Natural gas, its composition & classification
advertisement

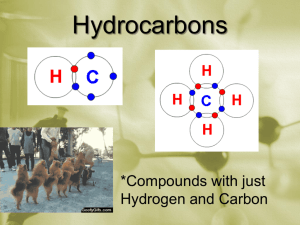
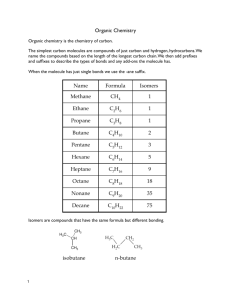
Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering By: Bilal Shams Memon NATURAL GAS COMPOSITION, CLASSIFICATION & ITS PROPERTIES. NATURAL GAS Gaseous form of hydrocarbon; homogeneous mixture of low density and low viscosity. NATURAL GAS IS PRODUCED FROM… Oil wells. Gas wells. Condensate wells. NATURAL GAS CHEMICAL COMPOSITION NATURAL GAS CHEMICAL COMPOSITION HYDROCARBONS Paraffins Cyclo Paraffins Aromatics NON HYDROCARBONS (impurities) CO2 H2S Complex compounds like N2, HE & H2O vapors NATURAL GAS ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION NATURAL GAS CLASSIFICATION 1. Wet Gas – Gas contains certain amount of water vapors or liquid hydrocarbons (e.g.. gasoline). 2. Dry Gas – Gas free from water vapors or liquid hydrocarbons. 3. Sour Gas – Gas containing excessive H2S. 4. Sweet Gas - Gas containing no H2S. 5. Rich Gas – Gas which contains impurities. 6. Lean Gas – Gas which is free from impurities. PROPERTIES OF NATURAL GAS Volume – Three dimensional space covered by gas (m³, cm³). Density – Mass per unit volume of gas (kg/ m³,g/cm³) Gas Formation volume factor – (Gas volume @ res. Cond. / Gas volume @ surface condition) Gas Expansion Factor – Reciprocal of Gas F.V.F. Compressibility Factor (z) – (volume @ actual cond. / volume @ ideal cond.) Specific Gravity – (Gas density / Air density) Specific Heat – number of BTU needed to raise the temp. up to 1⁰F of 1 lb. of material. Latent heat of vaporization – heat that is necessary to change a liquid into gas. PROPERTIES OF NATURAL GAS Critical Temperature (Tc)– Highest temp. @ which fluid can exist as liquid or vapor, above this temp. fluid is gas and can’t be liquid regardless of amount of pressure applied (⁰R). Critical Pressure (Pc)– pressure which is required to liquify or condense a vapor at it Tc. (Psi). Pseudo Critical Temperature (Tpc) – total molecular temperature. Pseudo Critical Pressure (Ppc)– total molecular pressure. Bubble point pressure (Pb) – pressure @ which first bubble of gas is liberated @ given temperature. Dew point pressure (Pd) – pressure @ which first drop of liquid forms or condensation starts @ given temperature.