Unit 9 _ ppt1 _ Post WWI
advertisement
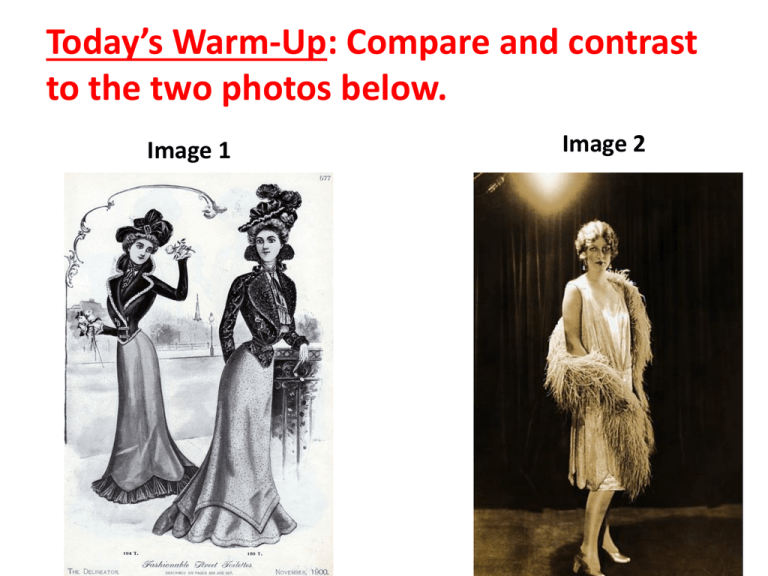
Today’s Warm-Up: Compare and contrast to the two photos below. Image 1 Image 2 The Roaring 20’s The Decade that Roared… • The 1920s is considered one of the wildest periods in American history • WWI was over – society rejoiced! • Americans roared to the wail of jazz, laughter of carefree youth, and the hum of American industry Beneath the Surface… • Beneath the surface, this era was more complex and filled with conflict • Americans grappled with important questions about race, immigration, religion, alcohol, women, wealth, and poverty As the War Ended . . . • Spanish influenza epidemic hits! –Most deadly for 20-40 year olds • Eventually killed 20-50 million worldwide – (By contrast, WWI killed about 15 million people) Philadelphia – October 1918 Emergency hospital at Camp Funston in Fort Riley, KS (1918) Over 50 Thousand! Mortality (Death) Rates from 1900 to 2000. Changes for African Americans • Great Migration = Blacks moved north to take advantage of booming wartime industry • Black ghettoes began to form, i.e. Harlem Prohibition Enforced • 18th Amendment took effect on January 16, 1920 and made the manufacture, sale, and transport of liquor, beer, and wine illegal. Prohibition Creates Unintended Consequences… • Limited supply and growing demand for liquor created a golden opportunity for crooks • Many Americans turned to bootleggers - suppliers of illegal alcohol. • Speakeasies – illegal, underground bars Organized Crime • The profit from selling illegal liquor helped lead to the rise of organized crime. • As rival groups fought for control in cities, gang wars & murders became common. Homicide Rate dramatically rises, then peaks in 1933 – the year prohibition ends! HOMICIDE 11 1 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 One of the most notorious criminals of this time was Al “Scarface” Capone, a gangster who rose to the top of Chicago’s organized crime network. Lawlessness, Violence, and Corruption Increase… • Many Americans began to believe prohibition caused more harm than good. • In 1933, the states ratified the Twenty-First Amendment which repealed prohibition Women Move Toward Greater Equality • Some of the most significant changes of the 1920s occurred in the lives of women – 19th Amendment granted women the right to vote – Expanded educational and job opportunities • With wider opportunities and greater incomes, women (esp. young women) rebelled against old customs Women Rebel Against Old Customs • Women began to cut their into short “bobs” and wore makeup –Lipstick, blush, and eye shadow were no longer signs of an “immoral” woman Women in 1900 • • • • Long hair Long sleeves Long dresses Shapely corset Women in 1920s • • • • Short hair Short sleeves Short dresses No corsets! The Flapper Image A type of bold, fun-loving young woman, came to symbolize a revolution in manners and morals that took place in the 1920s. Flappers • Flappers challenged conventions of dress, hairstyle, and behavior. • Many Americans disapproved of flappers’ free manners as well as the departure from traditional morals that they represented. Family Patterns Began to Change • Number of divorces per year more than doubled between 1914 & 1929 • Margaret Sanger coined the term “birth control” and opened the country’s first family planning clinic (arrested and jailed) – Distributing birth control info was illegal in every state, but Sanger was dedicated to altering those laws – Founded what became the nation’s leading family planning organization – Planned Parenthood Federation of America Mass Media Shape American Popular Culture • Popular culture is the culture of ordinary people and includes their music, art, literature, and entertainment • Shaped by industries that spread info and ideas, especially mass media – means of communication that reaches a large audience Print Media Bring Popular Culture to a National Audience • During the 1920s, the amount of print material expanded enormously • Americans were buying more than 200 million copies a year of popular national magazines – – – – Saturday Evening Post Ladies’ Home Journal Reader’s Digest Time • As newspaper and magazine circulation increased, more and more people read the same stories, events, ideas, and fashions Radio Gives Popular Culture a Voice • Radio unified the nation - featured news, sports, ads, soaps, & other shows • • • First radio broadcast was KDKA in Pittsburgh National Broadcasting Co. 1st national network Some shows like Amos ‘n Andy became so popular that people refused to answer their phones during the weekly broadcast Motion Pictures Create Movie Stars and Fans • After WWI, people flocked to movie theaters to escape the problems of postwar recession Movies promoted common values and created trends • – • In 1929, weekly attendance rose from 50 million to 90 million – ticket sales rose from $301 million to $721 million! 1st sound film – 1927 Automobiles Reshape American Life • By making cars affordable, automaker Henry Ford changed the way Americans lived – Made travel to faraway places more enjoyable – Stimulated growth of suburbs – Ended the isolation of farmers – Created shopping centers – Criminals used drive-bys – Changed leisure activities – Shaped sexual behavior in the young “Tin Lizzy” was the most popular model Americans Begin to Buy Now, Pay Later • In the past, most Americans thought it was shameful to borrow money to buy consumer goods • By the 1920s, such thrift became old fashioned • Expansion of credit made it possible to buy now, pay later • Growth of installment buying allowed buyers to make a down payment then pay back the loan in monthly installments (i.e. car payments) • Buying on credit was so easy that many Americans began to think the good times would go on forever… The Roaring Twenties Visual Summary • Using pictures, magazine clippings, or drawings, create a visual collage showing how the popular trends of the 1920s have influenced your life today. Use at least five trends from the chapter. For each, write a sentence or two that compares the 1920s trend with a similar trend from today. New Trends Shaped Popular Culture in the 1920s Mass Media Section 28.4 Trend: Consumerism (Section 28.2 – pg. 354-355) •THEN: New advertisements were created to increase demand for all sorts of new products •People started to use credit so they could buy now, pay later •NOW: Credit card companies are huge! Businesses will pay millions for advertisements – especially for a Superbowl commercial Women’s Rights Section 28.5 The Jazz Age Section 28.6






