Polysaccharides
advertisement
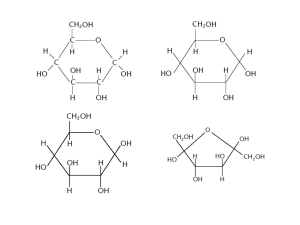
Biological Molecules Bio Do Now Silently and independently: Spend the next 10 minutes studying for the quiz. The quiz will cover everything since our last exam: 1. 2. 3. Chemistry review Water Mono/disaccharides Put away everything except a pencil and a cover sheet. Once done Turn it in on my desk Pick up the handouts Tape the orange sheet in your LAB notebook Today’s Announcements • • • • Lab report: due Thursday NEXT TUESDAY Lab makeups on Thursday Reminder: no tutoring after school on Tuesdays Pass back papers do NOT leave these in my room please Warm-up Can you… Draw on the diagram where a glycosidic bond will form and complete the diagram to show the disaccharide that will be produced. Can you… Draw on the diagram where a glycosidic bond will form and complete the diagram to show the disaccharide that will be produced. Review of Mono/disaccharides The many forms of glucose: Straight chain(linear) form (least common/stable) α-Ring form Alpha-ring (“OH” group is below the ring) β-Ring form Beta-ring (“OH” group is above the ring) Cyclic Structure of Glucose: Rotation Straight open-chain glucose is so reactive that almost all molecules quickly rearrange their bonds to form two new structures. These structures are six-membered rings like those below. The beta version is more stable. 10 How are the two monosaccharides joined? Glycosidic Bond Formed by condensation reactions Recall: what molecule is released when the glycosidic bond forms? H2O 6C 12H 6O 6C 12H 6O 12C 22H 11O How are the two monosaccharides joined? Glycosidic Bonds +H2O REDUCING SUGARS What is a “reducing sugar”? How do we test for it? Reducing sugars • Can cause reduction chemical reactions • • Benedict’s Test: when a reducing sugar is added to the reagent (copper sulfate dissolved in a base), it reduces the reagent and makes a red-brown precipitate Include the following: • • ALL monosaccharides SOME disaccharides • E.g. Maltose SUCROSE is an important example of a disaccharide that is NOT a reducing sugar Which of the following would NOT reduce Benedict’s Reagent? A. D. B. Ribose C. E. 8 minutes- silent, independent work time 8 minutes- group work time 4 minutes- class review Simple Sugar Practice Problems Polysaccharides Carbohydrates which are made from many linked monosaccharide monomers form long chain-like molecules called polymers. glycogen starch polysaccharides - made from glucose monomers cellulose Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose There are three main types of naturally occurring polysaccharides. They are cellulose, glycogen, and starch that are of major importance. What does cellulose do? (Hint: recall cell structures) 18 Polysaccharides • • • Functions: storage, structure, recognition Starch and glycogen are storage molecules Chitin and cellulose are structural molecules Cell surface polysaccharides are recognition molecules Starch A plant storage polysaccharide • Two forms: amylose and amylopectin • • • Most starch is 10-30% amylose and 70-90% amylopectin Branches in amylopectin every 12-30 residues Amylose has αβ(1,4) links and one reducing end Starch • • Amylose: compact, energetic spirals of α-glucose molecules Amylopectin: compact, branched, energetic shapes of α-glucose molecules Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose The unbranched structure of amylose. 22 Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose The branched structure of amylopectin. 23 Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose An important reaction during digestion is the hydrolysis of starchy foods as shown below. Starch is not soluble in cold water due to its large size and will form a colloidal dispersion in hot water. Starch solutions form a blue-black color in the presence of free iodine. 24 Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Glycogen is a carbohydrate polymer that is stored in the liver and muscle tissues in animals. It is the energy-storage carbohydrate in animals. Glycogen has a structure similar to amylopectin (starch) except that it is more highly branched with the a-1,6glycosidic linkages occurring more frequently along the polymer chain. Like amylopectin, glycogen gives a red-violet color with iodine 25 Carbohydrates: Summary • Polysaccharides – Storage: • Plants: storage • Animals: glycogen • Polysaccharides Structural: Cellulose~ most abundant organic compound; Chitin~ exoskeletons; cell walls of fungi; surgical thread Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Cellulose, like starch and glycogen, is a glucosebased polymer. The glucose units in cellulose are joined by -1,4glycosidic linkages instead of a-1,4-glycosidic linkages. There is extensive hydrogen bonding in cellulose. Therefore, it’s a long strong chain of -Glucose 27 Demonstration Time Form human glucose polymers for: • Amylose • Amylopectin • Cellulose Cellulose • Most abundant organic molecule. • It’s very slow to decompose. • Made of β glucose units. • Every other β glucose is rotated through 180° - this makes the chains straight, not coiled. • Hydrogen bonding between monosaccharide molecules in the chain gives strength. • Hydrogen bonding between cellulose molecules cause bundles called microfibrils to develop. These are held together in fibres. • 20-40% of the plant cell wall. • A cell wall will have several layers of fibres running in different directions - gives great strength almost equal to steel. • Provides support in plants and stops plant cells bursting. • Freely permeable to water and solutes. Figure 27.9 Two representations of cellulose. In the threedimensional model note the hydrogen bonding that links the extended cellulose polymers to form cellulose fibers. Three-dimensional model of cellulose 30 Which picture shows cellulose? How are the polysaccharides formed? Hint: Same type of reaction that forms a disaccharide from monosaccharies Condensation reactions Which type of reaction (condensation or hydrolysis) does this show? Hydrolysis Carb overload? Let’s practice this all some Sell that Saccharide Assignment Review handout When should this be due? Options for saccharide 36 Sell that Saccharide Example Glucose is the most important of the monosaccharides. It is an aldohexose and is found in the free state in plant and animal tissue. Glucose is also known as dextrose and grape sugar. Glucose is a component of the disaccharides sucrose, maltose, and lactose and is the monomer in the polysaccharides amylose, amylopectin, cellulose, and glycogen. Glucose is the key sugar of the body and is carried by the 37 bloodstream to all body parts.