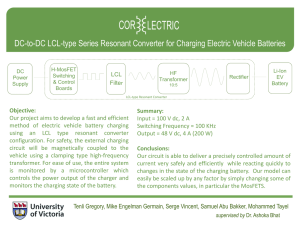
The (Very Near) Future of
Electric Transportation
Utility Challenges and
Opportunities
2009 APPA National Conference
June 16th, 2009
Mark Duvall
The Electric Power Research Institute
RD&D consortium for the electricity
industry founded in 1973
• Independent, unbiased, tax-exempt
collaborative research organization
• 460 participants in over 40
countries
• Major offices in Palo Alto, CA;
Charlotte, NC and Knoxville, TN
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
2
Plug-In Vehicles are Coming
Chevrolet
Dodge
Cadillac
Chrysler
Ford
BYD
BMW
Miles
Mercedes
Nissan
Saturn
Mitsubishi
Ford
Smart
Toyota
Tesla
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
3
PHEV Development Timeline
2008
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
Annual New Plug-In Vehicle Sales
Annual Sales (thousands)
Cumulative Sales (thousands)
18,000
16,000
14,000
3,000
12,000
2,500
10,000
2,000
8,000
1,500
6,000
1,000
4,000
500
2,000
0
20
09
20
10
20
11
20
12
20
13
20
14
20
15
20
16
20
17
20
18
20
19
20
20
20
21
20
22
20
23
20
24
20
25
20
26
20
27
20
28
20
29
20
30
0
Other OEM
PHEVs, EVs
Enter Market
2006
3,500
Cumulative Plug-In Vehicle Sales
4,000
First Announcements
of Production-Intent
PHEV Programs
1st PHEV Introduction
2010
Production Ramp Up
2012
4
2014
Launch of 1st
Gen 2 Programs
2016
Utility Challenges and Opportunities
Getting Ready
Opportunities
• Beneficial electrification
• Cost-effective emissions
reductions
– CO2
– Criteria emissions
• ‘New’ customers on existing
assets
• New potential business models
• Improve economics,
environment of your
communities
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
Challenges
• Understand customer needs
• Understand and minimize
system impacts
• Near-term rollout (2010) vs.
long-term planning
5
Plug-In Vehicles
Customers
Economics
Charging
Infrastructure
PHEV Development Timeline
2008
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
Annual New Plug-In Vehicle Sales
Annual Sales (thousands)
Cumulative Sales (thousands)
18,000
16,000
14,000
3,000
12,000
2,500
10,000
2,000
8,000
1,500
6,000
1,000
4,000
500
2,000
0
20
09
20
10
20
11
20
12
20
13
20
14
20
15
20
16
20
17
20
18
20
19
20
20
20
21
20
22
20
23
20
24
20
25
20
26
20
27
20
28
20
29
20
30
0
Other OEM
PHEVs, EVs
Enter Market
2006
3,500
Cumulative Plug-In Vehicle Sales
4,000
First Announcements
of Production-Intent
PHEV Programs
1st PHEV Introduction
2010
Production Ramp Up
2012
7
2014
Launch of 1st
Gen 2 Programs
2016
PHEV Development Timeline
2008
Annual New Plug-In Vehicle Sales
Annual Sales (thousands)
Cumulative Sales (thousands)
18,000
16,000
14,000
3,000
12,000
2,500
10,000
2,000
8,000
1,500
6,000
1,000
4,000
500
2,000
0
20
09
20
10
20
11
20
12
20
13
20
14
20
15
20
16
20
17
20
18
20
19
20
20
20
21
20
22
20
23
20
24
20
25
20
26
20
27
20
28
20
29
20
30
0
Other OEM
PHEVs, EVs
Enter Market
2006
3,500
Cumulative Plug-In Vehicle Sales
4,000
First Announcements
of Production-Intent
PHEV Programs
1st PHEV Introduction
2010
Production Ramp Up
2012
Launch of 1st
Gen 2 Programs
2014
2016
Production Implementation of
Smart Charging and
AMI Integration
Efficient
Building
Systems
Utility
Communications
Internet
Consumer Portal
& Building EMS
Auto – Utility
Collaborations
Finalize
Finalize
Connector Communications
(SAE J1772)
(SAE J2836)
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
8
Begin Smart
Charging
Development
Dynamic
Systems
Control
Distribution
Operations
Advanced
Metering
Renewables
PV
Control
Interface
Plug-In Hybrids
Data
Management
Distributed
Generation
& Storage
Smart
End-Use
Devices
Environmental Impact of Electric
Transportation
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
600
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Reductions (million metric tons)
• Results of detailed electric
sector and air quality
modeling
• ET creates definitive wellto-wheels CO2 reduction
• U.S. Potential:
400-500 million metric ton
annual (on-road)
100+ million mton (nonroad)
• ‘Credit’ for these reductions
still undetermined
• Nationwide improvement in
air quality—all gen sources
500
400
300
200
100
0
2010
2015
Low PHEV Share
2020
2025
2030
Medium PHEV Share
2035
2040
2045
2050
High PHEV Share
Annual Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
From PHEV Adoption
9
Community Economic Benefits
• Study of Cleveland Metro
area
– 2.9M residents
• EV adoption:
– Increases electricity
consumption
– increases household
income
– 6k – 10k jobs/yr
created
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
Electricity
0.090/kWh
Electricity
0.093/kWh
Gas
2.51/gal
Gas
3.51/gal
Reduced Petroleum
Demand
-1,010.2
-1,413.0
Increased Electricity
Demand
266.9
275.8
Increased HH Income
743.3
1,137.2
Reduced Petroleum
Demand
-84.9
-121.8
Increased Electricity
Demand
23.0
23.7
Increased HH Income
62.0
98.1
2020 Impact
Light Duty Vehicles
Heavy Duty Vehicles
10
GM/EPRI/Utility Collaboration
BC Hydro
Snohomish County PUD No. 1
Seattle City Light
Avista Corp.
Portland General Electric
PacifiCorp
Manitoba Hydro
Hydro-Québec
NY ISO
Hydro One Central Hudson G&E
Northeast Utilities
Consumers Energy
Rochester G&E United Illuminating
Dairyland Power We Energies
NYPA ConEd
EnWin
Madison G&E DTE
PSEG
PJM
Nebraska Public Power Dist.
Exelon
FirstEnergy Constellation Energy
Sacramento Municipal UD
Lincoln Electric
Pepco Holdings, Inc.
AEP
Hetch Hetchy Water and Power
Hoosier
Dominion Resources
Tri-State G&T
Great Plains Energy
Pacific Gas & Electric
Ameren
Duke Energy
Services
Southern California Edison
Progress Energy
Salt River Project
Tennessee Valley Auth.
Arkansas Electric Coop
San Diego Gas & Electric
Great River Energy
Southern Company
Austin Energy
Golden Valley Electric Assn.
CenterPoint Energy
CPS Energy
Hawaiian Electric Co.
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
12
EUROPE
Iberdrola, S.A.
Components of Grid Integration
AMI Path
Plug-In Vehicle
• Utility – Auto industry
collaboration
• Standardize interface
vehicle-to-grid
• Common
• Open systems
Standard
Interface
Back Office
Systems
Non-AMI Path
Mainframe
Smart Charging Back End
Energy Management, Cust ID, Billing
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
13
PHEV ‘Trouble Truck’ Program
• Migrate PHEV technology to high-volume applications
• Utility fleets act as early adopters
• Federal stimulus proposal
– 328 vehicles to utility and public fleets in large multiyear demonstration
• Production-ready design and facilities
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
14
Non-Road Electric Transportation
• Airports & Sea Ports
• Benefits
– Ground support equipment
• Saves customers money
– Ground power
• Beneficial electrification
– A/C & Refrigeration
• Reduce emissions
• Material handling
• Leverage existing
customer relationship
– Lift trucks
– Trucks & support vehicles
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
15
Distribution System Impacts
• Evaluate localized impacts of PHEVs
to utility distribution systems
• Participants – ConEd, AEP, HydroQuebec, Dominion, TVA, Southern,
NU, BC Hydro, SRP, Duke
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
11000
10000
9000
8000
10000-11000
9000-10000
8000-9000
7000-8000
6000-7000
5000-6000
4000-5000
3000-4000
2000-3000
1000-2000
0-1000
7000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
16
Nov
Sep
Jul
May
Mar
23
Jan
17
19
21
13
Hour
15
9
11
kW
6000
5
• Plug-in vehicle type
and range
• PEV market share and
distribution
• Charge profile and
power level
• Charger behavior
7
Thermal Loading
Losses
Voltage
Imbalance
Harmonics
Protection System
Impacts
• Advanced Metering
• EE devices
Peak - Jan and July and August
Peak Period @ July/Aug - 1pm - 8pm
Peak Period @ Jan - 8am - 11am & 5pm-9pm
Peak - 10.4MW @ July 27th, 2007 @ 5pm
Total Loading on Feeder Under Study (2007) kW
1
•
•
•
•
•
•
Plug-In Characteristics
3
Distribution Impacts
Month
Plug-in Vehicle Energy Consumption
CHEVY VOLT
PLASMA TV
Extended Range Electric Vehicle
Annual
Energy
623
kWh
SET TOP BOX
Annual Energy Consumption
Annual
Energy
= 2,500 kWh
263
kWh
~ 3 PLASMA TVs
and SET TOP BOXES
Annual Energy Consumption
= 886 kWh
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
17
Clarifying Infrastructure and
Charging Requirements
Utility Infrastructure Checklist
Single conductive connector
standard
• Bi-directional communication
standardized on both grid and
vehicle sides
• Develop and validate
interoperable applications for
smart charging into home
infrastructure
• Understand and support
municipal and customer needs
for public infrastructure
• Facilitate easy adoption—meet
each vehicle owner’s own
infrastructure needs.
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
Charging Requirements
Type
Power Level Vehicles
Level 1
120 VAC
15-20A circuit
1.2 – 2.0 kW PHEVs
(10-20 mi
range)
Level 2
208-240 VAC
2.5 – 17 kW
15-40A circuit
2.5 – 7.7 kW PHEVs,
EREVs,
some EVs
50-100A circuit
8 – 17 kW
EVs
DC-DC
20 – 250kW
Fast
Charging –
EVs
18
Distribution System Analysis
Smart Charging is a Key Technology to Reduce Impacts
July 27th 2007 24 hr: Total Loading for the Feeder Under Study
12000
Total Loading at Substation (KW)
11000
10000
9000
8000
off-peak load
7000
off-peak load
6000
5000
Base Load Scenario
4000
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Hours
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
19
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Distribution System Analysis
Smart Charging is a Key Technology to Reduce Impacts
July 27th 2007 24 hr: Total Loading for the Feeder Under Study
12000
Total Loading at Substation (KW)
11000
10000
9000
8000
off-peak load
7000
off-peak load
6000
Base Load Scenario
5000
PHEV Case 1:- (240V, 12A) Charging @6pm Penetration=10%
4000
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Hours
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
20
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Distribution System Analysis
Smart Charging is a Key Technology to Reduce Impacts
July 27th 2007 24 hr: Total Loading for the Feeder Under Study
12000
Total Loading at Substation (KW)
11000
10000
9000
8000
off-peak load
7000
off-peak load
6000
Base Load Scenario
5000
PHEV Case 1:- (240V, 12A) Charging @6pm Penetration=10%
PHEV Case 2:- (240V, 12A) Charging @9pm Penetration=10%
4000
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Hours
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
21
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Distribution System Analysis
Smart Charging is a Key Technology to Reduce Impacts
July 27th 2007 24 hr: Total Loading for the Feeder Under Study
12000
Total Loading at Substation (KW)
11000
10000
9000
8000
off-peak load
7000
off-peak load
6000
Base Load Scenario
5000
PHEV Case 3:- (240V, 12A) Diversified Charging @9pm-1am Penetration=10%
4000
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Hours
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
22
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Charging Infrastructure
• Residential – majority of units
– Seamless installations for
homeowners
– Permits, electricians,
inspections
– Rates and
• Workplace or Retail
– Commercial/Industrial
customers
• Public Charging
– Support municipalities
– Very expensive
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
23
Public
Workplace
or Retail
Residential
Going Forward – Getting Ready
• Create internal team—fleet, system planning, customer
service, etc
– Emphasis on planning and education/training
• Understand community wants/needs
– City governments, stakeholders
– Support infrastructure planning
• EPRI supporting information (through TVA)
–
–
–
–
–
Public outreach and education materials
OEM collaborative and vehicle demo programs
Infrastructure planning information and tools
Fleet adoption info
Grid impacts and environmental analyses
• Develop a high-level plan—but pace the implementation
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
24
Plug-In Vehicles as Distributed Energy Resources
• Definitions
– V2G – bidirectional transient
power & ancilliary services
– V2H – premise peak shaving
and DR
– Smart charging – load shaping,
DR, etc.
• Whether or not true V2G is
realized, vehicles will eventually
be aggregated for grid services
–
–
–
–
3rd party DR
Grid regulation, even if one-way
3rd party smart charging
Renewables integration
Point of
Connection
AREA
EPS
INV PEV
Point of
Common
Coupling
(PCC)
© 2009 Electric Power Research Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
26
End-use
Load
Local
EPS
© 2009
Image
from Electric
NASA Power
VisibleResearch
Earth Institute, Inc. All rights reserved.
27