File - Kelly Wiggins Nursing Portfolio
advertisement
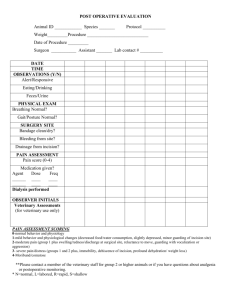
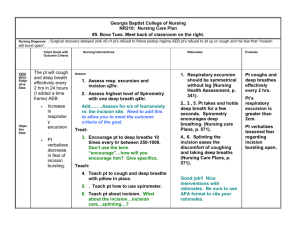
NURSING GRAND ROUNDS Kelly Wiggins 3/5/15 N421 INTRODUCTION TO PATIENT • S.G. is a 9 (almost 10) year old male admitted to CHKD with RLQ abdominal pain • He c/o nausea and vomiting for 4 days prior to admission, lethargic 7 days prior, and anorexia for 2 days prior • Diagnoses with ruptured appendix • admitted to CHKD on 1/24/15 and scheduled to undergo emergent appendectomy surgery • Other medical history-asthma HOSPITALIZATION COMPLICATIONS-TIME TABLE • Appendectomy 1/24/15 • Abcess develops • Drain placed 1/30/15 • Purulent drainage from appendectomy site 2/4/15 • Incision an drainage performed 2/5/15 RUPTURED APPENDIX • A ruptured appendix often results from Appendicitis • Appendicitis -acute inflammation of the appendix • Occurs when the lumen of appendix is obstructed • Infection results as bacteria invade the appendix wall • Mucosa secretes fluid, causing increase in internal pressure and a blood flow restriction • Symptoms-abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and anorexia • CT scan for diagnosis • Appendectomy as treatment APPENDECTOMY AND FURTHER COMPLICATIONS • An appendectomy, or a removal of his appendix, was done on 1/24/15. • One incision in RLQ • Abcess formed after appendectomy (RLQ) • Drainage tube placed 1/30/15 INCISION AND DRAINAGE • On 2/4/15, incision site draining large amounts of purulent fluid • Incision and drainage scheduled and performed on 2/5/15 • Throughout the day, the wound dressing remained dry and intact, with minimal drainage • S.G. developed post-op fever (39.3) that was gone by the end of the day CULTURE/CONCERNS THAT IMPACTED CARE •Hospitalized for 12 days •3 surgeries in that time •Not in usual setting •Regression •Not normal behavior according to mom DEVELOPMENTAL STAGE Piaget-Concrete Operational Stage (712 year olds) • -The child should be able to reason logically with concrete things and be able to add and subtract. He should understand conversation. • Patient met theoretical developmental stage norms DEVELOPMENTAL NORMS OF A 10 YEAR OLD • Likes mother and wants to please her • Demonstrates affection • Is successful in looking after own needs • Can use factitive words (think, know, believe) • Forms grammatically correct sentences • Can use telephone for practical purposes • Responds to advertising/television • Enjoys conversation • Slow height increase, rapid weight increase ASSESSMENT DATA Respiratory • wheezing bilaterally • dyspnea on exertion • Pt on O2 sat monitor Integumentary • incision RLQ • dressing clean, dry, intact GastroIntestinal • incision site RLQ covered with dressing • pain at incision site 3/10 Pain • 3/10-4/10 throughout day Musculoskeletal • needs assistance with ambulation & when being transferred • strength x1 in lower extremities • pt unable to stand up on own Psychosocial • mom only at bedside for 1 hour in 2 days • pt calls mom by her name and not “mom” • regression NURSING DIAGNOSIS 1 INFECTION Infection related to appendectomy as evidenced by • WBC count 15.5 (2/3/15) • Purulent drainage from appendectomy incision site • Abscess formation RLQ • Culture positive for E. coli and S. Pneumoniae bacteria • Medications-piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn) • Abscess developed in RLQ (Drained 2/5/5 via I&D • Post op day 12 for appendectomy, post op day 6 for drainage tube insertion of abscess, PICC line INTERVENTIONS • Assess WBC count, temperature daily • Administer Antibiotics as prescribed, on time • Promote increased fluid and nutrient intake • Assess incision site for drainage color, amount, odor • Teach patient about hand washing and proper hygeine EXPECTED OUTCOMES AND EVALUATION Expected Outcomes • Within one week the WBC count will reach normal limits, pt will learn ways to prevent infection spread, and incision site will be free of drainage. Evaluation • pt. WBC count down to 12.2 on 2/5 (down from 20.4 on 1/29/15, pt verbalized the importance of washing hands NURSING DIAGNOSIS 2 IMBALANCED NUTRITION: LESS THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS • Hx of nausea/vomiting 4 days prior to admission • Hx of anorexia for 2 days prior to admission • Weight drop from admission weight (admission weight 28.7 kg and weight on 2/5/15 25.9 kg) • Pt fatigued and weak (strength in extremities x1) • Decreased caloric consumption • Pt wouldn’t eat after TPN was discontinued • 5th percentile on the growth chart for weight on 2/5/15 INTERVENTIONS • Teach patient why he needs increased fluid and caloric consumption • Offer small frequent meals instead of large meals 3 times • Control pain prior to meal times • Monitor weight daily • Teach family to encourage him to eat • Find out food preferences EXPECTED OUTCOME AND EVALUATION • Expected outcomes-patient will eat ¾ of meals throughout the day and drink 1 full pediasure, progressing to eating full meal in 5 days. Evaluation • On 2/5/15 pt. ate two full meals, but didn’t drink any pediasure NURSING DIAGNOSIS 3 FATIGUE • Related to decreased caloric consumption • History of lethargy, anorexia, and nausea/vomiting before admission • Pt complaint of nausea when eating, not eating full meals or drinking pediasure as ordered • RBC count 3.27 (2/3/15) Hgb 9.4 (2/3/15) Hct (28.7%) • Anemia INTERVENTIONS • Encourage proper rest, no distractions, calm environment • Encourage proper caloric intake and consumption of meals and pediasure • Assess fatigue level before performing activities that are not critical • Allow patient to take his time with ambulation, repositioning-don’t make him feel rushed EXPECTED OUTCOME AND EVALUATION • Patient will verbalize that he has more energy and is less fatigued after consuming 3 meals/pediasure and resting quietly in bed Evaluation • Patient had 2 full meals, no physical activity throughout the day, is still very fatigued NURSING DIAGNOSIS 4 ACUTE PAIN Related to abdominal surgery (appendectomy and incision & drainage) • Reports pain 4/10 consistently throughout day at incision site • Facial grimacing when anyone goes near dressing/incision site • Acetaminophen/hydrocodone po q6h prn • Morphine IV drip INTERVENTIONS • Assess pain q4h using pain scale • Administer pain meds before pain becomes unbearable and assess for effectiveness (30 minutes after for Acetaminophen-hydrocodone) • Determine any alleviating/worsening factors affecting his pain EXPECTED OUTCOMES AND EVALUATION • Patient will report pain <3/10 on pain scale throughout the day and will ask for prn pain meds before pain > 5/10 Evaluation • Pain stayed around a 4/10 throughout day, pt verbalized when he was in pain and needed prn meds, but said 4/10 was tolerable for him NURSING DIAGNOSIS 5 KNOWLEDGE DEFICIENT-PARENT • Patient has hx of asthma, but mother continues to smoke around him • Mother not at bedside for more than 2 hours • She didn’t know what kind of surgery he had that morning (I&D) • Mother didn’t know/understand why fluid and caloric intake was so important INTERVENTIONS • Teach mother about patients condition • Allow her to ask questions and be receptive to them • Do not judge mother for knowledge/lack of knowledge, she needs to feel comfortable when discussing the patient • Carefully explain everything being done to the patient while its being done so she can see it EXPECTED OUTCOME • Mother will take active participation in care of patient and learn about his hospitalization, asking questions when need be • Mother will be able to verbalize back to nurse the importance of her son intaking the proper amount of fluid/nutrients • Evaluation • Mother left bedside after brief interaction with patient-said she now understands the reason for increased caloric demand/necessity TYING IT ALL TOGETHER Imbalanced Nutrition Infection Fatigue Acute Pain Knowledge Deficit CARE GIVEN • Nutritional support- TPN post-op (DC’d), Pediasure • Medications - Piperacillin-tazobactam, Acetaminophen-Hydrocodine, Morphine, Zofran • Play therapy TEACHING AND DISCHARGE PLANNING • Patient teaching needs • Dressing and incision site • Fluid and caloric consumption • Infection control • Parent teaching needs • Information about patient hospitalization • Caring for patient at home • Encouraging increased fluid and caloric intake • Play therapy Discharge Planning • Patient will need to complete antibiotics prior to discharge (IV) • Mother should monitor for signs of worsening infection once discharged • Monitor for further abscess formation • Instruction of caring for incision site prior to discharge NURSING RESEARCH • The use of non-pharmacological methods for children’s postoperative pain relief • Examined nurses use of non-pharmacological methods for school-aged children’s post op pain relief • Surveyed 134 RN’s in Singapore using questionnaires • Results showed that methods like relaxation techniques and breathing techniques were used most often, with massage and thermal regulation being used least often • Only 58% reported frequently using preparatory information, or telling the patient what to expect before doing any procedure SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION • S.G. 9 year old patient with ruptured appendix • Appendectomy -> abscess -> incision and drainage • Developmental considerations • Concept map discussion with expected outcomes and evaluation • Teaching and discharge planning • Research article QUESTIONS? REFERENCES • Hockenberry, M. J., & Wilson, D. (2011). Wong's nursing care of infants and children (9th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby/Elsevier. • He, H., Lee, T., Sinnappan, R., Vehvilainen-Julkunen, K., Polkki, T., & Ang, E. (2011). Use of nonpharmacological methods in children's postoperative pain relief: Singapore nurses' perspectives. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing, 16(1), 27-38. • Ignatavicius, D. D. (2011). Medical-surgical nursing: patient-centered collaborative care(7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Saunders/Elsevier.