Animal Behavior PPT
advertisement

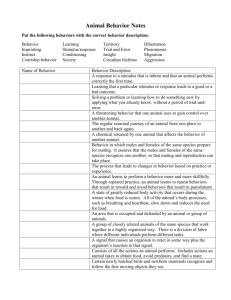
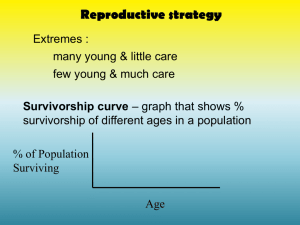
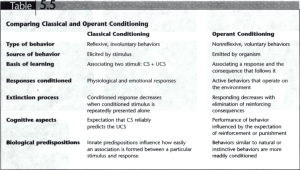
Goal 4.05: Animal Behavior http://www.simpletruths.tv/store/movies.php?movie=gqgl Stimulus = anything that elicits a response. Response = behavior resulting from exposure to a stimulus. z.about.com www.betaversion.org www.familyhealthnetwork.com 3.bp.blogspot.com Stimulus Response http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=5A73904F-063E-4264-BA0F67E286528E90&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US img2.timeinc.net bottledsky.com hiphappy.files.wordpress.com Innate (instinctive) Behavior = born with it/inherited visionsofspring.org INSTINCT vs. LEARNED http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=24A908BF-B21C-432C-8647- Instinct = behaviors that an organism is born knowing. Innate = referring to instinctive behaviors. www.zimfamilycockers.com www.biocrawler.com www.ruralni.gov.uk www.touchstonefarm.org Animal Instincts http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=3B2D0821-9886-4BA6-9C4026DFB11AB1B3&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Learned Behavior = resulting from experience Habituation: animals stops responding to a stimulus to which it repeatedly exposed. Classical Conditioning: animal makes a mental connection between a stimulus and reward/punishment. (Pavlov’s Dog Experiments) Operant Conditioning: (trial and error) animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in rewards and avoid behaviors that result in punishment. Learned Behaviors http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/11476-animal-intelligence-learned-response-video.htm Learned Behavior = resulting from experience Insight Learning: animal applies what it has already learned to a new situation. Social Behavior = behavior resulting from interactions with others. Horse dominance http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/22314-adapting-to-deserts-the-dominant-male-kathys-herd-video.htm Imprinting = learning based on early experience Usually learned immediately or very soon following birth. Some newborn animals will imprint on the first thing they see move following birth. Others imprint on a location. Example: Spawning salmon return to their hatching grounds to breed. kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca terrallectualism.files.wordpress.com www.sundancestablesfl.com www.psywww.com naturescrusaders.files.wordpress.com www.awakeningpotentials.com Circadian Rhythm = cycle that happens daily www.dietsinreview.com www.qfac.com www.moonbattery.com Migration = movement from one location to another based on seasonal changes neatorama.cachefly.net Sooty Shearwater – longest migration Sea Turtle migration routes Snow goose migration www.ontfin.com www.qc.ec.gc.ca ih1.redbubble.net www.wildlifeextra.com www.bahiamap.com africansafaris.co.ke Estivation vs. Hibernation Hibernation = sleeping during winter months squirrels hedgehogs bears bats ladybugs www.pwcs.edu jerseyhedgehogs.co.uk www.daviddarling.info ladybuglady.com www.bear.org Estivation vs. Hibernation Estivation = sleeping during summer months as a survival mechanism against environmental events such as heat, drought, etc. Very common in desert animals. Beaded lizard Spade foot toad Jersey snails tiger moths z.about.com open.live.bbc.co.uk http-server.carleton.ca absoluteastronomy.com