said Congress could not ban slaves in any territory since they were property and protected under rights of property owners in Constitution The decision increased tensions over slavery Northerners are angry because it made slavery legal everywhere in US DRED SCOTT LOST HIS CHANCE AT FREEDOM – From Library of Congress Prints and Photographs From Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Dred Scott and his wife sued for their freedom because they had lived for 9 years in free territory. The decision had more to do with property rights than whether they deserved their freedom. LINCOLN – DOUGLAS DEBATES • • • • The 1858 race for U.S. Senate in Illinois was hotly contested between Republican Abraham Lincoln (7) and Democratic Douglas One of the most celebrated debates in history ensued as the topic was slavery in the territories Douglas favored popular sovereignty while Lincoln wanted a Constitutional Amendment Made Lincoln a national figure Lincoln Douglas debate Du Page County Centennial, August 27th From the Library of Congress Prints and Photographs 8. What metaphor did Lincoln use in one his speeches? Lincoln used the metaphor from the Bible that “A house divided against itself cannot stand” at the Republican state nominating convention on June 16, 1858, as Republicans chose Lincoln to run against Douglas for the Senate. 9. What was Lincoln's view on slavery? He felt slavery was “a moral, a social, and a political wrong.” He did not suggest abolishing slavery where it existed but to not let it expand into new territory. 10. What was Douglas’s view? He did not share Lincoln’s belief that it was the national government’s role to prevent the expansion of slavery. He argued for popular sovereignty as the most democratic way to solve it. Douglas won the election (11) 12. How did it help Lincoln? Lincoln became a national figure and strengthened his standing in the Republican Party 13. What did John Brown plan to do in Harpers Ferry, Va., in 1859? • • ARSENAL • • BROWN While politicians debated the slavery issue, John Brown plotted a major slave revolt On October 16, 1859, he led a band of 21 men, black and white, into Harpers Ferry, Virginia He hoped to seize a large federal arsenal, but troops put down the rebellion Brown was tried and executed John Brown Attacks Harpers Ferry • Wanted to arm slaves to revolt for their freedom • Planned to capture weapons at the U.S. arsenal at Harpers Ferry, VA • Oct. 16, 1859, Brown and his followers captured the arsenal, killing 4 people • Brown sent out word to arm the slaves but none came • Marines attacked the fort and captured Brown 6 of his followers • Brown was hung for treason NEW POLITICAL PARTIES EMERGE • • • • Know-Nothing members answered questions by saying, “I know Nothing” The political landscape by 1856 was very different than it had been just a few years earlier Gone was the Whig Party The Democrats were still alive but faced increasing challenge from new parties An alternative was the Know-Nothing Party