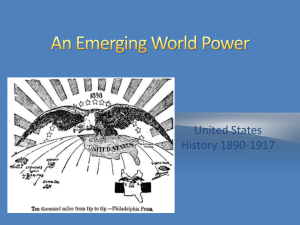
Imperialism 2014 IBHOA
advertisement

Opening Discussion • http://www.nbcnews.com/watch/nightlynews-netcast/nightly-news-with-brianwilliams-full-broadcast-december-3366971971939 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T_98ojjIZ DI The United States The Colonized Become Colonizers John Green: Crash Course in Imperialism Opening Questions • Define imperialism: – The economic and political domination of a strong nation over weaker nations. • Why do countries try to take over other countries or influence their policies? – – – – Obtain overseas markets Naval Bases Power/Prestige Resources • Should a country that fought for its independence from a foreign ruler embark on colonizing themselves? Westward Expansion Completing Manifest Destiny • U.S. purchases Alaska in 1867 What is the message of this painting? Government Encourages Western Settlement • Homestead Act – For a $10 filing fee, one could get a free “homestead” – Family could get up to 160 acres of land; receive deed to the land after 5 years – 10% of U.S. land settled under Homestead Act • Mining Industry • Wheat in the Great Plains • Ranching Government Encourages Western Settlement • Transcontinental Railroad – Closed the frontier • 40,000 arrive in NB alone w/in year – Improved quality of life in the Plains • Lumber, brick, coal, clothing – No longer had to go around S. America to ship goods – Economic Boom: Rapid exchange of goods between coasts • Opened up new settlements & markets • Revolutionized Communication: Unified the Nation • Spurred Industries needed to build Railroads – Iron, Timber, Coals What was the Cost of Westward Expansion? PLAINS INDIANS • Plains Indians: Dependent on the Buffalo Gen. Phillip Sheridan. “Let them skin, kill, and sell until the Buffalo are exterminated, as it is the only way to bring lasting peace.” • Make a list of anything a buffalo can be used for? • Systematic, Intentional Decimation – 1800: 65 million buffalo v. 5 million humans – 1890: fewer than 1,000 http://www.bluecloud.org/11.html Destruction of the Buffalo • Killed for the fur…not the food • So many buffalo killed, an entire pelt would only get 50 cents A World Closing In… • “More and more white eyes will come into Crow country. Where they come from there will be many more of them across a big body of water and they’re coming. They’re just like ants, you go and stomp on them on the ground but more keep coming up.” Spotted Horse, Crow Chief’s Spiritual Vision (1865) Sioux Response to White Settlement • “What has been done to my country, I do not want. The whites have surrounded me and left me nothing but an island. When we first had this country we were strong. Now we are melting like snow in the sunlight, while they are growing like spring grass.” Red Cloud, Lakota War Leader PLIGHT OF THE NATIVES • Repeated betrayals and broken treaties • Poverty, despair, compensatory payments never received • Buffalo annihilated Chief Joseph, Nez Perce: “Our chiefs are killed…The little children are freezing to death. My people…have no blankets… no food… Hear me my chiefs; I am tired; my heart is sick and sad. From where the sun now stands I will fight no more.” DAWES ACT (1887) • Dawes Act: U.S. Govt. Changes Policy from Reservation System – Assimilation of Natives to white culture – Divide reservations into individual allotments (160 acres for a family/80 single) – Remaining land sold to settlers Industrial Revolution in America The Rise of Industry: Opener • The Civil War spurred massive numbers to go work in industry/ factories • By 1914, GNP of US 8x higher than in 1865 • The U.S. went from being a “late arrival” to the Industrial Revolution, in early 1800s, to the leading industrial power by WWI. How did America accomplish this? Make a list of factors that enabled the U.S. to industrialize rapidly. Factors of Industrialization • • • • • Railroads Abundant Natural Resources Technological Advancements Laissez-Faire Economics Mass immigration Mass Immigration URBANIZATION • Where do immigrants settle? • Ethnic enclaves • What challenges do they face? Cities on the Rise • In 60 yrs.—number of cities increase by 12 times – By 1920, more live in urban areas than rural – Why? • Rising Skyscrapers • Mass Transit Emerges Big Business Takes Over • Corporations – A company owned by many people, but treated as if they were a person • Stockholders (owners) • Allows for growth – What are the benefits of issuing stocks? • Allows for larger projects/investments • Limited liability…spreads risk – What are the disadvantages? • High fixed costs • Can hurt small business Growth of Monopolies/Trusts • Vertical Integration – A company owning all of the different businesses necessary to produce a specific product • Andrew Carnegie: Carnegie Steel • Ex. Oil Company: finds oil deposits, drills/extracts the oil, ships the oil, refines it, and sells it to distributors and consumers • Horizontal Integration – Business merges/combines with another business in the same industry and at the same stage of production • John D. Rockefeller: Standard Oil • Ex. Honda merges with Hyundai and Kia • Monopoly: – A situation where 1 company owns all or nearly all of a given market for a product or service Rise of Robber Barons • Robber Barons – A term used for businessman who used “questionable” practices to amass their wealth • • • • Use ruthless business strategies to destroy competition Bribing politicians Manipulating workers…extremely low wages/poor cond. Combines sense of criminal, “robber,” with illegitimate aristocracy, “baron” • Examples: Rockefeller, Vanderbilt, J.P. Morgan • Social Darwinism – A belief that the “strongest” and the “fittest” should survive; while the “weak” and “unfit” should be allowed to die. Rockefeller/Standard Oil: Unscrupulous Business Practices • (1) Temporarily undercutting the prices of competitors until they either went out of business or sold out to Standard Oil. • (2) Buying up the components needed to make oil barrels in order to prevent competitors from getting their oil to customers. • (3) Using its large and growing volume of oil shipments to negotiate an alliance with the railroads that gave it secret rebates and thereby reduced its effective shipping costs to a level far below the rates charged to its competitors. • (4) Secretly buying up competitors and then having officials from those companies spy on and give advance warning of deals being planned by other competitors. • (5) Secretly buying up or creating new oil-related companies, such as pipeline and engineering firms, that appeared be independent operators but which gave Standard Oil hidden rebates. • (6) Dispatching thugs who used threats and physical violence to break up the operations of competitors who could not otherwise be persuaded. Robber Barons Robber Barons Robber Barons America Expands The Rise of an Imperial Power What Factors Contributed to the Rise of Imperialistic Actions by the United States? (What role do industrialization play?) John Green: Crash Course in Imperialism Factors Contributing to US Imperialism • Industrialization – Trade/Commerce – Technological advances—spur western dominance • Desire Overseas Markets – Industry and Farmers look for new markets – Open New Markets for goods; access to resources • Desire Overseas Naval Base – Naval Superiority • Yellow Journalism Factors Contributing to American Imperialism • Anglo-Saxonism/Manifest Destiny – Whites: “superior” race; “White Man’s Burden” – must Christianize the uncivilized world • Social Darwinism – Survival of the Fittest • Jingoism/Aggressive Nationalism – U.S. growing industry, wealth, population – Jingoism: Extreme Patriotism → Aggressive Foreign Policy – Breeds conflict with Germany, Chile, Canada, Britain • Competition—prestige/power…who were we competing with? Alfred T. Mahan Influences of Sea Power on History • Why does Mahan support a modern Navy? – Control the oceans, control the globe – Bolsters American strength – To protect merchant ships/trade/investments – Establish military bases, overseas, to operate from The Great White Fleet • What was it? – New U.S. Steel Naval Fleet • What was the goal of this expedition? – Intimidate the rest of the world – Signal to Japan and others—U.S. plans to protect Asian interests • Why Hawaii? – – – – U.S. Seeks Hawaii Need port to refuel and resupply in Pacific Provide a Naval Base American Sugar Interests Rising Japanese Power • Role of Sugar Planters – McKinley Tariff: 1890 • Hurts Hawaiin sugar farmers… why? – Hurt by subsidies given to American sugar farmers – American sugar interests, backed by army…Overthrow Queen Liliuokalani • Push for annexation, 1893, Why? • Why was it rejected in 1893? – Finally Annexed in 1898…Why in 1898? Diplomacy in Latin America • Goals: – Rising Pan-Americanism: • Belief that the U.S. and Latin America should “work together”…why? What’s U.S. motivations? – – – – Get L.A. to buy American, not European goods Access to raw materials Shorter trade/naval route from the Atlantic to the Pacific Keep Europeans out of the Western Hemisphere » Control L.A. debt to European nations • First Pan-American Conference (1889) – Lower Tariffs between participating nations – Open markets to American producers Spanish-American War • Causes: – U.S. Desire to remove European influence…Spain last European power in the W. Hemisphere – Cuba: Strategic Location (route to Panama) – Cuban Rebellion… • What role did tariffs play? • Destruction of U.S. Property by Cuban Rebels • Desire to Protect Economic Interests in Cuba – USS Maine explodes – Yellow Journalism • Joseph Pulitzer/William Randolph Hearst • Journalism based on sensationalism, mass exaggerations, and often falsehoods • Sells more newspapers…but also good for propaganda • Report on Spanish atrocities; SpanishGeneral Valeriano Weyler – What was the goal? Spanish-American War "Remember the Maine, to hell with Spain!" “You furnish the pictures and I'll furnish the war.”—William Randolph Hearst to his photographer in Cuba • April 1898: Pres. William McKinley calls Congress to declare war Spanish American War-Impact • Result: American Victory & an Empire is Built – Annex Puerto Rico (Foraker Act) – Teller Amendment • Promised Cuban Freedom once Spain overthrown… How well did U.S. live up to this? – Platt Amendment (Cuba) • US Naval Base in Cuba (Guantanamo) • U.S. has right to intervene to protect and keep order • Cuba must minimize its debt to Europe • U.S. can block treaties Cuba makes w/ other states Spanish American War: Impact in the Pacific • U.S. Already Acquired Samoan Islands (1898) – Sign Treaty of Berlin w/ Germany • Spanish American War Pacific Acquisitions – Buy the Philippines – Annex Guam – Leads to formal annexation of Hawaii… why? • Annex Wake Islands (1899) An American Empire Spanish American War: Effects on the U.S. • “A Splendid Little War” – America emerges as a World Power – Increased respect/prestige – Imperial power • Increased support at home for imperialism/ militarism • Unified the nation (North & South) • How did it effect America’s image in the developing world? Anti-Imperialist League • Anti-Imperialist League – Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie – Arguments: • Imperialism violation of America’s values/foundations – Declaration of Independence – Constitution • Defies concept of popular sovereignty – Government can only rule with people’s consent – Actions in the Philippines and Cuba were in direct conflict with ideals School Begins: 1/25/1899 Trading One Oppressive Government for Another? The Philippines America’s Problem in the Philippines • America Viewed as the “New Spanish” • Filipino demands for independence ignored • Feb., 1899 Emilio Aguinaldo sparks Filipino guerilla war for independence from America. – Rebellion crushed in 1901 – 4,200 American deaths – 525,000-600,000 Filipino casualties • Filipinos continue push for independence – Received following WWII (1946) “Opening the Door” to Asia • Philippines…Stepping Stone to Asia… • Prize Possession of Asia…China – Massive Markets – Christian Missionary Zeal • US Sec. of State, John Hay, gets U.S. involved in China’s lucrative trade • Open Door Policy (1899) – U.S., France, Germany, Britain, Italy, Russia, Japan agree to respect each others rights to trade competitively with China; also promised to respect “territorial/commercial sovereignty” of China – Guarantees place for China’s vast markets to U.S. goods Boxer Rebellion • China weak and taken advantage of by foreign powers…exploited for economic interests • Boxer Rebellion – Chinese nationalists/anti-imperialists attempt to throw off foreign influence – Crushed by International Forces – China remained open to western/ foreign manipulation • Mao Zedong closes off China to the West (1949) Theodore Roosevelt • Election of 1900 – Pres. McKinley Re-Elected – VP: Theodore Roosevelt • McKinley Assassinated: Enter Roosevelt – Imperialist; Loose Constructionist – Endorses Broad Executive Power • Flex U.S. Muscle; Civilize the World • Big Stick Diplomacy: – “Speak softly and carry a big stick”…what does this mean? • Great White Fleet Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine • Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine – What was the Monroe Doctrine? – Limit European Influence in the L. America • Required L. Amer. Countries to minimize their debt to Europe…why? – US will intervene in L.A. affairs to maintain econ./pol. Stability • U.S. will intervene, take-over customs houses in L.A. to pay off debts, if necessary • I.e. Dominican Republic (1905) – Roosevelt Corollary: Becomes justification for numerous American interventions in L. America • What impact did the Roosevelt Corollary have on U.S. relations w/ L. America? An Outside Look at “Big Stick Diplomacy” Roosevelt Intervention in Latin America: Panama • US seeks land in modern-day Panama (part of Colombia at time) – Why? – Why was this especially significant after Spanish American War? • Hay–Pauncefote Treaty (1901) • Colombia refuses to sell Panama Canal Zone to U.S….so what do we do? • US sparks and aids Panamanian rebellion v. Colombian govt. – US acquires Panama Canal Zone and land surrounding it • Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty Japan Rising • Introduced to Western Military Technology—1853, Matthew Perry’s expedition • Meiji Restoration – Japanese Industrial Revolution – By 1890, Modern Military Powerhouse • Create imperial empire – Japan Embarrasses Russians (1905): Russo-Japanese War • Peace Settlement negotiated by Roosevelt (alienates Russians and Japanese • Japan a force to be reckoned with in Asia… lone wolf in world dominated by western powers – Japan competing w/ U.S. for influence in Pacific – Annex Korea in 1910 • Tensions between U.S. and Japan Rising – Japanese expansion; poor treatment of Japanese immig. In U.S. – Leads to Gentleman’s Agreement Next Semester Woodrow Wilson in Mexico • Belief in “moral diplomacy” • Warns any group taking over in L.A. must set up a legal government – Refuses to recognize Victoriano Huerta in Mexico – Gets approval to wage war • American sailors attacked; block arm sales to MX – Mediated settlement • American supported ruler, Carranza placed in power • Pancho Villa raids SW border • Will intervene in Haiti, Nicaragua, Mexico, and Dominican Republic •How “moral” was Wilson’s foreign policy in Latin America? •What did the U.S. mean by “legal government?” Additional U.S. Intervention • Philippines (1899-1902) – Philippines: McKinley’s “benevolent assimilation” – Kills 25,000 Filipino soldiers; 500,000 civilians • Dominican Republic (1905) – Intervene in Dominican Republic (1905) • Nicaragua (1912) – Create Nicaraguan National Guard – Install Dictator Anastasio Somoza • Corruption, torture, and murder of dissidents for 45 years Dominican Republic (1930) • US installs anti-communist Rafael Leonidas Trujillo – 30 year dictatorship – Torture, executions – Owned 80% of sugar plantations – Slave Labor – Massacred 20,000 Haitian workers El Salvador (1931) • US supports Hernandez Martinez – Anti-communist death squads;Wipes out Indian culture – Streets littered with bodies – Peasants forced to dig massive graves, then kill themselves A further look into American Intervention (early 20th Century) • • • • • • • Panama (1946) Korea (1950-1953) Vietnam (1950-1973) Iran (1953-1979) Paraguay (1954) Guatemala (1954) And the list goes on… Anti-Imperialist League • Arguments against Imperialism – Goes against America’s core values/founding principles • • • • Declaration of Independence Constitution Washington’s Farewell Address Gettysburg Address