Deciduous Forest
advertisement

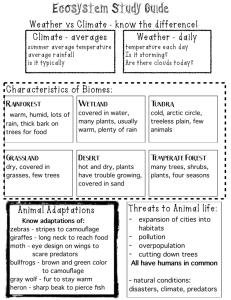
Warm, wet and humid all year round Nutrient poor soil-high rate of decomposition Different layers within the forest create a variety of niches Emergent, upper and lower canopies, forest floor Amount of sunlight determines what lives in each layer Plants Bengal bamboo, Strangler Figs, jambu, orchids Shallow roots systems Epiphytes (ex. Orchids) will grow on tree branches and tap into the tree with their root systems to obtain nutrients Fast growers Animals New World Monkeys, African Forest Elephants, King Cobra, Vampire Bat, Jambu Fruit Dove, Toco Toucan, Kinkajo Arboreal-live up in the trees; long arms, prehensile tails, etc. Camouflage Strong beaks to break open seeds Environmental Issues Deforestation Agriculture, cattle, resources, etc. Poachers Hunt and collect animals for exotic pet trades Biodiversity: high Most decidous forests lie between 30 and 60 degrees north and south latitudes 4 seasons: our weather patterns Fertile soil Plants Walnut trees, chestnut trees, maple trees, oak trees Lose leaves during fall Dormant during winter-saves water Animals American Black Bear, Coyote, Duckbill Platypus, Eastern Chipmunk, White-tailed deer Camouflage, hibernate-fat layer, store food, etc. Environmental Issues Deforestation Farmland Urbanization Resources Overhunting Pollution (air, water, land, etc.) Biodiversity: medium to high Think Canada 4 Seasons Colder temps than deciduous About the same precipitation than deciduous Acidic soils from the needles from the trees-deter other plants from growing around them Plants White Spruce, Balsam Fir, Pine, Cedar, Douglas Fir Triangular shape Branches are flexible Thick bark Needle-lie leaves to prevent water loss; needles are acidic Animals Lynx, Wolverines, Bobcats, Minks, Caribou, Elk, Moose, White Rabbits Thick fur coat Camouflage Hibernate in the winter-protective layer of fat Environmental Issues Deforestation For homes, roads, resources Pollution (air, water, land) Biodiversity-less then tropical or deciduous, more then everything else (medium to high) 4 seasons Less precip then forests more then desert/tundra Natural fires are common-rejuvenate land Windy Plants: Coyote bush, common sage brush, chaparral sweetpea, purple needle grass: lots of grasses and bushes-very few trees Deep roots, fire retardant leaves, waxy coatings on leaves Animals: Coyote, rattlesnake, jackrabbit, puma, golden jackal, bezoar goat Camouflage, nocturnal, go without water for long periods of time Environmental Issues Fire suppression Urbanization-causes erosion and destruction of habitat Used for agriculture Biodiversity Medium to low Hint: think The Lion King 2 seasons Wet and dry Natural fires are common Windy Nutrient poor soil Plants Grasses Grow in clumps to save water, grow quickly, deep roots Animals Elephants, lions, zebras, gazelles, giraffes, etc. Migrating herbivores camouflage Environmental Issues Overhunting Overgrazing Fire suppression Urbanization Biodiversity Medium to low Middle of the US Fertile soil Windy Natural fires are common to rejuvenate land Plants Grasses Deep root systems and able to rejuvenate quickly after fire Animals Badgers, coyotes, prairie dogs, etc. Burrow-strong front claws Camouflage Environmental Issues Land converted to farmland Less genetic diversity, more erosion, increased pesticide usage Fire suppression Biodiversity: medium to low Usually found between 15 and 30 degrees latitude Usually hot, always dry Winds shape landscape Nutrient poor soil Plants Cacti, brittle bush, joshua tree Sharp spines, fleshy insides, leathery leaves, shallow root systems Animals Lizards, desert tortoise, cactus wren, fennec fox, jerboa Camouflage, estivate: burrow during the day, nocturnal at night, large ears to release heat Environmental Issues Overgrazing Excessive off road vehicles usage, nuclear testing sites, etc. Biodiversity: low Cold and dry Permafrost 2 seasons: long cold winter and short warm summer Polar winds Plants Sedges, arctic willow, arctic moss, lichens, caribou moss Grow close to the ground, shallow root systems, short hairs No trees due to high winds and shallow root systems Animals Arctic fox, musk oxen, snowy owl, polar bear, caribou, arctic hare, lemmings Camouflage, thick fur, layers of fat Environmental Issues Extraction of nonrenewable resources-oil drilling, building of roads, etc. Global warming (from the burning of fossil fuels)-thaws permafrost-leads to a positive feedback loop Biodiversity: low