Petroleum Chemistry
advertisement

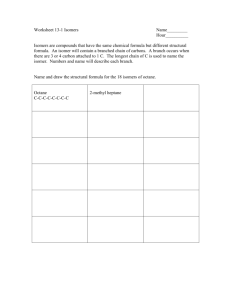
Petroleum Chemistry Petroleum • Petra (L. rock) • Oleum (L. oil) • Oil extracted from rock that lies just below the surface U.S. Primary Energy Flow by Source and Sector, 2009 (Quadrillion Btu) Total = 94.6 Petroleum Statistics, 2008 data • 1 barrel = 42 gallons • Top Oil Producing Country? – Saudi Arabia 10,782,000 barrels/day • Top Oil Consuming Country? – United States 19,948,000 barrels/day • Top U.S. Petroleum/Crude Oil Supplier? – CANADA 2,493,000 barrels/day More Statistics, 2008 • U.S. Motor Gasoline Consumption (per day)? – 8,989,000 barrels (378,000,000 gallons) Breakdown of cost of gasoline • Today’s price: $2.87/gallon Price comparison for other countries Country Price per gallon (US dollars) Spain $6.02 Canada $3.67 Mexico $2.12 Kuwait $0.87 Turkey $9.24 Australia $4.32 Japan $5.19 The place of the cheapest gasoline in the world? Venezuela $0.12/gallon Cost of gasoline compared to other liquids Liquid Price per gallon Milk $3.50 Windex $10.21 Red Bull Energy Drink $21.77 White Out $246.55 Black ink to refill printer cartridge1 $86.95 Renu contact lens solution $58.49 Tap water < $0.01 Bottled water (school cafeteria) $7.57 Garnier Fructis Shampoo $22.34 Dove Body Wash $29.01 All prices are from Sam’s Club Butler, PA unless otherwise stated. 1 from www.printerfilling station.com But how did they discover oil? How do they make gasoline from oil? How does gas make a car go? What does the catalytic converter do? A catalytic converter is a device that uses a catalyst to convert three harmful compounds in car exhaust into harmless compounds. • Hydrocarbons (in the form of unburned gasoline) • Carbon monoxide (formed by the combustion of gasoline) • Nitrogen oxides (created when the heat in the engine forces nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen) Why are these compounds bad? • Hydrocarbons are suspected carcinogens. – Gets converted into carbon dioxide and water • Carbon monoxide is a poison for any airbreathing animal. – Gets converted to carbon dioxide • Nitrogen oxides lead to smog and acid rain, and hydrocarbons produce smog. – Gets converted into nitrogen and oxygen What does it look like? • In a catalytic converter, the catalyst (in the form of platinum and palladium) is coated onto a ceramic honeycomb or ceramic beads that are housed in a muffler-like package attached to the exhaust pipe. Four Stroke Engine Spark plug fires, Combustion Heated gases igniting the products are expand very compressed swept outand of rapidly mixture of the cylinder push the gasoline and air through the piston down and begins the open exhaust turning the power stroke. port. crankshaft. Cylinder sealed Gasoline-Air asmixture both intake enters valve and cylinder exhaust throughvalve open are closed intake valve. Compression Exhaust Heat Power IntakeAdded Stroke Stroke So what is in gasoline that makes the engine work? • Gasoline is a mixture of over 500 hydrocarbon compounds that contain between 5 and 12 carbons. • Some of the compounds are: – – – – – – 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpropane 2,2-dimethylbutane 2,2-dimethylpentane 2,2,3-trimethylbutane 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane) Octane Rating • Fuel octane requirements for gasoline engines vary with the compression ratio of the engine. • Engine compression ratio is the relative volume of a cylinder from the bottom most position of the piston's stroke to the top most position of the piston's stroke. • The higher an engine's compression ratio, the greater the amount of heat generated in the cylinder during the compression stroke. Octane Rating, cont. • If fuel octane is too low for a given compression ratio, the fuel prematurely and spontaneously ignites too early and the fuel charge EXPLODES rather than BURNS resulting in incomplete combustion. • The net effect is a loss in power, possible engine damage, and an audible "knock" or "ping", referred to as detonation. Octane Rating, cont. • The octane number of gasoline is a measure of its resistance to knock. • The octane number is determined by comparing the characteristics of a gasoline to isooctane (2,2,4-trimethylpentane) and heptane. – Isooctane is assigned an octane number of 100. It is a highly branched compound that burns smoothly, with little knock. – On the other hand, heptane, a straight chain, unbranched molecule is given an octane rating of zero because of its bad knocking properties. Octane Ratings of Common Cpds found in gasoline Hydrocarbon Octane Rating n-butane 113 n-pentane 62 n-hexane 19 n-heptane 0 2-methylbutane 99 2,2-dimethylpropane 100 2,2-dimethylbutane 89 2,2-dimethylpentane 89 2,2,3-trimethylbutane 113 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane) 100 Trends of Octane Ratings • Octane ratings decrease with increasing carbon chain length. • Octane ratings increase with carbon chain branching. • Octane ratings increase in aromatics with same number of carbons. What octane rating should you purchase? • For most automobiles, use the lowest grade of 87 octane, unless they specifically say to use a higher octane gasoline. • Using higher octane grades does not provide any extra power or extra mileage. How they drill for the oil • Process for drilling oil and natural gas are basically the same. http://www.petrocasa.com/rigAnimation/index. html Click on all three slides and label the parts and a few words describing their function.