Practice Test 13
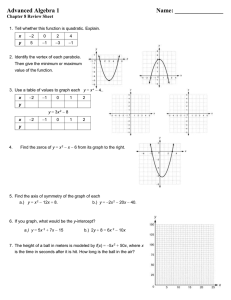
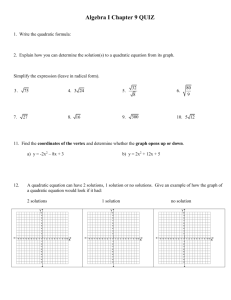
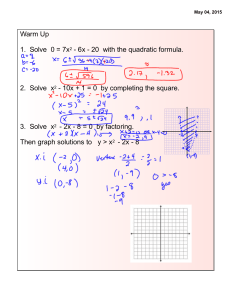
advertisement

COMPASS
Practice Test 13
Quadratics
Quadratics
• This slide presentation will focus on
quadratics.
• Quadratics will always have a variable
raised to the second power, like x2.
• Factoring is a skill that will help you find
solutions to quadratic equations.
0 = x2 - 6x - 16
0 = (x - 8)(x + 2)
x = {-2, 8}
Quadratic
Formula
b b 4ac
x
2a
2
• If you do not like to factor you can always
use the quadratic formula.
0 = x2 - 6x - 16
2
(6) (6) 4(1)( 16)
x
a=1
2(1)
b = -6
6
10
6
100
6
36
64
c = -16 x
2
2
2
6 10 16
6 10 4
x
{
8
,
2
}
x
x
2
8
2
2
2
2
1. If x = -1 and y = -2, what is the
value of the expression 2x2y- 3xy ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
-24
-10
-2
2
10
2 y – 3xy
2x
We start this practice with a
substitution
problem,
not a
= 2(-1)2 (-2)
– 3(-1)(-2)
quadratic.
COMPASS
often
= 2(1) (-2)- 3(-1)(-2)
starts with a substitution
=
-4
–
6
=
-10
problem.
Answer B
2. What are the solutions to the quadratic
x2 - 2x - 48 = 0?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
6 and 8
-6 and -8
-6 and 8
6 and -8
3 and 16
x2 - 2x - 48 = 0
(x - 8)(x + 6) = 0
Set each factor to 0
x-8=0
x=8
x+6=0
x = -6
x = { 8, -6}
2. What are the solutions to the quadratic
x2 - 2x - 48 = 0?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
6 and 8
-6 and -8
-6 and 8
6 and -8
3 and 16
2 14 16
8
x
2
2
Or you could find the answer
with the quadratic formula.
a = 1 b = -2 c = 48
(2) (2) 2 4(1)( 48)
x
2(1)
2 14
2 4 192 2 196
2
2
2
2 14 12
x
6
2
2
x {8,6}
2. What are the solutions to the quadratic
x2 - 2x - 48 = 0?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
6 and 8
-6 and -8
-6 and 8
6 and -8
3 and 16
(6Another
) 2 2(6) way
48 to
0 find the
solution
to check
each of
36 12is
48
0
the answers
24 48 back
0 into the
original equation.
24 0
This would take a long time,
False
but remember this test is
Thus wenotcan
eliminate
timed.
answers
A6and D
Try x =
This process of elimination is a good strategy if you get stuck.
3. What is the sum of the solutions to the
quadratic x2 - 2x - 48 = 0?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
14
-14
2
-2
19
To prevent people from using
the process of elimination
discussed on the previous
slide the questions are
sometimes written this way.
Find the solution set {-6, 8}
Add the solutions -6 + 8 = 2
4. What is the sum of the solutions of the
quadratic equation x2 + 3x = 28?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
3
-3
11
-11
10
First write the equation in standard form.
x2 + 3x - 28 = 0
Using the quadratic formula.
a = 1 b = 3 c = -28
(3) (3) 2 4(1)( 28) 3 9 112
x
2(1)
2
3 121 3 11
x {4,7}
2
2
3 11 8
3 11 14
x
4 x
7 4 (7) 3
2
2
2
2
5. What is the sum of the solutions of the
quadratic equation 2x2 - x = 15?
A. 1 First write the equation in standard form.
B.
C.
D.
E.
2
2x2 - x - 15 = 0
1
Using the quadratic formula.
2
a
=
2
b
=
-1
c
=
-15
11
2
(
1
)
(
1
)
4(2)( 15) 1 1 120
2x
4
2(2)
11
1 11
12
1 121
x 3
2
4
4
4
-1 x 1 11 10 5
5 1
3
4
4
2
2 2
6. If the equation x2 - x = 6 is solved for x,
what is the sum of the solutions?
A. 3
B. 2
C. 5
D. 1
E. -1
First write the equation in standard form.
x2 - x - 6 = 0
Using the quadratic formula.
a = 1 b = -1 c = -6
(1) (1) 2 4(1)( 6)
1 1 24
x
2
2(1)
1 25 1 5 x 1 5 6 3
2
2
2
2
1 5 4
x
2
3 2 1
2
2
7. What are the solutions to the quadratic
x2 - 5x = -6?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
-2, -3
2, 3
1, 6
-1, -6
-2, 3
First write the equation in standard form.
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
Using the quadratic formula.
a = 1 b = -5 c = 6
(5) (5) 2 4(1)(6) 5 25 24
x
2(1)
2
5 1
5 1
2
2
5 1 6
5 1 4
x
3
x
2
2
2
2
2
x {2, 3}
8. For all x ≠ 2,
A. (x + 5)
B. (x - 2)
C. (x + 2)
D. (x - 3)
E. (x + 3)
x 5x 6
?
x2
2
Factor the numerator.
( x 2)( x 3)
( x 3)
( x 2)
8. For all x ≠ 2,
x 5x 6
?
x2
2
A. (x + 5) Another way to work this problem
B. (x - 2)
C. (x + 2)
D. (x - 3)
E. (x + 3)
is to just make up a number for x.
Let x = 5
(5) 5(5) 6 6
2
3
52
2
Now plug x = 5 into each of the
answers until you find a match.
D ( x 3) 5 3 2
9. If x = -4 is a solution to the equation
x2 + 11x + K = 0, then K = ?
A. 16
B. 28
C. -28
D. 60
E. -60
First substitute x = -4 into the given
equation. Then solve for K.
x2 + 11x + K = 0
(4) 11(4) K 0
16 44 K 0
28 K 0
K 28
2
10. What are the solutions to the
quadratic x2 - 10x + 24 = 0?
x2 - 10x + 24 = 0
A. 4 and 6
(x
4)(x
6)
=
0
B. -4 and 6
x
4
=
0
C. -4 and -6
x
=
4
D. 2 and -12
x
6
=
0
E. -2 and 12
x=6
x = { 4, 6}