Work
advertisement

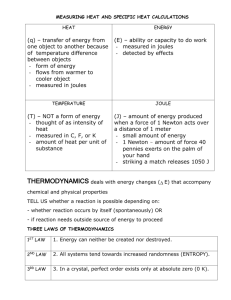
Work Physics Ms. Li Does he do work? waiter who carried a tray full of meals above his head by one arm straight across the room at constant speed Questions Strawberry uses a force of 0.75 Newtons to drags his pet mouse 3 meters to give to me as a gift. How much work did Straw do? Kiwi, mass 8 kg leaps from the ground to his cat tree a distance of 1.5 meters. How much work did he do? What is work Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction that the force is applied. Work is a scalar quantity The unit for work is the Joule (J) How is work done? A force must cause the object to move. No move, no work Only the force that acts in the direction of the movement applies. You need energy to do work. How do you calculate work Work = force times Displacement Displacement is the magnitude and direction from where an objects starts from, and where it ends up. (straight line) Example A wagon is pulled with a force of 100 N along the handle that is at an angle of 30 degrees. If the wagon moves 35 m horizontally, what is the work done on the wagon? 100 N On board Graphing The area under a force vs. displacement graph is the work done by the force. Example: a block is pulled at a constant speed along a table with a force of 10. N over a distance of 1.0 m. See graph (The area of the shaded part is the amount of work done on the block. Force (N) Displacement (m) Power Work can be done at different speeds The faster the work is done the more Power output. Formula: P = W/t P = (F*d)/t P = F*v Example How much work is done on a 40 kg boulder when you lift it 3m? What power is expended if you lift the boulder a distance of 3m in a time of 1.5s? What was the average speed the boulder was lifted? Vocab energy - ability to produce change in its itself or the environment - ability to produce work kinetic energy - energy resulting from an object in motion work - product of the force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves in the direction of the force work-energy theorem - Work is the transfer of energy by means of forces. The work done on the system is equal to the change in energy of the system joule - SI unit of work. It equals a Newton-meter. power - rate of doing work. That is power is the rate at which energy is transferred. Work done per second watt - SI unit of work. It equals a Joule per second. A kilowatt = 1000 watts. Units Variable Symbol Units Symbol kinetic energy KE Joules J Potential energy PE Joules J Work W Joules or Newton-meters J or N-m Power P Watts W Ready, Launch and Peak Positions