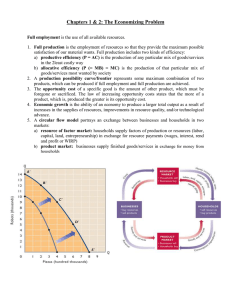
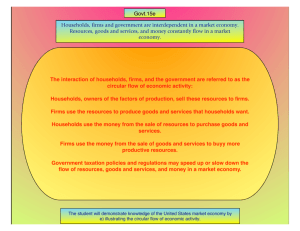
Circular Flow of the Economy
advertisement

The Economizing Problem Human economic wants are unlimited Resources are scarce All economics depends directly on these two facts/assumptions Economics is about doing the best with what we have it’s about using resources in the most efficient manner possible to create the most “stuff” to fulfill wants Resources – Factors of Production Types of resources: Land All natural resources (“gifts of nature”) Minerals, forests, arable land, oil, etc. Income from Land = Rent Capital: human/physical machinery, factories, storage facilities, transportation Income from capital = Interest Labor All physical and mental talents of individuals Income from Labor = Wages Entrepreneurship Initiative, Management, Innovation, Risk-taking Income from Entrepreneurship = Profit/Loss Economic Systems An economic system is a particular set of institutional arrangements and mechanisms that respond to the economizing problem The market system -- “capitalism” The command system -- “communism” The two economic sectors Households - Consumers individuals in their private lives acting as consumers and producers Business – Firms - Producers firms seeking to maximize their profit by purchasing productive resources The Market Economy and the Circular Flow Model Virtually all major economies work through some version of the market economic system In this system, there are a number of different aspects to the market a market to buy and sell resources a market to buy and sell products businesses households Building the Circular Flow Model - Step 1 RESOURCE FACTOR MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS PRODUCT MARKET Building the Circular Flow Model - Step 2 RESOURCE FACTOR MARKET RESOURCES INPUTS BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS PRODUCT MARKET Building the Circular Flow Model - Step 3 COSTS INCOMES RESOURCE MARKET RESOURCES INPUTS BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS GOODS & SERVICES GOODS & SERVICES PRODUCT MARKET Building the Circular Flow Model - Step 4 COSTS INCOMES RESOURCE MARKET RESOURCES INPUTS BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS GOODS & SERVICES GOODS & SERVICES PRODUCT MARKET Building the Circular Flow Model - Step 5 COSTS INCOMES RESOURCE MARKET RESOURCES INPUTS BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS GOODS & SERVICES REVENUE Profit from goods and services GOODS & SERVICES PRODUCT MARKET PAYMENT Goods+Services Factor Market Money for wages, rent, profit, interest Capital, land, labor, entrepreneurship BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS Goods and Services Money PAYMENT for Goods +Services Product Market How can An Economy become more productive??? Specialization Takes place when people, businesses, regions, and even countries concentrate on goods and services that they can produce better than anyone else Division of Labor the breaking down of a job into separate, smaller, tasks, which are performed by different workers. Assembly Line -A manufacturing process in which interchangeable parts are added to a product to create an end product Technological Advances Robotics: machines perform physical tasks Invention: new goods and services Innovation: Improving a good or service Automation: machines control production Labor/Workers -Blue-collar workers: working class employee who perform manual/unskilled labor Ex: factory worker -White-collar workers: perform tasks that require less physical labor. Skilled workers oftentimes are more highly paid than blue-collar workers. Ex: doctors, lawyers, administrators -Pink-collar workers: workers who work in the charitable sector Ex: Susan G. Koman -Green-collar workers: workers who work in the environmental sector Ex: Economic decision making requires people to consider all the costs and benefits of a decision Fixed Costs -Costs or expenses that are the same no matter how many units of a good are produced Ex: mortgage payments, rent Variable Costs -Costs or expenses that change with the number of products produced Ex: wages, raw materials, electricity bills, water bills -These costs increase when production increases and decrease when production decreases Total Costs -Fixed Costs + Variable costs= Total costs Key Terms and Concepts Economizing problem Utility Economic resources Land Capital Investment Labor Entrepreneurial ability Factors of production Full employment Full production Productive efficiency Allocative efficiency Consumer goods Capital goods Production possibilities table Production possibilities curve Opportunity cost Law of increasing opportunity costs Economic growth Economic system Market system Command system Resource market Product market Circular flow model