Document
advertisement

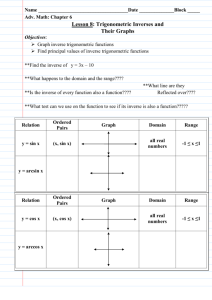
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions 1 4.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Objectives: Evaluate inverse sine functions. Evaluate other inverse trigonometric functions. Evaluate compositions of trigonometric functions. 2 Inverse Functions Recall that a function and its inverse reflect over the line y = x. What must be true for a function to have an inverse? It must be one-to-one, that is, it must pass the horizontal line test. 3 More Inverse Functions Are sine, cosine, and tangent one-to-one? If not, what must we do so that these functions will have inverse functions? Hint: Consider y = x2. We must restrict the domain of the original function. 4 Sine and Its Inverse f(x) = sin x does not pass the Horizontal Line Test It must be restricted to find its inverse. y 1 y = sin x 2 x 1 Sin x has an inverse x function on this 2 2 interval. 5 Inverse Sine Function The inverse sine function is defined by y = arcsin x if and only if sin y = x. Angle whose sine is x The domain of y = arcsin x is [–1, 1]. The range of y = arcsin x is _____________. Why are the domain and range defined this way? 6 What Does “arcsin” Mean? In an inverse function, the x-values and the y-values are switched. So, arcsin x means the angle (or arc) whose sin is x. Notation for inverse sine arcsin x sin -1 x 7 Examples If possible, find the exact value. 1 1. arcsin 2 2. sin 1 3 2 3. sin 1 2 8 Graphing Arcsine Create a table for sin y = x for –π/2 ≤ y ≤ π/2. y x –π/2 –π/4 –π/6 0 π/6 π/4 π/2 Graph x on horizontal axis and y on vertical axis. 9 Graph of Arcsine 10 Inverse Cosine Function f(x) = cos x must be restricted to find its inverse. y 1 y = cos x 2 x 1 Cos x has an inverse function on this interval. 0 x 11 Inverse Cosine Function The inverse cosine function is defined by y = arccos x if and only if cos y = x. Angle whose cosine is x The domain of y = arccos x is [–1, 1]. The range of y = arccos x is [0, π]. Notation for inverse cosine: arccos x or cos -1 x 12 Examples If possible, find the exact value 1 1. arccos 2 3 2. cos 2 1 13 Graphing Arccos Create a table for cos y = x for 0 ≤ y ≤ π. y x 0 π/6 π/3 π/2 2π/3 5π/6 π Graph x on horizontal axis and y on vertical axis. 14 Graph of Arccos 15 Inverse Tangent Function f(x) = tan x must be restricted to find its y inverse. y = tan x 2 3 2 3 2 x 2 Tan x has an inverse function on this interval. 2 x 2 16 Inverse Tangent Function The inverse tangent function is defined by y = arctan x if and only if tan y = x. Angle whose tangent is x The domain of y = arctan x is (–∞, ∞). The range of y = arctan x is (–π/2, π/2). Notation for inverse tangent: arctan x or tan -1 x 17 Examples If possible, find the exact value 3 1. arctan 3 2. tan 1 3 18 Graph of Arctan 19 Examples Evaluate using your calculator. (What mode should the calculator be in?) 1. cos 1 0.75 2. arcsin 0.19 3. arctan 1.32 4. arcsin 2.5 20 Summary 21 Composition of Functions Given the restrictions specified in the previous slide, we have the following properties of inverse trig functions. sin(arcsin x) x and arcsin(sin y ) y cos(arccos x) x and arccos(cos y ) y tan(arctan x) x and arctan(tan y ) y 22 Examples If possible, find the exact value. 1. tan arctan 5 5 2. arcsin sin 3 3. cos cos 1 23 Example Find the exact value of tan arccos 2 . 3 adj 2 2 Let u = arccos , then cos u . 3 hyp 3 y 3 32 22 5 u x 2 opp 2 tan arccos tan u 5 3 adj 2 24 Example 3 Find the exact value of cos arcsin . 5 25 Homework 4.7 Worksheet 4.7 26