The Brain Game answers
advertisement
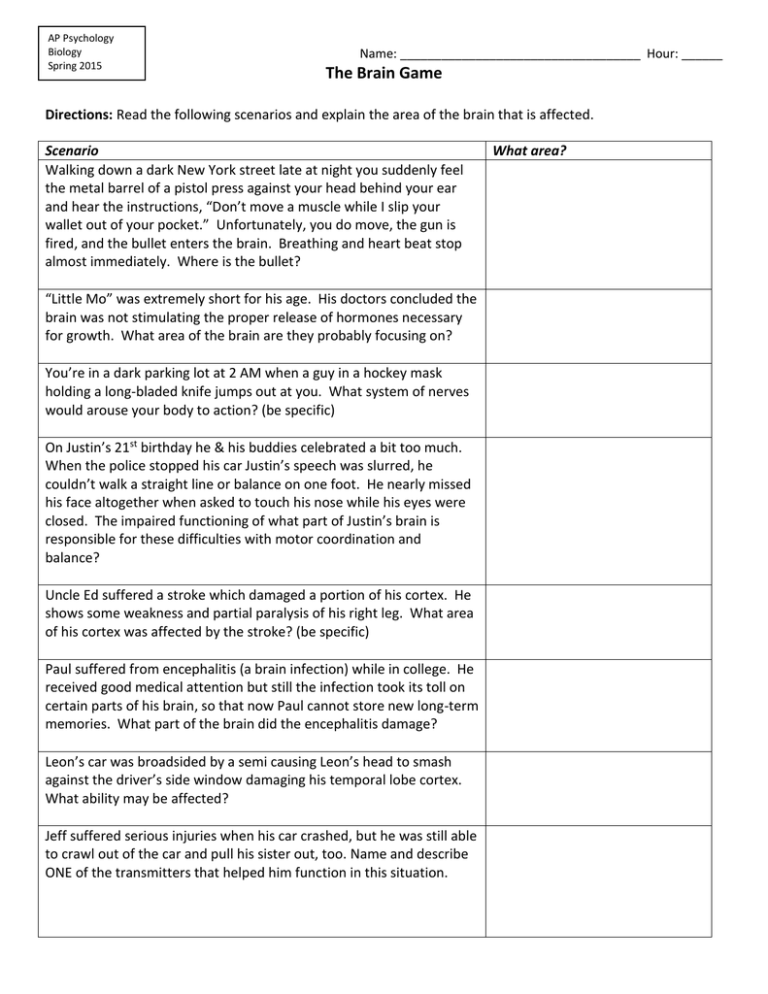
AP Psychology Biology Spring 2015 Name: ___________________________________ Hour: ______ The Brain Game Directions: Read the following scenarios and explain the area of the brain that is affected. Scenario Walking down a dark New York street late at night you suddenly feel the metal barrel of a pistol press against your head behind your ear and hear the instructions, “Don’t move a muscle while I slip your wallet out of your pocket.” Unfortunately, you do move, the gun is fired, and the bullet enters the brain. Breathing and heart beat stop almost immediately. Where is the bullet? “Little Mo” was extremely short for his age. His doctors concluded the brain was not stimulating the proper release of hormones necessary for growth. What area of the brain are they probably focusing on? You’re in a dark parking lot at 2 AM when a guy in a hockey mask holding a long-bladed knife jumps out at you. What system of nerves would arouse your body to action? (be specific) On Justin’s 21st birthday he & his buddies celebrated a bit too much. When the police stopped his car Justin’s speech was slurred, he couldn’t walk a straight line or balance on one foot. He nearly missed his face altogether when asked to touch his nose while his eyes were closed. The impaired functioning of what part of Justin’s brain is responsible for these difficulties with motor coordination and balance? Uncle Ed suffered a stroke which damaged a portion of his cortex. He shows some weakness and partial paralysis of his right leg. What area of his cortex was affected by the stroke? (be specific) Paul suffered from encephalitis (a brain infection) while in college. He received good medical attention but still the infection took its toll on certain parts of his brain, so that now Paul cannot store new long-term memories. What part of the brain did the encephalitis damage? Leon’s car was broadsided by a semi causing Leon’s head to smash against the driver’s side window damaging his temporal lobe cortex. What ability may be affected? Jeff suffered serious injuries when his car crashed, but he was still able to crawl out of the car and pull his sister out, too. Name and describe ONE of the transmitters that helped him function in this situation. What area? Wayne has been diagnosed as a paranoid schizophrenic. What neurotransmitter change seems to underlie schizophrenia? Siggy the Rat had a stimulating electrode implanted in his brain. Siggy presses a bar to activate that electrode-something he would rather do than eat, sleep or have sex. Sometimes he presses 7000 times/hr. What part of the brain is Siggy’s electrode stimulating? Brett was a superior student and had a full scholarship, but following a head injury he can no longer plan, organize or follow through with tasks necessary for school. (In addition he no longer shows concern for others or for common social courtesies. He’s rude and disinhibited.) Where was his injury? Jan suffered a concussion in a car accident. Since that day she has notice a dramatic decrease in her sexual libido, a lack of appetite and an absence of thirst. She never thinks of having a drink until her lips actually dry and crack. What part of her brain might have been affected by the car accident? Philip is hooked on cocaine. What neurotransmitter seems most closely related to the pleasure such drugs produce and their addictive qualities? Grandma Mary had a stroke which impaired her ability to speak fluently although she can move all the necessary muscles. What is the most likely location of her brain damage (be specific)? Some individuals who are blind have biorhythms and sleep/waking cycles that are very different than normal. The area of the brain responsible for these cycles malfunctions without normal visual input. What region is this? Michael J. Fox has Parkinson’s disease, a motor disorder related to a significant lack of the neurotransmitter _______. Gwen’s brain has a congenital anomaly (a difference in brain anatomy that she was born with) - it lacks the main connection between the right and left hemispheres. What was Gwen born without? Sara’s grandfather has developed Alzheimer’s disease. What can you tell her about probable changes in his brain chemistry? 2 You’re taking a short cut through a back yard to get to your car and encounter two unrestrained Dobermans who begin pursue you. You run faster than you have ever run before, and dive into your car just in the nick of time. It takes 10 minutes for your pulse and breathing to slow down to normal. What part of the nervous system slows heart rate and breathing down to normal afterwards? Amy was having a really bad week. On Monday her vision got blurrier and blurrier until she could no longer see at all. On Tuesday she found she couldn’t hear. On Wednesday her sense of taste went. On Thursday she lost her sense of touch. Her CAT scan revealed a single brain tumor was probably producing all of these deficits. What single part of the brain in involved in all of these sensory processes? Pete was struck by lightning when he insisted on finishing his 18 holes of golf despite the lightning packed thunderstorm. He was looking down; lining up a long putt shot and the bolt of lightning struck the rear of his head, frying his occipital lobes. What aspect of behavior is likely to be impaired if Pete survives? Dana is taking Prozac to help control her depression. Prozac works by increasing the availability of what neurotransmitter? Margie suffered damage to part of the surface of her brain after being struck by a golf club let loose by an irate golfer that had just sliced a key drive. As a result Margie has loss some sensory awareness of her left leg. Where is Margie’s brain damage? (be specific) Your grandmother has begun to lose her spatial abilities—she gets lost in the neighborhood where she has spent her whole life, she can no longer read a map, she can’t put dishes or clean laundry away because she no longer knows where things go in her home of 40 years. What part of the brain mediates these perceptual/spatial abilities? After falling through the ice on a local pond, little Johnny was trapped under the icy water for 10 minutes before the rescuers got him out. They were able to resuscitate his pulse and breathing but he did not regain consciousness for days. Disturbance of what specific part of Johnny’s brain might have resulted in an inability of the brain to regulate normal alertness? 3 Jeanette suffers from focal epilepsy (seizures localized in just one part of the brain). Her seizures are triggering extreme emotions- most often extreme fear followed by a rage response. What part of the brain is being affected? After Martin’s motorcycle accident he had difficulty understanding what others were saying to him. He could speak but what he said made little sense. Where is Martin’s brain damage? Julissa Gomez, a young American gymnast, unsuccessfully attempted a difficult vaulting move, and struck the back of her head. Damage to the cord resulted in paralysis and damage to a nearby region caused her to lapse into a coma. Where is the damage that caused her coma? Original source: Rod Plotnik / table created by Mary Ann Stedry: AP Psychology 4 The Brain Game answers... 1. The medulla—the bottom most part of the brainstem, takes care of life-sustaining reflexes like breathing and heart rate. 2. “Little Mo”—the hypothalamus and its connection to the pituitary gland-insufficient growth hormone is being released. 3. The sympathetic division-the sympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system in our “fight or flight” system arousing the body (HR, BP, breathing) for action when necessary. 4. Justin—The cerebellum—the cerebellum functions like a motor computer taking care of the underlying details of our movements- coordination, timing, targeting, balance. Oddly enough, it is often malformed in autism as well. 5. Uncle Ed—the motor cortex—Ed’s stroke must have deprived the blood flow to the strip of motor cortex in the frontal lobe of the left hemisphere. 6. Paul—Hippocampus—part of the limbic system called the hippocampus seems essential for our ability to store new memories into their permanent, long-term form. 7. Leon—auditory cortex—the part of the cortex devoted to making sense of what we hear is in the temporal lobe. The left temporal lobe is particularly important for comprehending speech—Wernicke” area. 8. Jeff—Endorphin—relieves his pain NE—Norepinephrine—arouses the body in emergencies Ach—Acetylcholine—carries messages to the muscles 9. Wayne—excess response to Dopamine-DA 10. Siggy—the pleasure reward system in the limbic system. 11. Brett—Prefrontal cortex (frontal lobe) the front-most portion of the frontal lobe is involved in planning, judgment, developing strategies, and inhibiting incorrect or appropriate responses. 12. Jan—the hypothalamus—just above the pituitary gland, the hypothalamus is critical for basic behaviors/motivations like hunger, thirst, & sex. 13. Philip—Dopamine—seems to be the key transmitter of the pleasure system. 14. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 15. The reticular formation is responsible for awareness and sleep cycles. 16. Michael J. Fox—the substantia nigra of the midbrain. 17. Gwen—Corpus Callosum—the corpus callosum is a large cable of axons connecting the corresponding parts of the right & left hemisphere. 18. Sara’s grandfather—Ach—Acetylcholine neurons have died off so there is less stimulation of his cortex. 19. The Parasympathetic nervous system—the parasympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system takes care of normal body maintenance functions including slow normal breathing & heart rate. 20. Amy—the Thalamus—just above the hypothalamus is the thalamus, the brain area the relays all sensory input except smell to the correct regions of the cortex. It also seems to play an important role in maintaining conscious awareness. 21. Pete—Vision 22. Dana—Serotonin 23. Margie—Somatosensory Cortex—the front strip of the right parietal lobe processes general sensory input from the left side of the body. 24. Grandmother—the right hemisphere—while the left hemisphere has better developed language areas, the right hemisphere is most important for the multitude of situations where we use perceptual / spatial information. 25. Little Johnny—the Reticular Formation—the reticular formation is a system of neurons running through the brainstem that arouses the upper parts of the brain, regulating our normal waking consciousness. 26. Jeannette—the Limbic System—the limbic system structures, hidden under the cortex of our right & left hemispheres, is best known for its control of emotion. Parts of it also play a role in memory. One part of the limbic system-the Amygdala-seems particularly important for emotional reactions & memories. 5 27. Martin—Wernicke’s Area—in the left temporal lobe is critical to language comprehension. 28. Julissa—the reticular formation of the brainstem. 6