Emotion - Unit 5

Agenda – Wednesday, April 1
st
M&E Reading Quiz
Finish Pink article
Begin facial expressions and emotion theories notes
Homework:
Exam #4 MOVED TO TUESDAY
Thought Hive Due by midnight on Friday,
April 3 rd
Agenda – Thursday, April 2nd
Facial expressions
Emotional theories notes
Can we detect a liar?
3 Volunteers will try to lie to the class.
They can either take or not take a dollar from an envelope & must successfully lie to us to keep the dollar & gain candy(Extrinsic
Motivators!)
They will enter the class one at a time & must answer any (reasonable) question that we ask of them to help us discern if they are lying or not.
The class will have 3 minutes to determine if they are lying or not
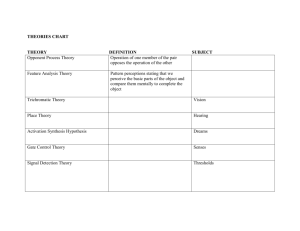
Facial Expression of Emotion
Paul Ekman had people from different cultures identify various facial expressions
& found they all responded similarly.
Ekman had the Fore Tribe in New Guinea match up photographs of facial expressions to events in stories. Same results as first study.
Most Facial Expressions are universal indicators of emotion.
Facial Expressions
Without using your notes, attempt to guess which facial expression is portrayed in each of the four images
Facial Expressions
If someone smiles because everyone around them smiles, and then they feel happy…what theory is this?
Facial Expressions
If someone scowls and tells themselves the situation they are in is stupid and beneath them, what theory is this?
Facial Expressions
If someone smiles and feels overwhelmingly happy at the same time, what theory is this?
Agenda – Monday, April 6 th
Finish theories of emotion
Practice terms and examples for test
Homework:
Test #4 (Cognition + M/E) TUESDAY
Disorders reading quiz THURSDAY
AP Countdown: 20 school days until test!
Emotions & the Body
The Autonomic
Nervous System
Sympathetic
Nervous System
(Speeds up body)
Parasympathetic
Nervous System
(Slows Down body)
The Brain
Right Hemisphere
Responsible for the
Identification of
Emotions
Limbic System (Amygdala)
Recognizes facial expressions and the appropriate emotion associated with that expression.
*Emotions alter the functioning of the ANS.
*Polygraph Tests only measure changes in the ANS (Not valid!)
17
James-Lange
Theory of Emotion
Physiological arousal:
Stimulus: Emotion: trembling snake fear increased heart rate
A stimulus prompts physiological arousal and THEN we experience Emotion
Ex. We feel sad because we cry.
Ex. We feel happy because we smile.
Problems:
1) Some Emotions have same physiological response.
(Ex. Fear, Anger, & Sexual Arousal all Similar)
2) People can experience arousal w/o experiencing emotion.
(Runners do not always fear what they are running away from)
3) Physiological responses happen to slow to cause emotion.
4) What about people with spinal cord injuries?
Cannon-Bard
Theory of Emotion
Stimulus: snake
Physiological arousal: trembling increased heart rate
Emotion: fear
The experience of emotion happens at the SAME TIME that physiological arousal happens.
One does NOT CAUSE the other.
Problems:
Despite feeling fear and physiological arousal at the same time, we may not know what we are afraid of
Two-Factor
(Schachter-Singer)
Theory of Emotion
Stimulus:
Snake
Physiological arousal: trembling increased heart rate
Cognitive interpretation:
“A snake is on the loose!”
Emotion fear
Emotions are the combination of physical arousal & a cognitive label. Emotion comes AFTER the combo of two other events
When you are aroused, you look to your environment for an explanation of the arousal.
(If aroused while in an angry mob of protestors, you might label your arousal
“Anger”)
(If aroused at a concert, you might label your arousal “Excitement)
Facial Expressions
You are walking down a dark alley late at night. You hear footsteps behind you and you begin to tremble, your heart beats faster, and your breathing deepens. Due to these physiological changes, your body prepares for a fearful situation. You then experience fear.
Answer: James-Lange (you label the emotion AFTER the physiological changes occur)
Facial Expressions
You are walking down a dark alley late at night. You hear footsteps behind you and you begin to tremble, your heart beats faster, and your breathing deepens. At the same time as these physiological changes occur, you also experience the emotion of fear.
Answer: Cannon-Bard (The emotion and physiological changes happen at the same time)
Facial Expressions
You are walking down a dark alley late at night. You hear footsteps behind you and you begin to tremble, your heart beats faster, and your breathing deepens. Upon noticing this arousal you realize that it comes from the fact that you are walking down a dark alley by yourself. This behavior is dangerous and therefore you feel the emotion of fear.
Answer: Two Factor (Your cognitive awareness of the setting and the physiological changes result in an emotional awareness)