Crime and Punishment
advertisement

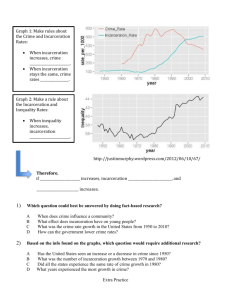
Crime and Incarceration ALC – Summer 2007 Alicia Simmons Questions for Today 1. How much crime is there? 2. What are the trends in incarceration? 3. What are the social impacts of incarceration? 1. How Much Crime? • Different types of crime – Property – Violent • The number of occurrences • The % of the population that are victims The Big Picture • 2005: approximately 23 million crimes in the U.S. Crime Distribution 20% Property Violent 80% Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2005 Property Crimes • Motor vehicle theft • Burglary • Theft Property Crime Statistics (2005) # of crimes % of victims 2.5 million 0.8 Burglary 8.9 3 Theft 35.1 12 Motor vehicle theft Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2005 What Cars are Stolen Most Often? Property crime • # of crimes = 46.5 million Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2005 • % victims in pop.= 15% Violent crimes • Simple & aggravated assault • Robbery • Rape • Homicide Violent Crime Statistics (2005) Simple assault # of crimes % of victims 4.1 million 1 Aggravated assault Robbery 1.3 0.4 785,000 0.3 Rape 151,000 0.05 Homicide 30,200 0.01 Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2005 Violent crime • # of crimes = 6.3 million Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2005 • % victims in pop.= 3% 2. Trends in Incarceration • Incarceration around the world • Current trends and their causes in the U.S. • Impacts on specific groups Incarceration Around the World 874,171 http://www.prisonstudies.org 1,548,498 2,193,798 Incarceration Rate (per 100,000 population) 737 United States French Guiana 630 Russian Federation 624 604 St. Kitts & Nevis 281 Taiwan 149 England & Wales 118 China 97 Republic of Korea 62 Japan 30 India 0 100 http://www.prisonstudies.org 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Bureau of Justice Statistics Causes of Prison Growth • Pre 1970s: Indeterminate Sentencing • 1970s – today: Tough on Crime – Politicization of crime – Growing conservative climate – American individualism Mauer, 2001 Determinant Sentencing • Moves us from an offender-based to an offense-based system • 88% of in incarceration from 19801996 is due to changes in punishment – 51% results from in the number of people doing time – 37% results from in term length Mauer, 2001 Bureau of Justice Statistics Did Prison Growth Cause the Crime Drop? • Ways an in incarceration could lead to a in crime – Rehabilitation: fixing criminals – Incapacitation: stopping current criminals – Deterrence: stopping future criminals • 1993-2001: incarceration the crime rate 2-5% Western, 2006 Impact on Specific Groups • Immigrants • Gender • Race • Social class Immigrants & Crime • Longstanding public fear of immigrant crime • 1st generations do not commit many crimes – 2nd and 3rd generations commit more Martinez & Valenzuela, 2006 Gender and Incarceration Bureau of Justice Statistics Race & Incarceration Free pop. Incarcerated pop. 12% 43 Lifetime likelihood of incarceration 30 Hispanic 35 35 20 White 70 36 4.4 Black Bureau of Justice Statistics Social Class & Incarceration % in Prison or Jail by Social Class and Race Males age 20-40 White 1.6% Hispanic 4.6 Black 11.5 Non-College Males age 20-40 White 3.2 Hispanic 5.5 Black 17.0 High School Dropout Males age 20-40 White 6.7 Hispanic 6.0 Black 32.4 Tying the Trends Together • Mass imprisonment: – “A rate of imprisonment and a size of prison population that is markedly above the historical and comparative norm for societies of this type.” (1) – “Social concentration of imprisonment’s effects.” (1) Garland, 2006 Why are things Unequal? • Racial bias in the following institutions – Police: racial profiling – Courts: unequal representation – Laws: powder vs. crack cocaine • A double standard exists for the upper vs. lower classes – Creates legitimacy issues Cole, 2001 3. What are the Social Impacts? • Stereotypes – Police interactions – Job opportunities • Stereotype: a conventional, formulaic, and oversimplified conception, opinion, or image that a person applies to both a group and each individual within it – Black men are stereotyped as criminals – Whites are stereotyped as law abiding citizens Interactions with the Police • Black men are often wary of interactions with the police • Worried about being innocent but getting into trouble – Demeanor with police • Convictions create records that follow throughout your life Anderson, 1990 Job Opportunities Effect of Criminal Record by Race 34 35 30 25 17 20 14 Record No record 15 10 5 5 0 Black Pager, 2003 White Questions for Today 1. How much crime is there? 2. What are the trends in incarceration? 3. What are the social impacts of incarceration?