CH 250 Block 3 2012 Exam #1 (100 points) Name: Date: Honor
advertisement

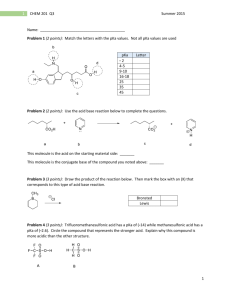
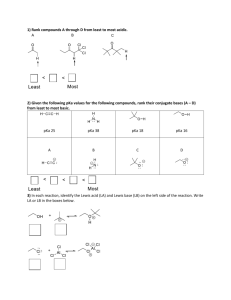
CH 250 Block 3 2012 Exam #1 (100 points) Name: Date: Honor Code: “Dans les champs de l'observation le hasard ne favorise que les esprits préparés.” “In the fields of observation chance favors only the prepared mind.” Louis Pasteur, Lecture, University of Lille (7 December 1854) The Rules: You have until noon to complete the exam unless you have provided me with documentation for extra time. When you are done with your exam, please place it in the box outside my office. In fairness to all, anyone who turns in an exam late will receive a grade of zero! You may use your model kits. A periodic table and pKa table are attached at the end of the exam packet. No notes or textbook allowed. This exam is an individual assessment—no teamwork, paid consultants, etc. You may take the exam in Olin 1 or the Olin fishbowl. Be sure to read the instructions for each question. It may be helpful to skim the entire exam and solve the easier questions first. 1 1) (3 points) Of the two vitamins, A and C, one is hydrophilic and water soluble and the other is hydrophobic and fat soluble. Which do you think is which? Explain your answer. Vitamin A Vitamin C 2) (12 points) Vitamin C is also known as ascorbic acid The pKas for the two most acidic protons on vitamin C have been reported: pKa 1 = 4.10 pKa 2 = 11.8 a) Approximately how much more acidic is the most acidic vs. second most acidic proton? b) Evaluate the structure of ascorbic acid and predict which proton is most acidic. Explain your reasoning. 2 c) Draw a mechanism for deprotonation of ascorbic acid with sodium hydroxide. Is sodium hydroxide an appropriate base for this reaction? Explain. 3) (10 points) The structure of caffeine is shown below. a) Draw all lone pair electrons b) Identify hybridization of the indicated atoms c) Draw 3 significant resonance structures d) Are the electrons on the starred N atom (*) localized or delocalized? Explain. 3 4) (14 points) Ethylene (CH2=CH2),a gas produced by fruits, accelerates their ripening process. a) Draw the atomic orbital diagrams for carbon and hydrogen. The structures of acetylene, ethylene, and ethane are described in Table 1.2. Can the structure of ethylene and the properties shown in Table 1.2 be adequately explained by a simple combination of the atomic orbitals? Explain. b) Draw a model of ethylene using hybridized atomic orbitals. Draw all orbitals (on C and H) and electrons involved in bonding and indicate which orbitals are involved in sigma bonds and pi bonds. 4 c) Explain whether the hybridization model from part b better explains the structure of ethylene than the atomic orbital model from part a. d) The boiling point of ethylene is -104 °C at atmospheric pressure. The boiling point of formaldehyde (CH2O) is -19 °C at atmospheric pressure. Explain this dramatic difference in physical properties. e) Using your pKa table, compare the acidities of ethylene and acetylene. Propose an explanation for the difference in acidity. 5 5) (10 points) An energy diagram for the conformational analysis of n-butane is shown below. Build a model of butane and look down the C2-C3 bond. a) Label the energy diagram above with Newman projections of the conformations corresponding to all of the energy minima and maxima observed during a 360° rotation about the C2-C3 bond. b) Label the anti, gauche, and eclipsed conformations. 6 6) (14 points) (a) Complete a qualitative diagram of potential energy vs. dihedral angle for rotation about the C2-C3 bond of 3-methylpentane (in analogy to the energy diagram in problem 5 for butane). Do not worry about assigning numerical values for the y axis. Rotation of C2-C3 Bond 180° 120 ° 60 ° 0° 60 ° 120◦ 180 ° (b) Label each maximum and minimum on your diagram with a corresponding Newman projection of 3-methylpentane. (c) How does the energy diagram for 3-methylpentane differ from that of butane? (d) Is 3-methylpentane chiral? Explain. 7) (3 points) Propylene is produced by cracking petroleum and is a useful precursor in the production of many polymers. Propylene has one constitutional isomer. Draw that isomer and provide its systematic (IUPAC) name. 7 8) (8 points) (R)-Limonene is found in many citrus fruits, including lemons and oranges: For each compound below, determine whether it is (R)-limonene or its enantiomer, (S)-limonene: 9) (10 points) Hydrogenation of (R)-Limonene produces the cis and trans isomers (A and B) shown below. Draw the most stable chair conformation of each compound (A and B). Explain. 8 10) (8 points) Exelon is a drug for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. (a) Assign the configuration of the chirality center in Exelon using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system. Show your work. (b) Draw the structure of the major product that would be formed by protonation of Exelon with HCl. Explain your answer. 9 11) (8 points) Octyl methoxycinnamate is an ingredient in some sunscreens and lip balms (including Olay Protective Renewal Lotion SPF 15, as posted by Audra on our PROWL blog for Day 2). Evaluate the structure and explain why this structure is appropriate for topical applications (e.g. lotions) but would not be an appropriate structure for orally dosed medicines. Extra credit (4 points) Explain (one paragraph) why the FDA approval of Nexium and the subsequent marketing campaign around this drug was controversial. “I've never lost a game I just ran out of time.” ― Michael Jordan, For the Love of the Game 10 11