Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Where is fresh water found?
advertisement

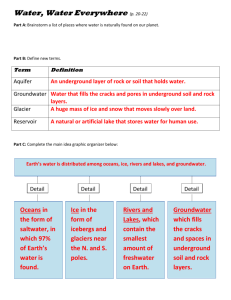
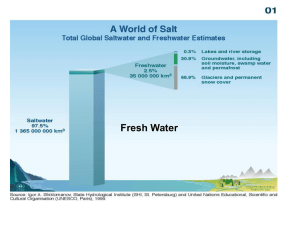
Chapter 5 - Water on Earth Standard ES 3.a ES 4.a ES 3.a Students know most of Earth’s water is present as alt water in the oceans, which voer most of Earth’s surface. ES 4.b Students know the influence that the ocean has on the weather and the role that the water cycle plays in weather patterns. Objective Students explain that nearly all of Earth’s water is alt water in oceans that cover three-fourths of Earth’s surface. Students relate ocean currents to changes in temperature. Bell Work 1. List foods that taste salty. 2. Why does the ocean water leave white grains on your skin? Chapter 5 – Water on Earth 1. Sea level- Interaction: Draw a picture to represent sea level. 2. salinity- Interaction: How can the oceans be described ? Chapter 5 Lesson 1 • What do you think the word hydrosphere means? The Hydrosphere • Earth is covered mostly in water. – Most of Earth’s water is in its salty oceans. – All of the waters on Earth make up the hydrosphere. • The hydrosphere covers ¾ of the Earth’s surface. • Only 3/100, or 3% of the hydrosphere is in a place other than the oceans. – What?!?!?! That means 97% of water on Earth is salt water?!?!? – Can we drink salt water?!?! Why or why not? • Group discussion and brainstorm – So how much of Earth’s water can we drink? • Drinking water is also called fresh water Oceans • • • • • The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean. Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean Southern Ocean Artic Ocean – All of the oceans are connected. – Each sea level differs slightly from ocean to ocean Earth’s Oceans • Ocean water is salty. • The oceans get salt from rivers, when rain falls over land, it dissolves salts and other minerals, which are then carried to the oceans by rivers. • When water evaporates from the surface of the ocean, the dissolved salts are left behind in the ocean. • Salinity is the measure of the amount of salt in water. • Ocean water is saltier in some places than in others. • The temperature of ocean water differs from place to place. • Cold water is heavier than an equal volume of warm water, so cold water sinks below warm water. • Refer to the illustration on pg. 174 • Location and currents affect temperature. Ocean Resources • Salt – Evaporating sea water • Magnesium • Fish – Other seafood Chapter 5 Lesson 2 – Where is fresh water found? Standard 3.d/3.e 3.d Students know that the amount of fresh water located in rivers, lakes, underground sources, and glaciers is limited and that its availability can be extended by recycling and decreasing the use of water. 3.e Students know the origin of the water used by their local communities. Objectives Students will identify Earth’s limited sources of fresh water, including rivers, lakes, underground sources, and glaciers. Students will describe ways to extend the availability of fresh water. Students locate sources of fresh water used by local communities. 1. Name and describe fresh water lakes and rivers near where you live. 2. Where do you think the water in rivers and lakes come from? Bell Work Ch. 5 Sec. 2 Where is fresh water found? ? 1. aquifer- 2. water table- Interaction: What roots are used in the word aquifer, what do they mean? Interaction: Sketch a picture of a water table. 3. watershed- 4. reservoir- Interaction: Interaction: List types of reservoirs. Which reservoir is closet to us? Where is fresh water found? Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Where is fresh water found? • Drinking water is also called fresh water. • Where does fresh water come from? – – – – Almost all of Earth’s fresh water starts as rain or snow. Some sinks into the ground Some collects in rivers and lakes Some is frozen in ice sheets and glaciers • Fresh water is NOT evenly spread over the world. • The amount of fresh water is limited – This means water should be used WISELY!!!!! Sources of Fresh Water • Groundwater – Rain or melted snow that soaks into the ground. • Groundwater keep sinking until it reaches a layer of rock or clay that it cannot move through. • This layer of rock and soil that groundwater moves through is an aquifer. – Aqua means water – Ferre means to carry • The top level of groundwater in an aquifer is called the water table. • Identify three places fresh water can be found – Group discussion and brainstorm • Identify three places fresh water can be found – Group discussion and brainstorm • • • • • Groundwater Rivers Lakes Ice sheets Glaciers Surface Water • Rivers, Streams, Lakes – Melting snow, rainwater, and groundwater • The area from which water drains into a river is called the river’s watershed. Lakes • Lakes are generally blocked by higher land or by a dam. • Lakes form when water collects in a low spot. • A reservoir is usually an artificial lake that forms behind a dam. Ice and Glaciers • Ice – About 7/10 of Earth’s fresh water is FROZEN in ice. – Frozen in ICE?!?!?! What?!?!? that means we have even less fresh water to drink!!!!!!! • Glaciers – Smaller areas of ice are called glaciers. – As they flow they scrape and move rock. – Glaciers and ice sheets form over time if snowfall is greater than the amount of snow that melts. • Floating pieces of ice are called icebergs. Group Discussion & Brainstorm • Where is most of the earth’s fresh water located? • Why is it important to conserve water? • How can we conserve water? Getting Water to Homes • Water towers • Groundwater • Surface Water – Pollution – Water treatment plants Water Pollution Questions to consider • How does a person use the most water? • Why does water need to be treated before it can be used? Chapter 5 Lesson 3 –California water sources? Standard 3.d/3.e 3.d Students know that the amount of fresh water located in rivers, lakes, underground sources, and glaciers is limited and that its availability can be extended by recycling and decreasing the use of water. 3.e Students know the origin of the water used by their local communities. Objectives Students will give examples of sources of fresh water found in CA, including rivers, lakes, and underground sources. Students know the origin of their community’s water supply. 1. List four sources of fresh water. 2. Where do you think water comes from when you turn on a faucet. Bell Work What are some California water sources? Chapter 5 Lesson 3 • Where does California get its water from? • California gets fresh water from lakes, rivers, and groundwater. • Because the amount of fresh water is limited, it is important to use water wisely. • Because most fresh water starts as rain or snow, the supply of fresh water in southern California is very limited. Transporting Water Throughout California • California Aqueduct system • An aqueduct is a system of pipes that carries water from a river or lake to the area where it is needed. Group discussion and brainstorm • Why are aqueducts important • What aqueduct does Riverside County get water from? • What is the purpose of aqueducts? • How would the supply of water for CA be affected if less snow fell during the winter than normal? Local Water Sources • Watershed – the land that water flows across or under on its way to a stream. – No matter where you live, you live in a watershed. • In which watershed do you live? What affects the water supply? • The amount of water available to an area depends on how much water is collected in the watershed. • It also depends on how much water is used. • Water quality also affects how much fresh water is available. Group discussion and brainstorm • What affects water quality? Reclamation • Water used in homes and business can be recycled. • Wastewater treatment plant Group discussion and brainstorm • List three ways people can reduce and recycle the water they use. • How is reclaimed water used on the farm? • How can the supply of water in lakes and rivers be affected? • Why does you community’s water source depend partly on how much water it needs? Chapter 5 - Section 1 - 3: How can the oceans be described? LoD Summary sea level salinity aquifer water table water shed reservoir hydrosphereAquifer reclamation Interaction Draw a flow chart of a watershed Water from rain or snow – small creeks – larger streams – rivers – most rivers flow to the ocean Reading Check Question What type of water source has a high level of salinity?