SOL Blast
advertisement

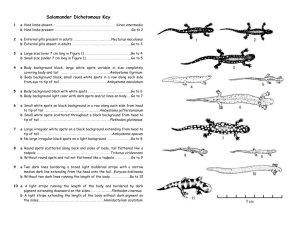
BIOLOGY SOL BLAST HOMEOSTASIS stable internal conditions in spite of changes in the external environment ENZYMES help organisms maintain homeostasis; increase the speed of chemical reactions; fit with substrate like a lock and key substrate active site enzyme IN AN EXPERIMENT . . . Control group •comparison group Independent variable •what the experimenter changes Dependent variable •the variable that is measured Remember . . . Only test one variable at a time. Can you name the cells to the left? Cell Organelles Mitochondria •powerhouse; produces ATP “mighty mitochondria” Ribosome Cell Membrane Chloroplast •where proteins are made •lipid bilayer; controls what enters and leaves cell •contains chlorophyll; needed for photosynthesis WATER Polar Universal solvent High heat of vaporization Less dense in its solid form Water has cohesive and adhesive properties allowing for capillary action to take place in trees. cohesion Water sticks to itself adhesion Water sticks to other substances Hyper-shrinks Hypo=expands Hypertonic = cell shrinks _________ Hypotonic = cell expands __________ Diffusion movement of substances from a high to low concentration Osmosis movement of water from a high to low concentration CELLULAR RESPIRATION transfer of energy in organic compounds to ATP Two Types: AEROBIC ANAEROBIC -requires oxygen (produces 36 ATP) -does not require oxygen (produces 2 ATP) What is used in cellular respiration is produced in photosynthesis---what is used in photosynthesis is produced in cellular respiration. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 What is the main purpose of photosynthesis? Produces food (C6H12O6 - glucose) for the plant Takes in which gas? Carbon Dioxide Releases which gas? Oxygen MITOSIS Somatic (body cell) division •DNA must replicate before division takes place •Results=2 diploid cells MEIOSIS •Gamete (sex cell) division •Results = 4 haploid cells When fertilization takes place, 2 haploid cells (sperm and egg) unite to create what? 1 diploid cell PUNNETT SQUARE diagram used to predict the probable outcome of a genetic cross B = pink b = white GENOTYPIC RATIO: 1:2:1 PHENOTYPIC RATIO: 3:1 BB = Homozygous dominant bb = Homozygous recessive Bb = Heterozygous DNA DNA is made of nucleotides which are made of: 1. Sugar (deoxyribose) 2. Phosphate 3. Nitrogen bases (A-T, C-G) DNA A -T G -C RNA A -U G-C CTA = GAT TAC = AUG DNA REPLICATION How are proteins made? A chain of amino acids = protein Amino Acids tRNA ANTICODON mRNA CODON ribosome If given the codon, AAC, what is the amino acid the tRNA will bring to the mRNA? Famous names in the discovery of DNA Double Helix Structure- Watson & Crick X-Ray Diffraction to determine structure- Franklin Base-pairing rules- Chargoff VIRUS What is this? Is it living? No Lytic Cycle Bacteriophage Host Cell Capsid Viral Nucleic Acid KINGDOMS OF LIFE -Cell walls of cellulose -No cell walls -Cell walls of chitin What are the two types of cells? Prokaryotic What organisms are prokaryotic? bacteria Eukaryotic What organisms are eukaryotic? animals, plants, fungi, and protists Bacteria Unicellular Prokarytotic Eubacteria / Archaebacteria Cell Wall Reproduce Sexually or Asexually (Binary Fission) Remember Sexual reproduction is the best because it creates variation in the species. Protists What do Paramecium move with? Cilia Unicellular or Multicellular Most diverse group What do Amoeba move with? First eukaryotes Pseudopodia “Catch-all Group” Plant-like, Fungus-like, Animal-like Can be Heterotrophic and/or What do Euglena Autotrophic move with? Flagellum Fungi Unicellular or Multicellular Eukaryotic Heterotrophic-absorption Cell walls made of chitin Reproduce sexually or asexually (spores) Visible portion is reproductive structure and body is mass of hyphae (mycelium) Plants Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Nonmotile Cell wall= Cellulose Starch Animals Multicellular Eukaryotic Heterotrophic No cell walls 95% Invertebrates 5% Vertebrates Isolation Condition in which two populations of the same species cannot breed with one another – Geographic-separated by a physical feature (i.e. canyon) – Reproductive-can no longer mate with each other (i.e. different mating times, physical differences, no longer attracted to the other) NATURAL SELECTION Process by which populations change in response to their environment as individuals better adapted to the environment survive and reproduce and pass those favorable characteristics on Who was the scientist who developed this theory? Darwin Dichotomous Key 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a Hind limbs absent Siren b Hind limbs present Go to 2 a External gills present in adults Mud puppy b External gills absent in adults Go to 3 a Large size (over 7 cm long) Go to 4 b Small size (under 7 cm long) Go to 5 a Body background black, large white spots irregular in shape and size completely covering body & tail Tiger salamander b Body background black, small, round, white spots in a row along each side fro eye to tip of tail Spotted Salamander a Body background black with white spots Go to 6 b Body background light color with dark spots and or lines on body Go to 7 a Small white spots on a black background in a row along each side from head to tip of tail Jefferson salamander b Small white spots on a scattered throughout a black background from head to tip of tail Slimy salamander a Large irregular black spots on a light background extending from head to tip of tail Marbled salamander b No large irregular black spots on a light background Go to 8 a Round spots scattered along back and sides of body, tail flattened like a tadpole Newt b Without round spots and tail not flattened like a tadpole Go to 9 a Two dark lines bordering a broad, light mid-dorsal stripe with a narrow median dark line extending from the head onto the tail Two-lined salamander b Without two dark lines running the length of the body Go to 10 a A light stripe running the length of the body and bordered by dark pigment extending downward on the sides Red-backed salamander b A light stripe extending the length of the body, a marked constriction at the base of the tail Four-toed salamander PRIMARY SUCCESSION What are the first organisms to colonize a new site (i.e. bare rock)? pioneer species SECONDARY SUCCESSION What is the name of a mature, stable community? climax community Food Web 1 10 100 1000 NUTRITIONAL RELATIONSHIPS Heterotroph •Organism that cannot make its own food; must consume food Examples: animals, fungi, some bacteria and protists (decomposers, herbivore, omnivores, carnivores) Autotroph •Organism that can produce its own food; usually by photosynthesis Examples: plants, some bacteria and some protists Read each question carefully. Go with your first instinct. If you don’t understand the question, try visualizing it or sketching it. With graphs and diagrams, most likely the answer is in the question . Make this the last time you look at the Biology SOL!