Capital
advertisement

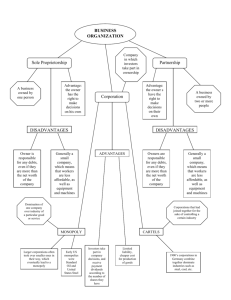
USHC Standard 4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the industrial development and the consequences of that development on society and politics during the second half of the nineteenth and the early twentieth centuries. USHC 4.2: Analyze the factors that influenced the economic growth of the United States and its emergence as an industrial power, including the abundance of natural resources; government support and protection in the form of railroads subsidies, tariffs, and labor policies; and the expansion of international markets. Main Idea: During and after the Civil War, the United States entered a period of rapid economic growth (boom) that was due in part to government policies that contributed to changes in the factors of production in the United States. What is… • Capital: the wealth, whether in money or property, owned or employed in business by an individual, firm, corporation, etc. • Entrepreneur: a person who organizes and manages any enterprise, especially a business, usually with considerable initiative and risk. When did economic growth in the U.S. begin? • Economic growth started in the first half of the century How did the economy grow? • It was fostered by both government actions and changes in each of the factors of production • The government provided the business environment in which entrepreneurs could be successful What else has the government done to increase economic growth? • (USHC 1.6) The national bank had provided needed capital and at the same time somewhat regulated lending • (USHC 2.1) Expansion to the West promoted by government actions through purchase, treaties and war opened up a vast region rich in natural resources such as coal and iron ore. • (USHC 2.1 and 4.1) The government also removed and/or controlled Native Americans who threatened to impede access to these resources • The growth of business was supported by court decisions that upheld the sanctity of contracts (Dartmouth vs. Woodward) and passed patent laws that protected the rights of the inventor. • (USHC 1.7) The national government regulated interstate commerce (Gibbons vs. Ogden) • (USHC 2.3) The national government protected infant industries with a protective tariff Government policies to promote economic growth: • Policies to foster economic growth were promoted by the Republican Party during and after the war. • Congress passed laws which stimulated westward expansion by offering subsidies in the form of land grants to railroads and by giving free land to settlers • The reorganization of banking fostered a more secure financial climate • Tariffs were raised throughout the period to protect industry from foreign competition. • Labor policies promoted the interests of business • The government generally promoted open immigration that supplied a ready force of workers • As workers began to organize into unions and strike to protect their interests, the government took the side of management and sent federal troops to break up strikes and to jail strikers How did these government policies affect workers and consumers? • The government’s actions supported the interests of “Big Business” rather than the workers whose wages were lowered by the supply of unskilled immigrant workers and whose organization into labor unions was undermined by government actions. • High tariffs protected the jobs of workers, but protective tariffs did not support the interests of consumers because prices of goods were kept artificially high MAIN IDEA: Industrial growth led to a surplus of products that could not be purchased by American consumers and became available for export. These surpluses prompted the United States government to support the expansion of international markets through foreign policy initiatives that expanded United States’ territorial influence, protected American investments abroad and promoted trade. USHC Standard 4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the industrial development and the consequences of that development on society and politics during the second half of the nineteenth and the early twentieth centuries. USHC 4.3: Evaluate the role of capitalism and its impact on democracy, including the ascent of new industries, the increasing availability of consumer goods and the rising standard of living, the role of entrepreneurs, the rise of business through monopoly and the influence of business ideologies. MAIN IDEA: Capitalism has played a central role in the development of the United States and the American economy since the first settlers landed. What is capitalism? • Capitalism is the economic system that is characterized by private ownership of property and the use of that property to make a profit for the individual or the corporation acting as an individual. • Capitalism supports the democratic ideal of individual freedom and opportunity CORPORATION a company or group of people authorized to act as a single entity (legally a person) and recognized as such in law. Corporations in America: • Corporations promoted early industrialization before the Civil War by raising capital through the sale of stock to invest in large scale business ventures • In the post Civil War period, corporations became larger and more powerful through mergers and monopoly and had a greater influence on the economy, politics and government policy • Critics began to question the compatibility of large unfettered corporations and the rights of workers and consumers in a democracy Corporations in America How did the railroad affect American industry and economy? • New industries rose to prominence in the post Civil War period • The railroad was the economic engine that drove the economy • The establishment of several transcontinental routes helped to unite the country and promoted economic growth and the development of a national market The industry that creates others! • The industry’s need for steel rails, wooden railroad ties and railroad cars and its ability to transport goods contributed to the growth of steel, the lumber, the meat packing, and the coal industries and many others • The railroad brought new settlers through aggressive advertising and land sales and provided farmers access to markets • New towns grew along its routes and older ones were able to specialize in particular products MAIN IDEA: Capitalism led to competition. Think Vanderbilt! What kind of problems did competition cause? • Competition caused some railroads to be forced to merge with others to survive • When the cut-throat competition drove some railroad companies into bankruptcy the national economy was thrown into depression • Unrestricted competition led to economic uncertainty and periodic depressions and eventually to a public call for government regulation of monopolistic practices • Concerns of the public over the political power of the monopolies later contributed to the Progressive Movement • Monopoly: exclusive control of a commodity or service in a particular market, or a control that makes possible the manipulation of prices. Concerns over monopolies vs. pro-business ideologies: • Public concerns over monopoly were offset by the popularity of pro-business ideologies • Captains of industry justified their sometime use of cut-throat practices with ideologies of Social Darwinism and laissez-faire capitalism • Social Darwinism: survival of the fittest • Laissez-faire: little to no government intervention in business Response to America the Story of Us: Cities 1. How did the video illustrate the idea of the “rugged American spirit”? Explain. 2. How did steel lead to development of cities and skyscrapers? Explain. 3. Do you think America is better off because of industrial development, or would it have been more beneficial to remain largely agricultural? Explain your answer!!