The Fall of the USSR World War II– Stalin in power
advertisement

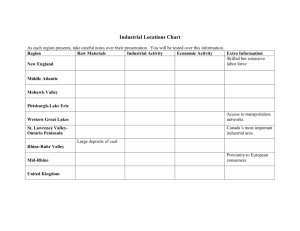
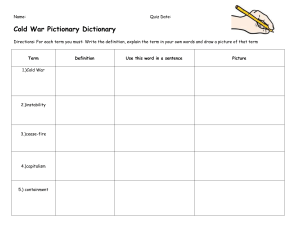
The Fall of the U.S.S.R World War II– Stalin in power •June 1941 Germany invaded the USSR •By the end of the war over 25 million Soviet citizens were killed •Even though they fought together, the war intensified Stalin’s mistrust of the west (U.S. and Britain delayed their promised invasion of Europe.) Cold War- End of WWII- Fall of the Berlin Wall and collapse of Soviet Union •Clash of ideas- Soviets need to control Eastern Europe, no common vision •Idea that conflict was inevitable between communism and capitalism •Leaders after Stalin fluctuated from moderate to hardline •Conflicts in Eastern Europe, Afghanistan, Vietnam, Cuba, Korea were Cold War events Global Superpower to decline…. 1970s- 1980s •military might, huge territory, great political influence and world’s second largest national economic base Soviet Problems that led to the END…. 1. On the domestic front (within the USSR), economic growth had practically stopped a. Declining labor productivity b. Failed agricultural programs c. Overly centralized decision making d. Too much military spending, graft and corruption e. Communism no longer inspiring ideology (old men dominated political system) 2. Political decline… a. 1980s relations with US, Japan and Western Europe all time low as a result of costly war in Afghanistan b. Unable to develop and maintain close relationships around the world c. 30 month leadership crisis 1982-1985– four different leaders! – difficult to initiate reform Soviet Problems that led to the END…. 3. Mikhail Gorbechev- last Soviet leader (1985) a. Instituted reforms so extensive they could only be termed a revolution! 1. perestroika- restructuring the economy (privatization) 2. glastnost- openness; freedom of expression, ideas, disclosure of graft and corruption, relaxed control on literature and the arts 3. democratization- multiple political parties were legal 4. no longer intervene militarily in Eastern Europe elections (forced communism) Reforms had unintended consequences…. •1989- Fall of the Berlin Wall- symbol of decline (Reagan’s famous line-“Mr. Gorbechev, tear down that wall.” ) •By 1991 the Soviet Union had dissolved into 15 separate countries •Boris Yeltsin first Russian president after the fall of the Soviet Union Political and Economic results….. (read domestic impacts) •Tension between supporters and opponents of reform, ethnic groups •Growing gap between rich and poor •Older, unemployed and ill people impacted by elimination of safety net •Relatively peaceful elections and changes in government •Organized crime, tax dodging •Lingering fear of government interference stunted growth, esp. middle class Economic needs/challenges •Infrastructure updates •Better goods that could sell internationally •Rules limiting movement of people, money and goods needed reform •Courts needed to be able to enforce laws, especially debt collection Environmental impact of Soviets… -change in population patterns after the fall of communism * people moving back to European heartland from “hinterlands” in Siberia or other distant areas -Soviet history of environmental pollution * 1986 Chernobyl- nuclear reactor explosion in Kiev (Ukraine) *Aral Sea (over irrigation, biological weapons testing) *Overuse of chemicals and pesticides contaminate water and farmland *Nuclear testing (eastern Kazakhstan)