Components of Earth2012
advertisement

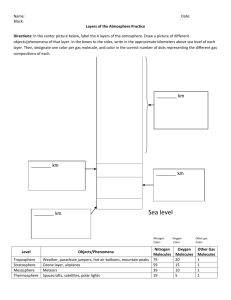
Components of Earth Biotic and Abiotic Factors Spaceship Earth • Closed System • Resources are limited Why is earth so favorable for life? • Distance from the sun (Temp range) • Size of the planet (Gravity) What sustains life on earth? • Earth’s 4 spheres help support organisms – Atmosphere – Hydrosphere – Geosphere – Biosphere Atmosphere Hydrosphere Geosphere Biosphere Biosphere •Abiotic and Biotic Factors •Uppermost part of the geosphere, most of the hydrosphere, and lower part of the atmosphere Ecosystems (Sun) • One – way flow of high – quality from the sun – Energy is lost as heat through process • • • • Warms atmosphere Evaporates and recycles water Generates winds Supports plant growth Cycling of Matter • Fixed supply of nutrients are continually recycled – Carbon – Nitrogen – Phosphorus – Potassium Ecosystem Components • Life exists in biomes and aquatic life zones • Biomes – Category given to regions of the world where the plant and animal life are defined by the region’s climate • Temperature • Precipitation – Savannas, deserts, tropical rain forests, alpine, temperate, arctic, taiga Population • Limiting factors – Resources – Law of tolerance • too much or too little of abiotic factor • Nutrients, precipitation, temperature Biological Components • Producers • Consumers • Biodiversity Producers • Autotrophs • Make their own food Consumers • Heterotrophs • Feed on other organisms – Omnivores – Carnivores – Herbivores – Detritivores Food Chain VS Food Web Feeding levels • Trophic levels – Producers are the lowest level – Primary consumers – Secondary consumer – Tertiary consumer and so on • 10% rule, 90% energy lost as heat, growth, reproduction Geosphere Composition of Earth • Crust, mantle, core • Crust - 1% Earth’s mass thinnest layer • Mantle - layers beneath the crust • Core - innermost layer Structure of the Earth • Four layers – Lithosphere – Asthenosphere – Outer core – Inner core Structure of the Earth • Lithosphere (outer layer) • crust and uppermost part of the mantle • divided into pieces called tectonic plates • Earthquakes (Ritcher Scale) • Asthenosphere – Solid layer of rock beneath the lithosphere – Flows very slowly allowing tectonic plates to move an top of it • Outer core – Dense liquid layer • Inner core – dense mostly made up of metals iron and nickel Atmosphere • Nitrogen (makes up the majority), oxygen, carbon dioxide • Insulates the Earth’s surface reducing the rate that Earth loses heat • Concentration of gases and particles are constantly changing • Gases and particles are pulled towards the Earth by gravity becoming densest by the Earth’s surface 4 Layers of the Atmosphere • • • • Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Troposphere • Closest to the Earth’s surface • Weather occurs in this layer of the atmosphere • Temperature decreases as altitude increases. (Particles become further apart) Stratosphere Located above the troposphere Ozone layer, O3 absorbs the sun’s UV energy, warms the air reduces the amount of radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface High temp Mesosphere • Lies between the stratosphere and the thermosphere • It is the coldest layer of the atmosphere Thermosphere • Layer farthest from the Earth’s surface – Nitrogen and oxygen absorb solar radiation causing them to become electrically charged – can produce radiant energy (light) known as the aurora borealis. Energy in the Atmosphere • Sun’s energy can be transferred by; radiation convection conduction Radiation • Heat travels across space and in the atmosphere Conduction • Heat from a warmer object flowing to a colder object when in direct contact Convection • Heat transfer by currents (Hot air rises, cold air sinks Movement of Energy in the Atmosphere • Air is constantly moving • Troposphere – currents of lighter air warmed by the Earth’s surface rise into the atmosphere – The currents of heavier air (cooler) sink towards the ground. • The rise and sink pattern of air creates a circular current known as convection current. Greenhouse Effect • Trapped gases heat the Earth – natural process that keeps the environment at temperatures in which life can exist • When these gases known as greenhouse gases become abundant – water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide – a thicker insulating layer forms trapping in more heat Hydrosphere Includes all of the water on or near the Earth’s surface • Water; % Fresh? % Salt? % Ice? • Do you know? Earth’s Oceans •Important role in regulating our world’s environment •Absorbs over half the solar radiation