Ch. 1 Consumer Behavior vs.
Marketing Strategy
What is Consumer Behavior?
• The dynamic interaction of affect and cognition,
behavior, and environmental events by which
human beings conduct the exchange aspects of
their lives.
• The study of individuals, groups, or organizations
and the processes they use to select, secure, use,
and dispose of products, services, experiences, or
ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these
processes have on the consumer and society.
Why Is It Important?
• “The purpose of a business is to create and keep a
customer.” -- Ted Levitt
Ex: Federal Express
• A deep understanding of consumers is extremely
useful for developing effective marketing
strategies.
Ex: Pizza, Coffee
• It is also important to public policy makers.
Relationships among Action-Oriented
Groups Interested in Consumer Behavior
Marketing
organizations
Marketing
strategies
Public
Policy
Consumer
activities
Consumers
Government
and political
organizations
Marketing Strategy
A plan
designed to
influence
exchanges to
achieve
organizational
objectives.
Marketing
Strategy
Internal
Influence
Typically, a
marketing
strategy is
intended to
increase the
probability or
frequency of
certain
consumer
behaviors.
Marketing Strategy and Consumer Behavior
1-1
Outcomes
Consumer
Decision
Process
Marketing
Strategy
Marketing
Segmentation
Marketing
Analysis
Individual
Firm
Society
Problem Recognition
Information Search
Alternative Evaluation
Purchase
Use
Evaluation
Product, Price, Distribution,
Promotion, Service
Identify product-related need sets
Group Customers with similar need sets
Describe each group
Select attractive segment(s) to target
Company
Competitors
Conditions
Consumers
Copyright © 2001 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights
reserved.
Overall Model of Consumer Behavior
1-5
EXTERNAL INFLUENCES
Culture
Subculture
Demographics
Social Status
Reference Groups
Family
Marketing Activities
INTERNAL INFLUENCES
Perception
Learning
Memory
Motives
Personality
Emotions
Attitudes
Experiences and Acquisitions
SITUATIONS
Problem
Recognition
Information
Search
SELF-CONCEPT
and
LIFESTYLE
Needs
Alternative Evaluation
and Selection
Desires
Outlet Selection
and Purchases
Postpurchase
Processes
Experiences and Acquisitions
SITUATIONS
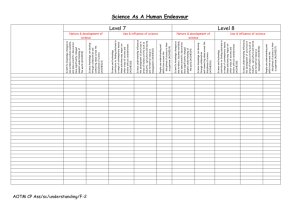
Approaches to the Study of Consumer
Behavior
Approach
Interpretive
Core
Disciplines
Cultural anthropology
Primary
Objectives
Understand consumption and its
meaning
Primary
Methods
Long interviews & focus groups
Approaches to the Study of Consumer
Behavior (cont.)
Approach
Traditional
Core
Disciplines
Psychology & Sociology
Primary
Objectives
Explain consumer decision
making and behavior
Primary
Methods
??
Approaches to the Study of Consumer
Behavior (cont.)
Approach
Marketing Science
Core
Disciplines
Economics & Statistics
Primary
Objectives
Predict consumer choice and behavior
Primary
Methods
??