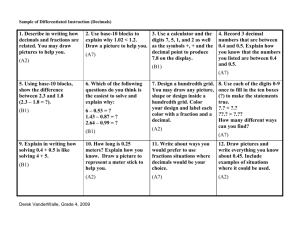
Mathematics Grade 6
advertisement

Year: 2014-15 Teacher: CORE Math Grade 6 Course: Math Grade 6 Month: All Months Lessons 1-10 + Investigation 1 Standards Essential Questions 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.2.6.C-Apply the associative, commutative, distributive, and/or identity properties to evaluate numerical expressions. What is the proper process for Lesson 1 - Practice Compute the sum and difference of two or more whole adding and subtracting whole Set a-f 9/7/2014 numbers numbers? Written Practice Identify the commutative and identity property of addition What property allows the 9/7/2014 order of addends to be changed? What property shows that adding zero does not change the original value? Saxon Math Course 1 pg 711 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.2.6.C-Apply the associative, commutative, distributive, and/or identity properties to evaluate numerical expressions. What is the proper process for Practice Set a-h multiplying and dividing whole 9/8/2014 numbers? Written Practice What property allows the 9/8/2014 order of factors to be changed? What property shows that multiplying by one does not change the original value? Saxon Math Course 1 pg 1217 2.8.6.C-Recognize, describe, extend, create, replicate, form a rule, and/or find a missing element for a variety of whole number patterns, sequences, and relationships verbally, numerically, symbolically, and graphically. Assessments Skills What is the process for Practice Set a-i finding a missing minuend in 9/9/2014 a subtraction problem? Written Practice What is the process for 9/9/2014 finding a missing subtrahend in a subtraction problem? hat is the process for finding a missing addend in an addition problem? What is the process for evaluating the correctness of the unknown value in an equation? 2.8.6.C-Recognize, describe, What is the process for Practice Set a-i extend, create, replicate, form finding a missing dividend or 9/10/2014 a rule, and/or find a missing divisor in a division problem? Written Practice element for a variety of whole What is the process for 9/10/2014 number patterns, sequences, finding a missing factor in a and relationships verbally, multiplication problem? numerically, symbolically, and graphically. 2.2.7.C-Use the order of What is the process for Practice Set a-i operations to evaluate solving an expression with 9/13/2014 numerical expressions. two or more operations? Content Lessons Resources addends Lesson 1 commutative property of addition difference fact family identity property of addition inverse operation minuend subtrahend sum Identify the expressions that indicate division and Commutative property Lesson 2 multiplication of multiplication Compute the product and quotient of two whole numbers Identity property of Identify the commutative property, identity property, and zero multiplication property of multiplication zero property of multiplication quotient dividend divisor factors products Identify an unknown addend in an addition problem using Equation Lesson 3 subraction Unknown Saxon Math Course 1 pg 1822 Evaluate answer by substituting the answer in for the variable in original problem Identify the unknown minuend in a subtraction problem by adding the subtrahend and the difference Identify the unknown subtrahend in a subtraction problem by subtracting the difference from the minuend Identify an unknown factor in a multiplication problem using division Identify the unknown dividend in a division problem using multiplication Identify the unknown divisor in a division problem using division Unknown Equation products factors divisor dividend Lesson 4 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 2327 Simplify an expression that uses more than one operation by associative property of Lesson 5 following the correct order of operations addition associative property of Saxon Math Course 1 pg 2831 2.1.6.A-Model and compare values of whole numbers, mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. 2.3.6.D-Perform basic conversions within the metric and within the customary systems. Which property states that the Written Practice grouping of addends or 9/13/2014 factors does affect the answer? Identify the Associative Property of Addition and the Associative Property of Multiplication How do you use a fraction to name a part of a whole? How do you divide to find fractional parts of a number? How do you find the measure of a line in inches and centimeters? How can you differentiate between line, segments, and rays? Identify a fraction to name a part of a whole Denominator Identify a fraction to name a part of a group Fractions Divide a number into equal parts to find a fractional part of Numerator that number Identify lines, segments, and rays Endpoints Measure line segments to the nearest quarter inch using an Line inch ruler ray Measure line segments in centimeters and millimeters using a Segment centimeter ruler Metric System International System Practice Set a-h 9/14/2014 Written Practice 9/14/2014 Practice Set a-h 9/15/2014 Written Practice 9/15/2014 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify How do you find the perimeter Practice Set a-h measurements of length, of a room? 9/16/2014 perimeter, area, volume, How do you compute the Written Practice capacity, temperature, time, distance around a figure? 9/16/2014 weight, and angles. 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of perimeter, area, and volume. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.1.6.D-Apply place value How are numbers arranged Practice Set a-h concepts to order and compare on a number line? 9/17/2014 decimals; use the number line What symbols are used to Written Practice to order and compare represent greater than, less 9/17/2014 decimals, fractions, and mixed than, and equal to? numbers. 2.8.6.C-Recognize, describe, What are ways to find a rule Practice Set a-h extend, create, replicate, form of a sequence? 9/20/2014 a rule, and/or find a missing What are the uses of even Written Practice element for a variety of whole and odd numbers? 9/20/2014 number patterns, sequences, and relationships verbally, numerically, symbolically, and graphically. Test 1 9/21/2014 2.6.6.A-Gather data from a variety of appropriate sources. 2.6.6.B-Select an appropriate method to organize data; select an appropriate format to display data. When is it appropriate to make a frequency table? When is it appropriate to make a histogram? multiplication order of operations Lesson 6 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 3235 Lesson 7 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 3641 Lesson 8 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 4245 counting numbers negative numbers number line whole numbers Lesson 9 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 4649 Celsius scale even numbers fahrenheit scale odd numbers scale sequence digit term Lesson 10 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 5053 Test 1 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 7377 U.S. Customary System Compute the perimeter of a shape by adding the length of the perimeter shape's sides Compute the length of a side of a square when the perimeter of the square is known order numbers on a number line from least to greatest identify greater than, less than, and equal to symbols write comparisons that are stated in words using symbols identify addition and multiplication sequences analyze the rule for a sequence and use it to find missing numbers in the sequence identify even and odd numbers read the number indicated on a scale Interpret a frequency table Count and write tally marks make a frequency table make a histogram interpret a histogram interpret survey results Saxon Math Course 1 pg 3235 bar graph frequency table histogram sample survey Investigation Saxon Math 1 Course 1 pg 5457 Lessons 11-20 ~ Standards This unit covers lessons 11-20, Tests 2 & 3, and Investigation 3 Essential Questions 2.5.5.A-Develop a plan to When looking at a pattern, analyze a problem, identify the when should you combine or information needed to solve separate? the problem, carry out the plan, What steps do you follow check whether an answer when solving a word makes sense, and explain how problem? the problem was solved in grade appropriate contexts. 2.8.6.C-Recognize, describe, extend, create, replicate, form a rule, and/or find a missing element for a variety of whole number patterns, sequences, and relationships verbally, numerically, symbolically, and graphically. 2.1.6.A-Model and compare How do you determine the values of whole numbers, place value of a number? mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. 2.1.6.D-Apply place value concepts to order and compare decimals; use the number line to order and compare decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.3.6.C-Use given How do you determine the measurements to calculate a time difference between one missing length, perimeter, time to another? area, and/or volume; Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across days. 2.1.6.D-Apply place value When is a number line concepts to order and compare needed? decimals; use the number line How is it determined if to order and compare numbers are opposite? decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.6.A-Model and compare Why is it important to learn values of whole numbers, how to do equal groups? mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources Practice Set a-c 9/23/2014 Written Practice 9/23/2014 identify the addition and subtraction pattern in word problems combining about combining and separating separating follow a four step problem to solve word problems write an equation to solve word problems about combining and separating Lesson 11 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 5862 Practice Set a-e 9/24/2014 Written Practice 9/24/2014 identify place value through trillions of a digit in a whole number write through trillions using words and digits place value Lesson 12 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 6367 Practice Set a-b 9/27/2014 Written Practice 9/27/2014 write an equation to solve an elapsed time problem elapsed time Lesson 13 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 6872 Practice Set a-l 9/28/2014 Written Practice 9/28/2014 order and compare numbers using a number line identify numbers that are opposites subtract a larger number from a smaller number using a number line integers opposites positive numbers negative numbers Lesson 14 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 7377 Practice Set a-b 9/29/2014 Written Practice 9/29/2014 Test 2 9/30/2014 Practice Set a-o 10/1/2014 Written Practice 10/1/2014 identify the pattern in a word problem about equal groups write an equation to solve a word problem about equal groups Equation factor Unknown Lesson 15 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 7881 round whole numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, and thousand round numbers to obtain estimated answers estimate round represent a fraction or mixed number on a number line measure the length of segments to the nearest sixteenth of an inch mixed numbers 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify When is it appropriate to measurements of length, estimate numbers? perimeter, area, volume, Why is it important to use capacity, temperature, time, rounding? weight, and angles. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units When is it needed to measure Practice Set a-g to measure perimeter, area, to the nearest sixteenth of an 10/4/2014 and volume; use a protractor to inch? Written Practice Where on the number line 10/4/2014 Test 2 Lesson 16 Lesson 17 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 8286 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 8792 measure angles between 0 does a fraction or mixed and 180 degrees. number lie? 2.6.6.C-Select and use, as Why is average important? appropriate, the mean, median, What is a line graph used mode, and/or range to describe for? sets of data. 2.6.6.E-Interpret data displayed in a table, histogram, graph, or data summarized by numerical measures. 2.1.5.E-Develop and apply How is a prime number number theory concepts (e.g., identified? primes, factors, multiples, What are factors? composites) to represent numbers in various ways. 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory How is the greatest common concepts to calculate the GCF factor computed? (Greatest Common Factor) and/or LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers. Practice Set a-h 10/5/2014 Written Practice 10/5/2014 make equal groups to find an average Compute the average of several numbers identify a number halfway between two numbers by finding the average of the two numbers interpret a line graph average line graph mean graph Lesson 18 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 9398 Practice Set a-l 10/6/2014 Written Practice 10/6/2014 identify all the factors of a given number identify prime numbers prime number factor Lesson 19 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 99104 Practice Set a-i 10/7/2014 Written Practice 10/7/2014 Identify the greatest common factor of two or more numbers greatest common factor Lesson 20 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 105-108 Test 3 10/8/2014 2.1.6.B-Represent whole How are fraction problems numbers, fractions, mixed solved with manipulatives? numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent the concept of equivalent forms of a fraction, decimal, and/or percent. Lessons 21 to 30 ~ manipulate fraction bars to solve problems improper fractions nonexamples Test 3 Investigation Saxon Math 2 Course 1 pg 109-111 This unit covers lessons 21 to 30, tests 4 and 5, and investigation 3 Standards 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory concepts to calculate the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) and/or LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Essential Questions Assessments What rules make it Practice Set a-d possible to determine 10/13/2014 whether or not a number Written Practice is divisible by 2, 3, 5, 9, or 10/13/2014 10? What is the correct Practice Set a-f process for solving equal 10/14/2014 groups problems with Written Practice fractions? 10/14/2014 How does dividing objects into equal groups help to find a fractional part of a number? 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion How are ratios used to Practice Set a-e to model relationships between describe relationships 10/15/2014 quantities. between numbers? Written Practice 2.1.7.F-Understand the concepts What are the different 10/15/2014 of ratio, proportion, percents, forms of representing a and rates to determine unknown ratio? quantities in equations. What makes rate problems like equal groups problems? Skills Content Lessons Resources identify whether a number is or is not divisible by 2, 3, divisibility rules 5, 9, or 10 factors identify factors of given numbers using the divisibility rules Lesson 21 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 112-116 divide objects into equal groups to find the fractional equal groups part of a number fractional parts calculate the fractional part of a group using two steps Lesson 22 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 117-121 write a ratio to represent a numerical relationship calculate rates for speed, mileage, and unit price Lesson 23 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 122-126 ratio rates mileage speed unit price 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, What is the correct Practice Set a-g and divide whole numbers, process for adding and 10/18/2014 decimals, fractions, and mixed subtracting fractions with Written Practice numbers. like denominators? 10/18/2014 2.4.6.A-Use models, properties, How can manipulatives be and relationships to draw used to model the process conclusions and explain reasons of adding and subtracting for conclusions. fractions? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole How can a division Practice Set a-i numbers, fractions, mixed answer be expressed as a 10/19/2014 numbers, decimals, and mixed number? Written Practice percents in equivalent forms. How can an improper 10/19/2014 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory fraction be expressed as a concepts to calculate the GCF mixed number? (Greatest Common Factor) What is the process for and/or LCM (Least Common finding multiples of a given Multiple) of two numbers. number? 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Test 4 10/20/2014 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent How can manipulatives be Practice Set a-i the concept of equivalent forms used to model reducing 10/21/2014 of a fraction, decimal, and/or fractions? Written Practice percent. What is the correct 10/21/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, process for adding and and divide whole numbers, subtracting mixed decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers? numbers. What is the correct process for reducing fractions and/or mixed numbers? 2.3.7.C-Use measurement What is the relationship Practice Set a-d formulas to calculate volume, between the radius and 10/22/2014 area, and perimeter and to diameter of a circle? Written Practice calculate circumference and What is the relationship 10/22/2014 area of circles. between the diameter and circumference of a circle? 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.3.7.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. What are the different Practice set a-k types of lines and angles? 10/25/2014 What is the proper way to Written Practice name an angle? 10/25/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. What is the correct process for multiplying fractions? What is the correct process for reducing fractions? add and subtract fractions with like denominators common denominator model the process of adding and subtracting fractions fractional parts using fraction manipulatives Lesson 24 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 127-131 write the answers to a division problem as a mixed number write improper fractions as mixed numbers list the multiples of a given number mixed number improper fractions multiples Lesson 25 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 132-135 reduce fractions with and without the use of manipulatives add and subtract mixed numbers reduce answers when adding and subtracting mixed numbers reduce fractions mixed numbers identify the circumference, diameter, and radius of a circle draw a circle with a given radius using a compass calculate the diameter of a circle when the radius is known calculate the radius of a circle when the diameter is known identify parallel, perpendicular, and oblique lines identify right, acute, and obtuse angles name angles using one letter, three letters, or one number circumference compass diameter radius circle concentric circles acute angle angles intersect oblique lines ray obtuse angle parallel lines perpendicular lines plane right angle vertex naming an angle practice set a-j 10/26/2014multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction reduce Written Practice reduce a fraction by using the GCF or another common GCF 10/26/2014 factor factor Test 4 Lesson 26 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 136-140 Lesson 27 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 141-144 Lesson 28 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 145-149 Lesson 29 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 150-155 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory concepts to calculate the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) and/or LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers. What is the correct process for identifying the multiples of a given number? What is the product of a number and its reciprocal? 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.3.7.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. How is a protractor used to find the measure of an angle? How is a protractor used to draw an angle with a given measure? practice set a-m 10/27/2014 Written Practice 10/27/2014 identify common multiples of two numbers LCM identify the LCM of two numbers reciprocal identify reciprocals as numbers that have a product of 1 term create the reciprocal of a given number by reversing multiple the numerator and denominator Test 5 10/28/2014 Lessons 31 to 40 ~ Standards measure an angle in degrees using a protractor degrees draw an angle with a given measure using a protractor angles protractor acute angle obtuse angle right angle straight angle Lesson 30 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 156-160 Test 5 Investigation Saxon Math 3 Course 1 pg. 161-163 This unit will cover lessons 31 to 40, tests 6 and 7, and investigation 4 Essential Questions Assessments Skills 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of Why are units squared Lesson 31 practice perimeter, area, and volume. when measuring area? set a-h 11/1/2014 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure What is the correct process Lesson 31 Written perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to for measuring the area of a Practice 11/1/2014 measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. rectangle? 2.3.6.C-Use given measurements to calculate a What is the relationship missing length, perimeter, area, and/or volume; between the length of the Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across sides of a square and the days. area of the square? 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.11.6.C-Estimate areas and volumes of shapes and solids as the sums of areas of tiles and volumes of cubes. 2.1.7.B-Represent and use numbers in equivalent What is the proper way to Lesson 32 practice forms (e.g. integers, fractions, decimals, percents, represent the time that has set a-h 11/2/2014 exponents, powers, roots, absolute values). past between two events? Lesson 32 Written 2.3.6.C-Use given measurements to calculate a How do you represent the Practice 11/2/2014 missing length, perimeter, area, and/or volume; value of each digit within a Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across large whole number? days. 2.1.6.A-Model and compare values of whole How can you represent a Lesson 33 practice numbers, mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. value as both a fraction set a-j 11/3/2014 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, and percent? Lesson 33 Written mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in Practice 11/3/2014 equivalent forms. 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent the concept of equivalent forms of a fraction, decimal, and/or percent. 2.1.6.A-Model and compare values of whole How is the value of a digit Lesson 34 practice numbers, mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. within a decimal set a-f 11/4/2014 2.1.6.D-Apply place value concepts to order and represented and Content Lessons Resources identify square units as the units used to measure area multiply length by width to find area of a rectangle calculate the side length and perimeter of a square when the area is known area rectangle length width square units Lesson 31 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 164-168 write a number in expanded notation write a number in standard notation rename units of time to solve elapsed-time problems elapsed time expanded notation standard notation a.m. p.m. place value Lesson 32 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 169-173 write a percent as a reduced fraction percent Lesson 33 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 174-177 identify the value of decimal places through decimal place values Lesson 34 the millionths decimal point name the digit that occupies a specific decimal Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 178-181 compare decimals; use the number line to order and compare decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. determined? Lesson 34 Written Why is thinking about Practice 11/4/2014 money a helpful way to remember decimal place values? 2.1.6.A-Model and compare values of whole How can you represent a Lesson 35 practice numbers, mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. value as both a decimal set a-o 11/5/2014 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, and a fraction? Lesson 35 Written mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in How does knowing decimal Practice 11/5/2014 equivalent forms. place values help to read 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent the concept of and write a decimal equivalent forms of a fraction, decimal, and/or numeral? percent. 2.1.6.D-Apply place value concepts to order and compare decimals; use the number line to order and compare decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Test 6 11/8/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the correct process Lesson 36 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed for subtracting fractions set a-j 11/9/2014 numbers. and mixed numbers from Lesson 36 Written whole numbers? Practice 11/9/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the correct process Lesson 37 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed for adding and subtracting set a-j 11/10/2014 numbers. decimals? Lesson 37 Written Practice 11/10/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the proper process Lesson 38 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. for adding and subtracting set a-q 11/11/2014 2.1.7.B-Represent and use numbers in equivalent decimal numbers and Lesson 38 Written forms (e.g. integers, fractions, decimals, percents, whole numbers? Practice 11/11/2014 exponents, powers, roots, absolute values). What exponent can be used to represent square units? place in a number name the decimal place occupied by a given digit in a number write a decimal number as a fraction equivalent decimals Lesson 35 write a fraction as a decimal number and fractions read and write decimal numbers in word form word form write the word form of a decimal number subtract a fraction from a whole number subtract a mixed number from a whole number add decimal numbers subtract decimal numbers fraction mixed number whole number subtraction addition subtraction decimal numerals write a whole number with a decimal point base add decimal numbers and whole numbers exponent subtract whole numbers from decimal perfect square numbers square root square a number and use an exponent of 2 to indicate the squaring of a number simplify an expression by applying exponents and then perform operations calculate the square root of a number 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the correct process Lesson 39 practice multiply a decimal number by a decimal multiplication numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed for multiplying decimal and set a-k 11/12/2014 number decimal number numbers. whole numbers? Lesson 39 Written multiply a decimal number by a whole number whole number Practice 11/12/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole Why is it important to use 0 Lesson 40 practice fill in any empty decimal places with 0 circle graph numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. as a placeholder when set a-j 11/15/2014 interpret information displayed in a circle graphbar graph 2.6.6.E-Interpret data displayed in a table, using decimals in the four Lesson 40 Written generalize information from bar graph to circle decimal numbers histogram, graph, or data summarized by operations? Practice 11/15/2014 graph and placeholders numerical measures. How can it be determined if compare data displayed in a bar graph and a circle graph is the best circle graph method of portraying data? What information can you get off of a circle graph? Test 7 11/16/2014 2.6.6.A-Gather data from a variety of appropriate What makes data either describe whether data is quantitative or Data sources. qualitative or quantitative? qualitative in nature line plot 2.6.6.B-Select an appropriate method to organize What is a sample not create a survey population data; select an appropriate format to display data. representative of a explain sample vs. population qualitative data 2.6.6.E-Interpret data displayed in a table, population? identify bias in a survey quantitative data histogram, graph, or data summarized by What is the proper process conduct surveys and collect data statistics numerical measures. for conducting a survey bar graph and collecting data? sample Test 6 Lesson 36 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 182-186 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 187-190 Lesson 37 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 191-194 Lesson 38 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 195-199 Lesson 39 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 200-204 Lesson 40 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 205-210 Test 7 Investigation Saxon Math 4 Course 1 pg. 211-215 Lessons 41-50 ~ This unit covers lessons 41 to 50, tests 8 and 9, and investigation 5 Standards Essential Questions Assessments Skills 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. How can a percent be Lesson 41 practice expressed as a decimal? set a-q 11/18/2014 What is the correct process Lesson 41 Written for determining sale tax of Practice 11/18/2014 a purchase? 2.1.6.A-Model and compare values of whole How can you form Lesson 42 practice numbers, mixed numbers, fractions, and decimals. equivalent fractions? set a-h 11/19/2014 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, What is the process for Lesson 42 Written mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in adding or subtracting Practice 11/19/2014 equivalent forms. fractions with uncommon 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent the concept of denominators? equivalent forms of a fraction, decimal, and/or percent. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, Why is it important to creat Lesson 43 practice mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent division set a-f 11/22/2014 equivalent forms. problems? Lesson 43 Written 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the process for Practice 11/22/2014 numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. finding an unknown 2.8.6.C-Recognize, describe, extend, create, number in a fraction or replicate, form a rule, and/or find a missing decimal number? element for a variety of whole number patterns, sequences, and relationships verbally, numerically, symbolically, and graphically. 2.1.6.D-Apply place value concepts to order and How can you determine Lesson 44 practice compare decimals; use the number line to order which decimal number is set a-j 11/23/2014 and compare decimals, fractions, and mixed larger, smaller, or if they Lesson 44 Written numbers. are equal when they do not Practice 11/23/2014 have the same number of decimal places? 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is the correct process Lesson 45 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed for dividing a decimal set a-jk 11/24/2014 numbers. number by a whole Lesson 45 Written number? Practice 11/24/2014 Test 8 11/30/2014 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole How do you represent the Lesson 46 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. value of each digit within a set a-o 12/1/2014 2.1.5.D-Apply place value concepts to order and large whole number? Lesson 46 Written compare decimals and to express whole numbers Practice 12/1/2014 and decimals in expanded notation. 2.3.7.C-Use measurement formulas to calculate What does the value of Pi Lesson 47 practice volume, area, and perimeter and to calculate represent? set a-g 12/2/2014 circumference and area of circles. What is the relationship Lesson 47 Written between the circumference Practice 12/2/2014 and diameter of a circle? What is the relationship between the circumference and radius of a circle? Content Lessons Resources write a percent as a decimal calculate the percent of a number calculate sales tax on a purchase percent reduce sales tax Lesson 41 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 216-220 rename fractions by multiplying by fractions equal to 1 add or subtract fractions with different denominators equivalent fractions Lesson 42 addition/subtraction of fractions Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 221-224 create equivalent division problems to find division answers identify the value of the unknown in a fraction or decimal problem Unknown variable Equation division problems Lesson 43 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 225-230 simplify decimal numbers compare and order decimal numbers decimal numbers comparison ordering Lesson 44 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 231-234 divide a decimal number by a whole number division divisor dividend quotient Lesson 45 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 235-238 write a decimal number in expanded notation mentally multiply a decimal number by 10 or 100 mentally multiply whole numbers by 10 or 100 expanded notation decimal numbers mental multiplication determine the value of Pi Calculate the circumference of a cirlce using the formula C = Pi x diameter Pi circumference Test 8 Lesson 46 Lesson 47 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 239-243 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 244-249 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. What is the correct process Lesson 48 practice subtract mixed numbers through regrouping for subtracting mixed set a-h 12/3/2014 numbers when regrouping Lesson 48 Written is involved? Practice 12/3/2014 regrouping Lesson 48 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 250-253 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. What is the correct process Lesson 49 practice divide a decimal or whole number by a for dividing a whole set a-k 12/6/2014 decimal number number by a decimal Lesson 49 Written number? Practice 12/6/2014 What is the correct process for dividing a decimal number by a decimal number? division decimal number divisor Lesson 49 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 254-258 locate and identify decimal numbers on a number line divide a whole number by a fraction number line reciprocal Lesson 50 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 250-253 create bar graphs, pictographs, and circle graphs to display qualitative data creat line plots and stem-and leaf plots to display quantitative data calculate mean, median, mode, and range for a set of data points bimodal mean median mode pictograph range stem-and-leaf plot circle graph line plot 2.1.6.D-Apply place value concepts to order and compare decimals; use the number line to order and compare decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. How is the position of a Lesson 50 practice decimal number set a-h 12/7/2014 determined on a number Lesson 50 Written line? Practice 12/7/2014 What is the correct process for dividing a whole number by a fraction? Test 9 12/8/2014 2.6.6.B-Select an appropriate method to organize How can you determine data; select an appropriate format to display data. which type of graph is best 2.6.6.C-Select and use, as appropriate, the mean, to display data? median, mode, and/or range to describe sets of What is the correct process data. of finding the mean, 2.6.6.D-Use measures of central tendency to median, mode, and compare two sets of data. range? 2.6.6.E-Interpret data displayed in a table, histogram, graph, or data summarized by numerical measures. Lessons 51 to 60 ~ Test 9 Investigation Saxon Math 5 Course 1 pg. 264-267 This unit covers Lessons 51 to 60, Tests 10 and 11, and Investigation 6 Standards Essential Questions Assessments 2.1.6.D-Apply place value How does place value effect the concepts to order and compare rounding of a decimal number? decimals; use the number line How is sales tax determined to order and compare when the decimal number has decimals, fractions, and mixed more than 2 decimal place numbers. values? 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Skills Lesson 51 Practice Set a- round money amounts to the nearest cent k 12/10/2014 Lesson 51 Written Practice 12/10/2014 round decimal numbers to the nearest hundredth, tenth, and whole number How can mental math be used toLesson 52 Practice Set a-i divide a decimal number by 10 mentally divide decimal numbers by a 12/13/2014 divide a decimal number by 100 mentally multiple of 10? Lesson 52 Written Practice 12/13/2014 What are the important rules to Lesson 53 Practice Set a- calculate the sum, difference, product, and/or quotient follow when adding, subtracting, e 12/14/2014 of decimal and/or whole numbers multiplying, and dividing decimal Lesson 53 Written simplify an improper fraction into a mixed number numbers? Practice 12/14/2014 How can an improper fraction be represented as a mixed number? Content Lessons Resources cents Lesson 51 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 268-271 Lesson 52 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 272-275 operations involving Lesson 53 decimal numbers Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 276-279 sales tax decimal place values rounding decimal numbers mental math improper fractions mixed numbers 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.5.B-Use number theory concepts and models to represent or rename whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. How can grouping factors help reduce a fraction? What is the correct process for dividing a fraction by a fraction? 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory concepts to calculate the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) and/or LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Why do fractions have to have the same denominator in order to add or subtract them? How do you find a common denominator of two or more fractions? Lesson 54 Practice Set a- reduce a fraction by grouping factors in the numerator numerator e 12/15/2014 and denominator that are equal to 1 Lesson 54 Written divide a fraction by a fraction denominator Practice 12/15/2014 factor Lesson 54 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 280-284 Lesson 55 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 276-279 division fractions 2.1.6.D-Apply place value How do you find a common concepts to order and compare denominator of two or more decimals; use the number line fractions? to order and compare Why do fractions have to have decimals, fractions, and mixed the same denominator in order numbers. to add or subtract them? 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory How can fractions with different concepts to calculate the GCF denominators be compared? (Greatest Common Factor) and/or LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, What is the 3 step method for and divide whole numbers, adding and subtracting decimals, fractions, and mixed fractions? numbers. Lesson 55 Practice Set ag 12/16/2014 Lesson 55 Written Practice 12/16/2014 reciprocal find the least common denominator of two fractions common rename one fraction so that two fractions have denominators common denominators add or subtract two fractions that do not have common denominators Test 10 12/17/2014 Lesson 56 Practice Set a-i rename two fractions so that the fractions have common 12/20/2014 common denominators denominators Lesson 56 Written add or subtract two fractions that do not have common (continued) Practice 12/20/2014 denominators compare two fractions with unlike denominators by renaming one or both fractions Lesson 57 Practice Set a-f add or subract fractions using 3 steps- shape, operate,addition and 12/21/2014 simplify subtraction of Lesson 57 Written fractions (3 steps: Practice 12/21/2014 shape, operate, simplify) 2.7.6.A-Collect data and How is the likelihood (probability)Lesson 58 Practice Set a-l express the probability of an event as a reduced chance estimate the likelihood of of an event occuring or not 12/22/2014 fraction, decimal, or percent probability outcomes of an event. calculated? Lesson 58 Written express the probability that an event will NOT occur assample space 2.7.6.C-Express the probability How can the probability be Practice 12/22/2014 a reduced fraction, decimal, or percent complement of an of a simple event as a fraction, expressed as a decimal, fraction, Find the probability of an event by dividing the number event decimal, and percent. and percent? of outcomes in the event by the number of possible 2.7.6.D-List the possible outcomes outcomes for two independent events and compare the outcomes. 2.7.6.E-Find and interpret the experimental probability of an outcome of a simple event. 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory Can the three step method of Lesson 59 Practice Set a-f add mixed numbers that do not have a common common concepts to calculate the GCF shape, operate, simplify, used to 12/23/2014 denominator using the three step method (shape, denominators (Greatest Common Factor) add fractions be used to add Lesson 59 Written operate, simplify) addition of mixed and/or LCM (Least Common mixed numbers too? Practice 12/23/2014 numbers (3 step Test 10 Lesson 56 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 289-294 Lesson 57 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 295-298 Lesson 58 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 299-305 Lesson 59 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 306-309 Multiple) of two numbers. Why do mixed numbers have to 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, have a common denominator and divide whole numbers, when adding? decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.3.6.C-Use given How are polygons named? Lesson 60 Practice Set ameasurements to calculate a What is the relationship between e 1/3/2015 missing length, perimeter, area, the perimeter of a regular Lesson 60 Written and/or volume; Calculate polygon and the length of its Practice 1/3/2015 elapsed time across am/pm sides? and across days. Test 11 1/4/2015 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, How are the number of faces, and/or describe properties of 1- edges and vertices determined , 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes for a given geometric solid? and their related parts, and What are the names of some classify and compare 2- and 3- common geometric solids? dimensional shapes on the How is volume of a geometric basis of their properties. slid determined? Lessons 61-70 ~ method: shape, operate, simplify) identify a polygon by the number of sides it has calculate the length of a side of a regular polygon when given its perimeter polygon regular polygon congruent recognize, name, and draw common geometric solids geometric solids identify the number of faces, edges, and vertices in polyhedron various geometric solids faces find the surface area of a polyhedron edges determine the volume of a geometric solid by counting vertices cubes volume surface area Lesson 60 Saxon Math Course 1 pg. 310-313 Test 11 Investigation Saxon Math 6 Course 1 pg. 314-319 This unit includes lessons 61-70, Investigation 7, and Tests 12 and 13 Standards 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Essential Questions Assessments Skills What is the process Practice Set a-h 1/6/2015 add three or more fractions or of adding three or Written Practice 1/6/2015 mixed numbers more fractions or mixed numbers together? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole How is a mixed Practice Set a-j 1/7/2015 convert a mixed number to an numbers, fractions, mixed number converted to Written Practice 1/7/2015 improper fraction numbers, decimals, and percents an improper in equivalent forms. fraction? 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory How are least Practice Set a-j 1/10/2015 Rename fractions with common concepts to calculate the GCF common Written Practice denominators (Greatest Common Factor) and/or denominators related 1/10/2015 subtract mixed numbers LCM (Least Common Multiple) of to common two numbers. denominators? 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, What are the Practice Set a-f 1/11/2015 identify, classify, and draw and/or describe properties of 1-, characteristics of Written Practice quadrilaterals according to 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes certain polygons? 1/11/2015 characteristics of their sides and and their related parts, and angles classify and compare 2- and 3dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. M5.A.1.6-Apply number theory What is the Practice Set a-h identify a composite number concepts (i.e., primes, factors, difference between a 1/12/2015 write the prime factorization of a multiples, composites). prime number and a Written Practice given composite number (Reference: 2.1.5.E) composite number? 1/12/2015 make a factor tree to find the How is a factor tree prime factorization of a given used? number Test 12 1/13/2015 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, What is the correct Practice Set a-k multiply a mixed number by a and divide whole numbers, process of 1/14/2015 whole number decimals, fractions, and mixed multiplying mixed Written Practice multiply a mixed number by a numbers. numbers? 1/14/2015 mixed number Content Lessons Resources least common denominator Lesson 61 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 320-323 improper fraction Lesson 62 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 324-328 sea level Lesson 63 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 329-332 parallelogram rectangle rhombus square trapezium trapezoid Lesson 64 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 333-336 composite number prime factorization factor tree Lesson 65 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 337-341 terms mixed number whole number Test 12 Lesson 66 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 344-345 2.1.6.E-Apply number theory How does prime Practice Set a-d model prime factorization to reduce concepts to calculate the GCF factorization help you 1/18/2015 reduce fractions prime factorization (Greatest Common Factor) and/or reduce fractions? Written Practice LCM (Least Common Multiple) of 1/18/2015 two numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, How do you divide Practice Set a-j 1/19/2015 divide a mixed number by a whole fraction and divide whole numbers, mixed numbers? Written Practice number reciprocal decimals, fractions, and mixed How do you divide 1/19/2015 divide a mixed number by a mixed numbers. fractions? number 2.3.7.F-Estimate and verify How are Practice Set a-f 1/20/2015 identify supplementary angles complementary angles measurements of length, complementary and Written Practice calculate the measure of the supplementary angles perimeter, area, volume, capacity, supplementary 1/20/2015 complement of an angle temperature, time, weight, and angles the same? calculate the measure of the angles. How are supplement of an angle complementary and supplementary angles different? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole Why reduce fractions Practice Set a-i 1/21/2015 reduce fraction terms before fraction numbers, fractions, mixed before multiplying Written Practice multiplying reduce numbers, decimals, and percents How do you reduce 1/21/2015 in equivalent forms. fractions before multiplying? Test 13 1/24/2015 2.9.6.C-Identify on a 2What is a coordinate graph points on a coordinate coordinate plane dimensional coordinate system plane? plane coordinates the location of points with nonWhat is an ordered locate coordinates on a graph negative fractional or decimal pair? coordinate plane ordered pair coordinates; plot in a twoorigin dimensional coordinate system a x-axis point represented by an ordered y-axis pair of nonnegative fractions, mixed numbers, or decimals. Lesson 71-80 ~ Lesson 67 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 347-348 Lesson 68 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 351-352 Lesson 69 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 355-357 Lesson 70 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 360-362 Test 13 Investigation Saxon Math 7 Course 1 pg 363-367 This lesson includes lesson 71-80, investigation 8, and Tests 14 and 15 Standards Essential Questions 2.9.6.B-Predict and describe the How do you classify result of a translation (slide), a quadrilateral? rotation (turn), or reflection (flip) of a 2- dimensional shape. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed Assessments Skills Content Practice Set a-g 1/26/2015 Written Practice 1/26/2015 calculate the measure of an angle base in a parallelogram height calculate the area of a perpendicular parallelogram supplementary angles identify opposite and adjacent adjacent angles on a parallelogram multiply three fractions together Fractions How do you multiply Practice Set a-e fractions? 1/27/2015 When do you multiplyWritten Practice fractions? 1/27/2015 How can numbers be Practice Set a-j 1/28/2015 read expressions with exponents power both the same and Written Practice calculate the value of expressions mixed number different? 1/28/2015 with exponents What are the rules of write the prime factorization of a exponents? number write a decimal number as a fraction or mixed number What is the Practice Set a-j 1/31/2015 convert fractions and mixed cubed relationship between Written Practice numbers to decimal numbers fractions and 1/31/2015 use a calculator to convert a Lessons Resources Lesson 71 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 372-374 Lesson 72 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 376-379 Lesson 73 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 382-384 Lesson 74 Saxon Math Course 1 pg numbers, decimals, and percents decimals? in equivalent forms. How can numbers be the same and different? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole What is the Practice Set a-n 2/1/2015 numbers, fractions, mixed relationship between Written Practice 2/1/2015 numbers, decimals, and percents fractions, decimals, in equivalent forms. and percents? Test 14 2/2/2015 2.1.6.A-Model and compare How do decimals, Practice Set a-f 2/3/2015 values of whole numbers, mixed fractions, and whole Written Practice 2/3/2015 numbers, fractions, and decimals. numbers relate to 2.1.6.B-Represent whole each other? numbers, fractions, mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. 2.8.6.F-Interpret the results of Why is it important to Practice Set a-j 2/4/2015 solving equations in one variable find unstated Written Practice 2/4/2015 in the context of the situation that information? motivated the model. 2.3.6.D-Perform basic How does capacity Practice Set a-d 2/7/2015 conversions within the metric and affect our daily lives? Written Practice 2/7/2015 within the customary systems. What is the 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify difference between measurements of length, metric and U.S. perimeter, area, volume, capacity, Customary System? temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to How do you use the Practice Set a-e 2/8/2015 measure perimeter, area, and formula to find area Written Practice 2/8/2015 volume; use a protractor to of a triangle? measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.11.6.B-Describe the relationship How are ratios useful Practice Set a-b 2/9/2015 between rates of change and in solving problems? Written Practice 2/9/2015 another variable (e.g., time, temperature). fraction to a decimal number convert ratios to decimal numbers 387-389 write a fraction as a percent write a decimal as a percent shift Lesson 75 compare fractions by converting each fraction to decimal form compare Test 14 Lesson 76 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 396-398 diagram fractional-parts fractional-parts statements calculate unstated information from fraction-parts statements convert between units of capacity capacity within the U.S. Customary System Metric System convert between units of capacity U.S. Customary System within the metric system Lesson 77 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 401-403 Lesson 78 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 406-407 calculate area of a triangle using congruent the formula Lesson 79 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 410-413 draw and use a ratio box ratio calculate the constant factor when the ratio and one actual count is known multiply a ratio term by the constant factor to find the actual count Lesson 80 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 414-416 Test 15 2/10/2015 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to How is a bisector measure perimeter, area, and constructed? volume; use a protractor to How is a bisector measure angles between 0 and helpful? 180 degrees. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. Saxon Math Course 1 pg 392-394 use a compass and a ruler to construct the perpendicular bisector of a given line segment use a compass and a ruler to construct the bisector of a given angle angle bisector bisect construction perpendicular bisector Test 15 Investigation Saxon Math 8 Course 1 pg 417-420 Lessons 81-90 + Investigation 9 ~ This unit includes lessons 81-90, Investigation 9, and Tests 16 & 17 Standards 2.3.6.D-Perform basic conversions within the metric and within the customary systems. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion to model relationships between quantities. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion to model relationships between quantities. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. Essential Questions Skills Content Lessons Resources Why is measurement Practice Set a-d important in our 2/14/2015 world? Written Practice Why convert one unit 2/14/2015 of measure to another? How does computing Practice Set a-d volume affect our day- 2/15/2015 to-day lives? Written Practice How are area and 2/15/2015 volume related? add, subtract, multiply, and divide units of measure measurements Lesson 81 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 421-425 calculate the area of the base of a rectangular prism volume base layer Lesson 82 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 426-430 What is a proportion? Practice Set a-d How is a proportion 2/16/2015 read? Written Practice 2/16/2015 read a proportion proportion write a proportion ratio identify a ratio that forms a proportion with a stated given ratio identify a missing term in a proportion using a scale factor solve an expression using a order of order of operations operations Lesson 83 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 431-435 Lesson 84 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 436-440 determine whether two fractions or ratios are cross product equal using cross products calculate a missing proportion using cross products Lesson 85 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 441-446 What is order of operations? Why do you have to follow a certain order when solving a multistep problem? What is a proportion? Assessments Practice Set a-f 2/17/2015 Written Practice 2/17/2015 Practice Set a-e 2/18/2015 Written Practice 2/18/2015 Test 16 2/22/2015 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole How do you calculate Practice Set a-e numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. area of a circle? 2/23/2015 2.3.6.C-Use given measurements to calculate a What is the value of Written Practice missing length, perimeter, area, and/or volume; Pi 2/23/2015 Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across days. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole How do you find the Practice Set a-e numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. value of an unknown 2/24/2015 2.2.6.D-Estimate solutions of problems involving number? Written Practice whole numbers and decimals and check the 2/24/2015 reasonableness of those estimates. 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion to model What is a proportion? Practice Set a-f relationships between quantities. How does a ratio 3/3/2015 relate to a proportion? Written Practice 3/3/2015 2.1.7.B-Represent and use numbers in equivalent How do you estimate Practice Set a-l forms (e.g. integers, fractions, decimals, percents, a square root? 2/25/2015 exponents, powers, roots, absolute values). Written Practice 2/25/2015 calculate the volume of a rectangular prism estimate the area of a circle drawn on a grid enclosed calculate the area of a circle using a formula area Test 16 Lesson 86 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 447-451 calculate a missing factor problem in which the unknown factor is a mixed number calculate a missing factor problem in which the unknown factor is a decimal factor mixed number Lesson 87 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 452-455 solved ratio problems using a proportion accumulation Lesson 88 Saxon Math Course 1 pg 456-459 identify the square root of a number of a irrational number Lesson 89 perfect square over 100 estimate the square root of a number that are not perfect squares using guess and check Saxon Math Course 1 pg 460-464 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 degrees. How many degrees in a full circle? How many degrees in an half circle? Which directions are counterclockwise and clockwise? Practice Set a-c 2/28/2015 Written Practice 2/28/2015 approximate the square root of a number using a calculator describe turns measured in degrees solve problems involving turns clockwise Lesson 90 counterclockwise Test 17 3/1/2015 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole How do you determind numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. the likelihood of an 2.7.6.A-Collect data and estimate the likelihood of event occuring? outcomes of an event. 2.7.6.C-Express the probability of a simple event as a fraction, decimal, and percent. 2.7.6.D-List the possible outcomes for two independent events and compare the outcomes. 2.7.6.E-Find and interpret the experimental probability of an outcome of a simple event. Rational Numbers ~ estimate the probability of an event from data experimental gathered by performing a probability probability experiment theoretical present data in a relative frequency table probability conduct probability experiments Saxon Math Course 1 pg 465-469 Test 17 Investigation Saxon Math Course 1 9 pg 470-473 Digits Standards 6.G.3-Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. 6.NS.5-Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in realworld contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 6.NS.6-Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. 6.NS.7-Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. 6.NS.6a-Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g., –(– 3) = 3, and that 0 is its own opposite. 6.NS.6b-Understand signs of numbers in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane; recognize that when two ordered pairs differ only by signs, the locations of the points are related by reflections across one or both Essential Questions Assessments Skills determine a rational number and its opposite to represent a situation (9.1) compare rational numbers and their absolute values (9.2) order rational numbers (9.3) plot and write the coordinates of rational numbers on the coordinate plane (9.4 - 9.5) write the coordinates, including rational numbers, of a point that is reflected (9.4) determine the length of a segment on a coordinate plane (9.5) Content Lessons Resources axes. 6.NS.6c-Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. 6.NS.7a-Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. 6.NS.7b-Write, interpret, and explain statements of order for rational numbers in real-world contexts. 6.NS.7c-Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation. Ratios ~ Digits Essential Questions Standards Assessments 6.RP.1-Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. 6.RP.3-Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve realworld and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. Lessons 91-100 ~ Standards Skills Content Lessons Resources write a ratio to represent a situation (10.1) write equivalent ratios (10.2 - 10.3) represent ratios in three different forms (10.4) simplify ratios (10.4) convert ratios to its decimal equivalent (10.5) This unit includes lessons 91-100, Tests 18 & 19, and Investigation 10 Essential Questions Assessments Skills 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole Why is it easier to use a Practice Set a-g numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. formula to solve a real 3/4/2015 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe world problem? Written Practice properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and What are the different 3/4/2015 their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- geometric formulas? dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. 2.3.5.C-Calculate perimeter and area, and sums and differences of measurements. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What is order of Practice Set a-g numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. operations? 3/7/2015 Why do you have to Written Practice follow order of operations 3/7/2015 when solving a multistep problem? 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe What are the two ways Practice Set a-e properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and traingles are classified? 3/8/2015 their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3Written Practice dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. 3/8/2015 Content Lessons Resources Calculate the perimeter and area of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and triangles using formulas. area perimeter Lesson 91 Saxon Course 1pg 474-478 write the powers of 10 with exponents simplify expressions with exponents and roots use exponents with fractions and decimals expanded notation order of operations Lesson 92 Saxon Course 1pg 479-483 classify triangles by the lengths of their sides classify triangles by the measure of their angles acute triangle Lesson 93 isosceles triangle equilateral triangle obtuse triangle right triangle scalene triangle Saxon Course 1pg 484-487 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. How are common fractions, decimals and percents alike and different? Why reduce fractions before multiplying? Practice Set a-q 3/9/2015 Written Practice 3/9/2015 Practice Set a-g 3/10/2015 Written Practice 3/10/2015 Test 18 3/11/2015 What is the best way to Practice Set a-e represent a fraction? 3/14/2015 What does a function Written Practice look like on a graph? 3/14/2015 2.8.6.D-Determine a functional rule from a table or graph. 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.9.6.C-Identify on a 2- dimensional coordinate system the location of points with non-negative fractional or decimal coordinates; plot in a twodimensional coordinate system a point represented by an ordered pair of nonnegative fractions, mixed numbers, or decimals. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, Can you identify and Practice Set a-e area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles name the angles formed 3/15/2015 between 0 and 180 degrees. by a transversal crossing Written Practice 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, two or more lines? 3/15/2015 perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe How do you find a properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and missing angle in a their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- quadrilateral when given dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. the other three? How do you find a missing angle in a triangle when given the other two? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed How are common numbers, decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. fractions, decimals and 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole percents alike and numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. different? 2.2.7.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole What are integers? numbers, decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, or How do you add integers. integers? What are the rules for adding integers? Practice Set a-f 3/16/2015 Written Practice 3/16/2015 Practice Set a-l 3/17/2015 Written Practice 3/17/2015 Practice Set a-o 3/18/2015 Written Practice 3/18/2015 change a fraction, a decimal, or a mixed number to a percent by multiplying by 100% Lesson 94 Saxon Course 1pg 488-492 cancel units of measure before multiplying unit of measure Lesson 95 Saxon Course 1pg 493-496 identify the rule of a function identify a missing number in a function table make a table for a funtion graph a function on a coordinate plane fraction decimal percent function Lessons 101-110 ~ Saxon Course 1pg 497-502 identify transversals, interior angles, alternate exterior Lesson 97 alternate interior angles, exterior angles, angles alternate exterior angles, and alternate interior corresponding angles angles identify the measures of the angles formed corresponding by a transversal intersecting two parallel angles lines when the measure of one angle is transversal known parallel lines supplementary identify the interior and exterior angles of a exterior angle Lesson 98 polygon interior angle calculate the sums of the interior angles of a triangle and of a quadrilateral calculate the measure of one interior angle in a triangle or quadrilateral when the measure of the other interior angles are known Complete a table that shows equivalent decimal Lesson 99 fractions, decimals, and percents percent fraction Saxon Course 1pg 503-507 add integers using a number line algebraic identify the opposite of an integer integers subtract integers using algebraic addition Saxon Course 1pg 517-523 Test 19 3/21/2015 2.7.6.A-Collect data and estimate the likelihood of How do you find the outcomes of an event. liklihood of multiple 2.7.6.C-Express the probability of a simple event as a outcomes to occur? fraction, decimal, and percent. 2.7.6.E-Find and interpret the experimental probability of an outcome of a simple event Test 18 Lesson 96 create a tree diagram that shows all possible outcomes of a compound experiment determine the probability of the possible outcomes of a compound experiment This unit will cover Lessons 101-110, Tests 20 and 21, and Investigation 11 compound experiment compound outcomes tree diagram Lesson 100 Saxon Course 1pg 508-512 Saxon Course 1pg 513-516 Test 19 Investigation Saxon Course 1pg 10 524-527 Standards 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion to model relationships between quantities. 2.1.7.F-Understand the concepts of ratio, proportion, percents, and rates to determine unknown quantities in equations. 2.3.6.D-Perform basic conversions within the metric and within the customary systems. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. Essential Questions Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources How can the ratio box from Lesson 80 be used when totals are given in the word problem? Lesson 101 practice set a-c 3/23/2015 Lesson 101 Written Practice 3/23/2015 solve ratio problems that involve totals using a ratio box ratio boxes actual count Lesson 101 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 528532 identify and convert units of mass in the metric system identify and convert units of weight in the US Customary System add and subtract measures in pounds and ounces mass Lesson 102 weight customary and metric units of mass and weight Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 533537 calculate the perimeter of a complex shape perimeter of Lesson 103 identify the missing lengths of complex complex shapes shapes using given sides Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 538542 add positive and negative numbers (integers) addition of integers Lesson 104 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 543547 solve percent problems by using a ratio box, setting up a proportion, and solving the proportion proportions percent ratio box Lesson 105 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 548552 calculate the value of the variable in the equation using 2 steps check the answer to the equation using substitution variables two-step equations calculate the area of a complex shape complex shapes Lesson 107 area How can the mass of an Lesson 102 practice object be measured? set a-e 3/24/2015 How can the weight of an Lesson 102 Written object be measured? Practice 3/24/2015 What is the relationship between ounces and pounds? How are weight and mass different? 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of How can missing lengths Lesson 103 practice perimeter, area, and volume. be determined on a set a-b 3/25/2015 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, complex shape? Lesson 103 Written area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles What makes a shape Practice 3/25/2015 between 0 and 180 degrees. complex? 2.3.6.C-Use given measurements to calculate a How can the perimeter of missing length, perimeter, area, and/or volume; a complex shape be Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across calculated? days. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.2.7.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole How can numbers with Lesson 104 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, or different signs be added set a-f 3/28/2015 integers. together? Lesson 104 Written How do the signs of the Practice 3/28/2015 addends affect the sign of the sum? 2.1.7.C-Use ratio and proportion to model How is a ratio box used Lesson 105 practice relationships between quantities. to create a proportion? set a-e 3/29/2015 2.1.7.F-Understand the concepts of ratio, proportion, How can a ratio box and Lesson 105 Written percents, and rates to determine unknown quantities proportion help solve a Practice 3/29/2015 in equations. word problem in which percents are given? Test 20 3/30/2015 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole Using only two steps, Lesson 106 practice numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. how can the value of a set a-f 3/31/2015 2.8.7.B-Evaluate and simplify algebraic expressions variable in an equation Lesson 106 Written and solve and graph linear equations and be determined? Practice 3/31/2015 inequalities. How can one check to be sure the calculated value is correct? 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of How can the area of a Lesson 107 practice perimeter, area, and volume. complex shape be set a-b 4/1/2015 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, calculated? Lesson 107 Written area, and volume; use a protractor to measure angles Practice 4/1/2015 between 0 and 180 degrees. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. Test 20 Lesson 106 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 553556 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 557560 2.9.6.B-Predict and describe the result of a translation How can the position of aLesson 108 practice (slide), rotation (turn), or reflection (flip) of a 2figure be changed set a-f 4/4/2015 dimensional shape. without changing the Lesson 108 Written dimensions of the figure? Practice 4/4/2015 What terms can be used to describe the change in position of a figure? 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe If two figures are Lesson 109 practice properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and congruent, how can their set a-f 4/5/2015 their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- corresponding sides and Lesson 109 Written dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. angles be determined? Practice 4/5/2015 What does it mean when one says that two sides or angles are corresponding? 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe How can one determine Lesson 110 practice properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and if a figure is set a-c 4/6/2015 their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- symmetrical? Lesson 110 Written dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. How can one determine Practice 4/6/2015 the amount of lines of symmetry a figure or object has? How can one determine if an object or figure has rotational symmetry? Test 21 4/7/2015 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of How can one create a perimeter, area, and volume. smaller model of a large 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe figure using a scale properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and factor? their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- How can the actual dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. measurements of an object be determined from a scaled model? Rates ~ identify and describe rotations, translations, and reflections change the position of a figure using transformations reflection rotation transformation translation Lesson 108 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 561565 identify the corresponding sides and angles of two congruent figures identify similar triangles and their corresponding angles and sides identify similar rectangles and their corresponding angles and sides corresponding parts similar figures Lesson 109 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 566572 identify symmetrical figures draw lines of symmetry in figures and objects identify figures with rotational symmetry symmetry Lesson 110 lines of symmetry rotational symmetry Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 573577 calculate the actual measurements of the object being represented using the legend in the scale drawing or model calculate an unknown measurement in a scale drawing or model problem using a proportion calculate the dimensions of an actual object using the scale factor of a model legend scale drawings scale factor scale model Test 21 Investigation Saxon Math 11 Course 1 pgs. 578581 Digits Standards 6.RP.2-Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ? 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. 6.RP.3-Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve realworld and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. 6.RP.3b-Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. 6.RP.3d-Use ratio reasoning to convert measurement units; manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. Essential Questions Assessments Skills convert a rate to a unit rate (11.1, 11.5) analyze a situation using a unit rate (11.1, 11.5) calculate a unit price (11.2, 11.5) calculate constant speed (11.3, 11.5) analyze a situation using constant speed (11.3, 11.5) convert units using ratios (11.4, 11.5) Content Lessons Resources Ratio Reasoning ~ Digits Essential Questions Standards 6.EE.9-Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. For example, in a problem involving motion at constant speed, list and graph ordered pairs of distances and times, and write the equation d = 65t to represent the relationship between distance and time. 6.RP.2-Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ? 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. 6.RP.3-Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve realworld and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. 6.RP.3a-Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole-number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. 6.RP.3c-Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent. Lessons 111-120 ~ Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources represent a ratio/rate using a table and a graph (12.1) determine proportional relationship (12.2) convert ratios, fractions, and percents (12.3) compute a percent of a quantity (12.4) This unit will cover Lessons 111-120, Tests 22 and 23, and Investigation 12 Standards Essential Questions Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. 2.4.6.A-Use models, properties, and relationships to draw conclusions and explain reasons for conclusions. 2.5.6.A-Develop a plan to analyze a problem, identify the information needed to solve the problem, carry out the plan, check whether an answer makes sense, and explain how the problem was solved in grade appropriate contexts. 2.2.7.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, decimals, fractions, mixed numbers, or integers. When a real-world situation is Lesson 111 Practice interpret the remainders to presented in a division problem, Set a-e 4/11/2015 division problems that have how can it be determined Lesson 111 Written real-world applications whether to round the remainder Practice 4/11/2015 up or down? remainders division problems real-world appllication How can numbers with different Lesson 112 Practice calculate the product of two signs be multiplied together? Set a-h 4/12/2015 integers How can a number be divided Lesson 112 Written calculate the quotient of two by a number with a different Practice 4/12/2015 integers sign? 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, What is a mixed measure and Lesson 113 Practice rename units to add and decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. how does one add or subtract Set a-f 4/13/2015 subtract mixed measures 2.3.6.D-Perform basic conversions within the metric and within the them? Lesson 113 Written multiply a number by a power customary systems. How can powers of 10 be used Practice 4/13/2015 of ten to rewrite a number in 2.1.7.B-Represent and use numbers in equivalent forms (e.g. in mutlipliction to create standard notation numbers in standard notation? Lesson 111 Saxon Math Course 1 pgs. 582-586 multiplication Lesson 112 Saxon Math of integers Course 1 pgs. division of 587-591 integers addition and Lesson 113 Saxon Math subtraction of Course 1 pgs. mixed 592-596 measures multiplication integers, fractions, decimals, percents, exponents, powers, roots, by powers of absolute values). ten 2.3.6.D-Perform basic conversions within the metric and within the What does a unit multiplier look Lesson 114 Practice write unit multipliers for unit multiplier Lesson 114 Saxon Math customary systems. like and how are they created? Set a-g 4/14/2015 equivalent measures Course 1 pgs. Once created, how does a unit Lesson 114 Written convert from one unit to 597-601 multiplier help with conversions Practice 4/14/2015 another using a unit multiplier between units? 2.1.6.B-Represent whole numbers, fractions, mixed numbers, How can a percent that Lesson 115 Practice convert a percent that conversion of Lesson 115 Saxon Math decimals, and percents in equivalent forms. contains a fraction already be Set a-e 4/15/2015 contains a fraction to a percent to Course 1 pgs. 2.1.6.C-Use models to represent the concept of equivalent forms of converted into a fraction that is Lesson 115 Written fraction fraction 602-605 a fraction, decimal, and/or percent. equivalent? Practice 4/15/2015 Test 22 4/26/2015 Test 22 2.2.6.B-Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, What is the difference between Lesson 116 Practice calculate compound interest compound Lesson 116 Saxon Math decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. simple interest and compound Set a-c 4/27/2015 using paper/pencil and/or a interest Course 1 pgs. 2.4.6.B-Use if…then statements to express conditional interest? Lesson 116 Written calculator interest 606-611 relationships. How can one calculate the Practice 4/27/2015 principal 2.11.6.B-Describe the relationship between rates of change and amount of interest earned on a simple another variable (e.g., time, temperature). given amount of money? interest 2.5.6.A-Develop a plan to analyze a problem, identify the How can a diagram help find a Lesson 117 Practice draw a diagram to find a fractional parts Lesson 117 Saxon Math information needed to solve the problem, carry out the plan, check whole in a fractional-parts Set a-e 4/28/2015 whole in a fractional-parts of a whole Course 1 pgs. whether an answer makes sense, and explain how the problem problem when only a fraction is Lesson 117 Written problem when a fraction is diagraming 612-616 was solved in grade appropriate contexts. known? Practice 4/28/2015 known 2.5.6.B-Use appropriate mathematical terms, vocabulary, language, symbols, and graphs to explain clearly and logically solutions to problems. 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of perimeter, area, What is an irregular shape? Lesson 118 Practice estimate the area of an estimation of Lesson 118 Saxon Math and volume. Since the shape is irregular, Set 4/29/2015 irregular shape using a grid area Course 1 pgs. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, how can the area of it be Lesson 118 Written 617-620 area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. determined? Practice 4/29/2015 2.8.6.E-Use combinations of symbols and numbers to create How can an equation be Lesson 119 Practice write and solve an equation to percents Lesson 119 Saxon Math expressions, equations, and inequalities that model mathematical created to help determine a Set a-g 5/2/2015 find a whole when a percent is Equation Course 1 pgs. situations. whole when a percent is Lesson 119 Written known 621-625 known? Practice 5/2/2015 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of perimeter, area, How is the volume of a cylinder Lesson 120 Practice calculate the volume of a volume of a Lesson 120 Saxon Math and volume. calculated? Set 5/3/2015 cylinder using the given cylinder Course 1 pgs. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and What is the relationship Lesson 120 Written formula 626-629 volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 between the volume of the Practice 5/3/2015 degrees. cylinder and the area of its 2.3.6.C-Use given measurements to calculate a missing length, circular bases? perimeter, area, and/or volume; Calculate elapsed time across am/pm and across days. 2.3.6.F-Estimate and verify measurements of length, perimeter, area, volume, capacity, temperature, time, weight, and angles. 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe properties of 1-, 2-, and 3- dimensional shapes and their related parts, and classify and compare 2- and 3- dimensional shapes on the basis of their properties. Test 23 5/4/2015 Test 23 2.3.6.A-Use models to illustrate the meaning of perimeter, area, How were the formulas for calculate the volume of formulas for Investigation Saxon Math and volume. volume and surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, volume, and 12 Course 1 pgs. 2.3.6.B-Use appropriate units to measure perimeter, area, and prisms, pyramids, cylinders, and cones using the correct surface area of 602-605 volume; use a protractor to measure angles between 0 and 180 and cones derived? formula prisms, degrees. How can these formulas be calculate the surface area of pyramids, 2.9.6.A-Identify, define, label, and/or describe properties of 1-, 2-, used to calculate the actual prisms and cylinders using the cylinders and and 3- dimensional shapes and their related parts, and classify and volume and surface area of correct formula cones compare 2- and 3- dimensional shapes on the basis of their these 3 dimensional solids? properties. Area ~ Digits Standards Essential Questions Assessments Skills 6.G.1-Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Surface Area and Volume ~ Content Lessons Resources calculate a side length of a rectangle or square when given the area (13.1) calculate the area of a rectangle or square (13.1) calculate the area of a right triangle (13.2) caluculate the area of a parallelogram (13.3) calculate the base or height of a parallelogram when given its area (13.3) calculate the area of acute and obtuse triangles (13.4) calculate the area of a trapezoid (13.5) calculate the area of a regular polygon (13.5) Digits Standards 6.G.2-Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with fractional edge lengths by packing it with unit cubes of the appropriate unit fraction edge lengths, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths of the prism. Apply the formulas V = l w h and V = b h to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. 6.G.4-Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Essential Questions Assessments Skills describe 3-D figures (14.1) identify a 3-D figure when given a net (14.2) draw a net of a given 3-D figure (14.2) compute the surface area of a prism (14.3) compute the surface area of a pyramid (14.4) compute volume of rectangular prisms (14.5) Content Lessons Resources