Fossil fuel
advertisement
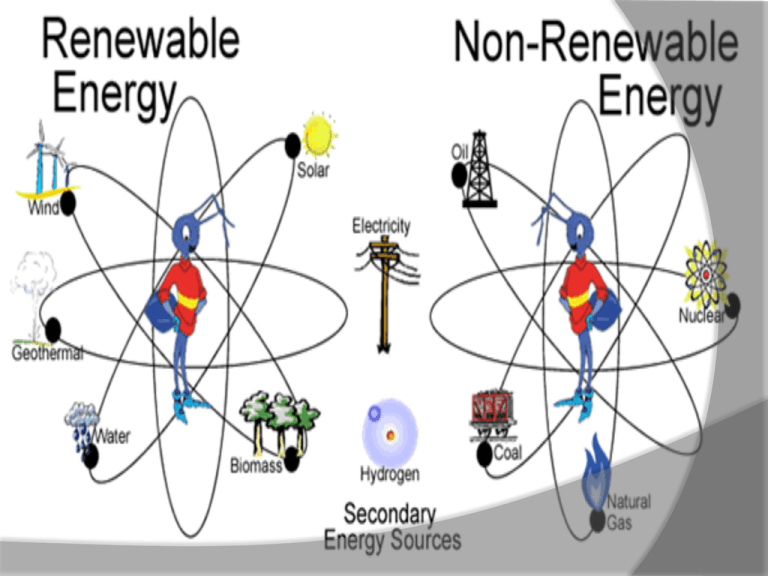
Objectives • Describe fossil fuels and explain why coal is a fossil fuel • Summarize the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. • Explain how nuclear fission generates electricity • Explain how geothermal energy may be used as a substitute for fossil fuels • Compare passive and active methods of harnessing energy from the sun • Explain how water and wind can be harnessed to generate electiricty Fossil Fuels • Fossil fuel: a nonrenewable resource formed from the remains of organisms • Oil • Coal • Natural gas • Nonrenewable resources: resources which form at a rate much slower than the rate at which they are consumed • Much of the energy humans use every day comes from the burning fossil fuels. Problems with Fossil Fuels • Impurities in fossil fuels are a major source of pollution • Burning fossil fuels produce large amounts of CO2, which contributes to global warming Coal Energy • Coal is the most abundant fossil fuel in the world. 2/3 of all coal deposits are in the US, Russia, and China. • Coal is formed during carbonization, which occurs when partially decomposed plant material is buried in swamp mud and becomes peat. • As bacteria consume some of the peat, methane and CO2 are released, and the contents gradually change until mainly carbon remains. • Alternative Energy: Nuclear Nuclear fission: process by which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more fragments • releases neutrons & energy • Newly released neutrons strike and split nearby nuclei, which causes the release of more neutrons and energy, initiating a chain reaction • Uncontrolled fission reactions escalate quickly and result in a nuclear explosion • Controlled reactions produce heat which can be used to generate electricity How Fission Generates Electricity • Nuclear reactor: specialized area where controlled nuclear fission is carried out • Chain reaction from nuclear fission causes fuel rods to become very hot. • Water is pumped around the rods to absorb heat • The water is then pumped into an area where it becomes steam and turns turbines which provide power for electric generators. • A third water area carries away excess heat and releases it into the environment. www.bio.miami.edu/beck/esc101/Chapter14&15.pp t Advantages/Disadvantages of Nuclear Fission • Nuclear power plants do not burn fossil fuels or produce air pollution. • However, they produce radioactive material which decay slowly, so they must be stored for thousands of years • The material emits doses of radiation which may be harmful if not stored properly Yucca Mountain www.geology.fau.edu/course_info/fall02/ EVR3019/Nuclear_Waste.ppt Geothermal Energy • Renewable resource: a natural resource which can be replaced at the same rate at which it is consumed • Geothermal energy: energy produced by heat of the Earth • The steam from hot water passing near magma produces a large amount of energy • Scientists drill wells to reach the hot water • The hot water drives turbines, which generate electricity. Solar Energy • Solar energy: energy from the sun • Solar energy can be converted to heat • In a passive system, sunlight enters the house and warms it • An active system includes solar collectors, which convert solar energy into electricity. Energy from Moving Water • Hydroelectric energy: electrical energy produced by the flow of water • Energy can be harnessed from the running water of rivers, streams, or ocean tides • 11% of the electricity in the US is derived from hydroelectric power • At a hydroelectric plant, massive dams hold back running water and channel the water through water spins turbines, which turn generators and produce electricity. Energy from Biomass • Biomass: plant material, manure, or any other organic matter used as an energy source • major source of energy in many developing countries • Bacteria which decompose organic matter produce gases or liquids, which can be burned. • More than half of all trees that are cut down are used as fuel for heating or cooking. Energy from Wind • Wind energy may be used to produce electricity in locations with constant wind. • Wind farms: hundreds of giant turbines which produce enough energy to meet the electric needs of entire communities. • Not practical everywhere because the wind does not always blow Preserving the Environment • Conservation: preservation of natural resources • Recycling: recovering valuable or useful materials from waste or scrap • requires energy, but uses less than manufacturing new resources • Fossil fuels can be conserved by reducing the amount of energy used every day • Reducing the amount of driving, using insulation for a house, energy-efficient appliances, all help conserve energy