Competences
advertisement

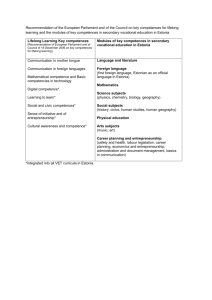
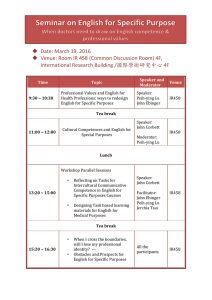
THE ICT-SUPPORTED PROCESS OF FORMING LEARNERS´ COMPETENCES IN NATURAL SCIENCE/CHEMISTRY Martin Bílek Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Hradec Králové, Czech Republic Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Constantine the Philosopher University in Nitra, Slovakia Hradec Králové, CZ Nitra, SK Curriculum Inovation Interest – What is my interest?; What I want to learn about? What I will need? Context – ideal (school), application, society, life Content – standards (?), RVP (?), tradition (!), new topics Competences – Scientific literacy, science activities Interest: Project ROSE Natural science school subjects are interesting + I would like more natural sciences in the school Thanks science and technology will increase possibilities and opportunities for next generation – + Science and Technology help to poor people – Context: Projekt ROSE (J. Lavonen, 2006) Ideal (school) context (more answers (-), more negative at girls) Application context (technology) (big differences between boys (+) and girls () Social context (different preferences) Human context (without clear preferences) Content of natural science subjects Two level curriculum approach Core curriculum (guidelines) No prescribed subjects but educational areas Man and Nature (Phy, Che, Bio, Geo) School curriculum as own product Challenges for new approaches (integration, project instruction, relations with environment etc.) Competences (key) Learning competence; Problem solving competence; Communication competence; Social and personal competences; Citizen competence; Working competence. Main competences for area Man and Nature Inquiry of nature facts and phenomena and their relations with using of empirical (observation, measuring, experiment) and theoretical (modelling) methods of thinking and working, Formulation of question about nature phenomena and their processes and answers searching Formulation of hypothesis and their verification Etc. Methodological approach supported by ICT (Hellberg and Bílek, 1996) Competences in activities Observing and Measuring Comparing and Ordering Exploring and Experimentation Foreseeing and Verification Discussion and Interpretation Modelling and Mathematization Searching and Communication Registration of values of the measured item in time-intervals “Pyrosis“ (Rennie – Tums – Gastrogel) The single-step mode measurements = a step-by-step registration of values within one experiment within a set of analysed samples within the set of experiments The single-step mode measurements within a set of samples Acidity scale of kitchen samples – miniproject The single-step mode measurements within the set of experiments Method of isomolar series (NaOH + HCl) Competences in activities Observing and Measuring Comparing and Ordering Exploring and Experimentation Foreseeing and Verification Discussion and Interpretation Modelling and Mathematization Searching and Communication Prognosing and Verification Competences in activities Observing and Measuring Comparing and Ordering Exploring and Experimentation Foreseeing and Verification Discussion and Interpretation Modelling and Mathematization Searching and Communication Chemical compound DHMO (Dihydrogenmonooxid) DHMO is chemical compound using as solution means in chemical industry and raw material for different applications (dyes, cooling means etc.) In the big amount it can be deadly. It has next negative effects: – – – – – It causes emission of sweat and throwing up, It is main part of acid rain, It causes erosion, It causes lower effectivity of brakes in the cars, etc. 100 80 60 40 20 0 Forbid Permit I dont know In the survey among people (n = 100) was resulted opinions on the graph. What is Your oppinion about this chemical compound? H2O Thank You for Your attention! martin.bilek@uhk.cz