Food Webs Notes
advertisement
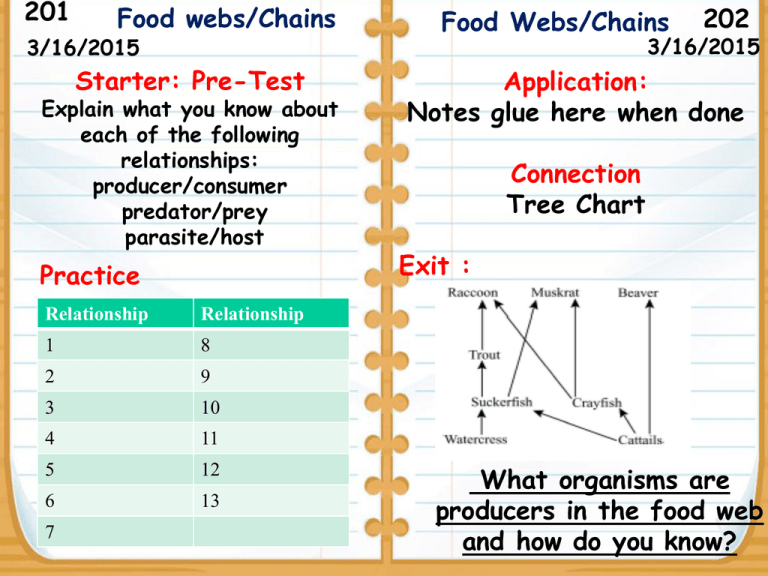
201 Food webs/Chains 3/16/2015 Starter: Pre-Test Explain what you know about each of the following relationships: producer/consumer predator/prey parasite/host Practice Relationship Relationship 1 8 2 9 3 10 4 11 5 12 6 13 7 Food Webs/Chains 202 3/16/2015 Application: Notes glue here when done Connection Tree Chart Exit : What organisms are producers in the food web and how do you know? March 16, 2015 AGENDA Objective 8.11 A I can describe relationships as they occur in food webs by reading and writing while completing notes. 1. Starter 2. Practice 3. Notes 4. Connection/Exit Table of Contents Title/ Topic My 3/3 CBA Review 197-198 3/5 Stellar Finger Prints 199-200 3/16 Food Webs/Chains 201-202 Practice 1. An animal the eats only meat. carnivore herbivore 2. This organism makes nutrients decomposer producer available for producers to reuse by breaking down decaying matter. 3. An organism that cannot makes producer consumer its own food. 4. An animal the eats only plants. omnivore herbivore 5. A ______ ______ shows one possible pathway for energy. Food web food chain 6. An organism that makes food from the sun. producer consumer 7. An animal the eats meat or plants. carnivore omnivore 8. The natural world that surrounds energy an organism is called the organism’s: 9. A ______ ______ shows many possible pathways for energy. environment Food web food chain 10. The source of energy for almost sunlight all life on Earth is water 11. An example of a biotic factor in a waterfall a tree forest ecosystem is: 12. An example of a biotic factor in a temperature fish pond ecosystem is: 13. An example of a producer is a: moss caterpillar 14. This is a/n ______. 15. In an energy pyramid, the lowest level has the __?__ energy. energy pyramid Food chain most least Practice Answers 1. An animal the eats only meat. carnivore herbivore 2. This organism makes nutrients available for producers to reuse by breaking down decaying matter. decomposer producer 3. An organism that cannot makes its own food. 4. An animal the eats only plants. producer consumer omnivore herbivore 5. A ______ ______ shows one possible pathway for energy. Food web food chain 6. An organism that makes food from the sun. producer consumer 7. An animal the eats meat or plants. carnivore omnivore 8. The natural world that surrounds energy an organism is called the organism’s: environment 9. A ______ ______ shows many possible pathways for energy. Food web food chain 10. The source of energy for almost all life on Earth is sunlight water 11. An example of a biotic factor in a waterfall a tree forest ecosystem is: 12 An example of a biotic factor in a temperature fish pond ecosystem is: 13. An example of a producer is a: moss caterpillar 14. This is a/n ______. energy pyramid 15. In an energy pyramid, the lowest most level has the __?__ energy. Food chain least The Sun The sun is the primary source of energy for most living things. The energy flows through nature through the food chain. The Food Chain There are three main parts to most food chains A. Producers-Plants Producers (plants) are the primary source of matter and energy in most food chains. The sun provides energy to the producers. Producers use the sun to create their own source of food or nutrients. Producers (and consumers) also need water, air and certain climates to survive. B. Consumers- Animals Primary consumers (herbivores) get their energy and matter directly from plants (producers). Secondary consumers (carnivores) get their energy and matter from eating the primary consumers. Tertiary consumers (carnivores) get their energy and matter from eating secondary consumers. Omnivores eat plants and animals so they can be more than one level of consumer (Humans belong in this category) C. Decomposers-bacteria and fungi Decomposers are mostly bacteria or fungi like mold, mildew and mushrooms. They feed on the tissues of dead organisms (producers or consumers) and return or recycle gases and nutrients to the environment. FOOD CHAIN The flow of energy and matter in nature nutrients D. Food Chain: • ONLY ONE source of food • Less stable E. Food Web: • More than one choice of food • Several food chains linked together • More stable F. Energy moves through ecosystems in food chains, passing from photosynthesizes (producers) to herbivores (consumers) to carnivores(consumers) creating a food web. • G. The energy that is transferred between trophic levels transfers only 10 percent of its energy into the next trophic level 10% energy transfer 10% energy transfer 10% energy transfer 10% of the energy is passed on as biomass 90% is Lost as Waste Or Used for Reproduction of molecules of organism of next level Trophic levels do have limits. For example: Transfer of energy from level to level is inefficient Exit What organisms are producers in the food web and how do you know? 201 Food webs/Chains 3/16/2015 Starter: Pre-Test Explain what you know about each of the following relationships: producer/consumer predator/prey parasite/host Practice Relationship Relationship 1 8 2 9 3 10 4 11 5 12 6 13 7 Food Webs/Chains 202 3/16/2015 Application: Notes glue here when done Connection Tree Chart Exit : What organisms are producers in the food web and how do you know?





