verb usage - Laurel County Schools
advertisement

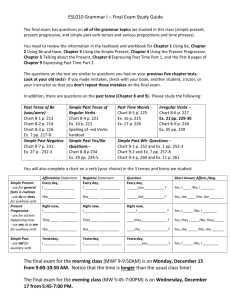
VERB USAGE DARTS: I can: 1.Identify and use the six major verb tenses correctly. 2.Identify and understand the four principal parts of verbs. 3.Conjugate regular and irregular verbs correctly. VERB TENSES: A tense is the form of a verb that shows the time of an action or condition. The SIX Verb Tenses—Each tense has a basic and progressive form. --The progressive tenses are identified by their tense names PLUS the word progressive. Progressive tenses show that an action is or was happening for a period of time. THE EMPHATIC FORM—EXISTS ONLY FOR THE PRESENT AND PAST TENSES. PRESENT EMPHATIC Uses “do” “does” or “did” Jeff does play tennis more often than Jimmy. PAST EMPHATIC Uses “did” Michael and Jake did play guitar in the band. PRACTICE: Identifying Verb Tenses Page 426—Practice 17.1A and 17.1B WRITING: Write an 8-10 sentence paragraph about a trip you would like to take or have taken. Use at least eight different verb forms or tenses in your paragraph. Highlight the verb forms and tenses in your paragraph. THE FOUR PRINCIPAL PARTS OF VERBS Every verb in the English language has four principal parts from which all of the tenses are formed: the present, the present participle, the past, and the past participle. Present watch Present Participle watching Past Past Participle watched (have) watched THE PRESENT: Used for basic forms of the present and future tenses, as well as for the emphatic forms or tenses. The future is formed with the helping verb “will.” The present emphatic is formed with “do” or “does.” The past emphatic is formed with “did.” PRESENT PARTICIPLE: Is used with helping verbs for all of the progressive forms. Ex: I am walking. THE PAST: Used to form the past tense. The past tense of a verb can change its spelling. Ex: I ran. THE PAST PARTICIPLE: Is used with helping verbs to create the perfect tenses. Ex: I have walked. PRACTICE MAKES “PERFECT” TENSE…. Page 428—17.1C AND 17.1D WRITING APPLICATION: Write a mock radio broadcast about the weather. Use six verb tenses in your description. You will read these to a partner, who will list the verb tenses that you use. Can you trick them??? DARTS: I can use verb tenses correctly. I can use verb tenses to establish sequencing. I can use modifiers with verb tenses to establish time. PRESENT, PAST, AND FUTURE TENSE The three forms of the present tense show present actions or conditions as well as various continuing actions or conditions. I ride. (Present) I am riding. (Present Progressive) I do ride. (Present Emphatic) HISTORICAL PRESENT The present tense may also be used to express historical events. This is used in narration to make past actions or conditions sound more lively. People gather around a store window to watch the first television. People watching the television cannot believe that a picture can come through the air. USES OF THE PRESENT EMPHATIC TENSE Emphasize a Statement—Jane does want to go to the store. Deny a Contrary Assertion—No, she does not want to walk downtown. Ask a Question—Does she enjoy shopping? Make a Negative Sentence—Jane does not want to stay all day. CRITICAL PRESENT TENSE Most often used to discuss deceased authors and their literary achievements. O. Henry writes many stories with surprise endings. O. Henry is the author of several volumes of short stories. PRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSE Used to show a continuing action or condition of a long or short duration. Mark is practicing soccer every afternoon. (Long continuing action) He is trying to make the team. (short continuing action) He is hoping to make the first team someday. (continuing condition) PAST TENSE The seven forms that express past tense show actions and conditions that began at some time in the past. THE MOST COMMON FORM OF PAST: Completed Action—Julian worked on his speech. Completed Condition—He was an interesting speaker. PRESENT PERFECT TENSE ALWAYS expresses indefinite time. Use it to show actions or conditions continuing from the past to the present. We have come to the school dance. We have been excited all day. THE PAST PERFECT TENSE Expresses an action that took place before another action. The coaches had analyzed the other team’s game before they created their own game plans. FUTURE TENSE Expresses actions that have not yet occurred. I will wait. I will have babysat. SEQUENCE OF TENSES When showing a sequence of events, do not shift tenses unnecessarily. Ursula will walk to school, and then she will take the bus home. *Sometimes, it is necessary to shift tenses, especially when a sentence is complex or compound-complex. The tense of the main verb often determines the tense of the verb in the dependent clause. The form of the participle or infinitive often depends on the tense of the verb in the main clause. VERBS IN DEPENDENT CLAUSES The tense of a verb should follow logically from the tense of the main verb. I will understand that Michael was late. (incorrect) I understand that Michael was late. (correct) TIME SEQUENCE WITH PARTICIPLES AND INFINITIVES The form of a participle or an infinitive should logically relate to the verb in the same clause or sentence. Watching the race, they cheer. Having watched the race, they are cheering. MODIFIERS THAT HELP CLARIFY TENSE The time expressed by a verb can often be clarified by adverbs such as often, sometimes, always, or frequently and phrases such as once in awhile, within a week, last week, or now and then. Use modifiers when they help clarify a tense. EX://Richard plays computer games every night. He practices once a day. EXERCISES TO PRACTICE: • Page 450: 17.2H • Page 451: 17.2J • WRITING: Create a twenty silly sentences that follow the following rules: • 1. They all must be complex and compound-complex. • 2. Each sentence must be the chain of the first. For example, the verb in the first sentence becomes the present participle in the second sentence and a perfect participle in the third sentence, and so on. Watching a scary movie, we screamed. Screaming loudly, we felt foolish. 3. Underline and identify all tenses of your verbs.