key Cryptography
advertisement

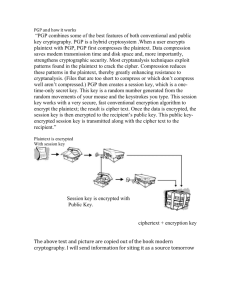
Dr. Susan Al Naqshbandi S.alNaqshabandi@uvt.nl The word “Cryptography” is derived from Greek words κρυπτός kryptós meaning “hidden” and γράφω gráfo meaning “to write”. Cryptography is the science of using mathematics to encrypt and decrypt data. Cryptography enables you to store sensitive information or transmit it across insecure networks (like the Internet) so that it cannot be read by anyone except the intended recipient. Cryptography is the practice and study of hiding information. In other words, Cryptography is a method to enlock and unlock a document using a personal key. Encryption Decryption Key The process of disguising a message in such a way as to hide its substance is encryption. An encrypted message is cipher text. The process of turning cipher text back into plaintext is decryption. Plain Text Encryption Cipher Text Decryption Plain Text A key is a value that works with a cryptographic algorithm to produce a specific cipher text. Keys are basically really, really, really big numbers. Key size is measured in bits; In public key cryptography, the bigger the key, the more secure the cipher text. Based on the type of key used, Cryptography is broadly categorized into: Symmetric Key Cryptography (Private, Conventional) Asymmetric Key Cryptography(Public) For a sender and recipient to communicate securely using conventional encryption, they must agree upon a key and keep it secret between themselves. Caesar Cipher: An extremely simple example of conventional cryptography is a substitution cipher. A substitution cipher substitutes one piece of information for another. Suppose you have a message as: “I HAVE SENT YOU THREE EUROS” with a key = 3. Assign Numerical equivalent to each letter: A B C D E F G H I J K L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 N O P Q R S T U V W X Y M Z 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Now add your key to your message from assigned numerical values from table Key T =19 + 3 = 22 = W (Converted letter) Entire converted message would appear as: “I HAVE SENT YOU THREE EUROES” Encrypted Message “L KDYH VHQW BRX WKUHH HXURHV” Public key cryptography is an asymmetric scheme that uses a pair of keys for encryption: a public key, which encrypts data, and a corresponding private, or secret key for decryption. PRIVATE KEYS 1)Only one key is used for encryption & decryption. 2)Private keys are shared. 3)Known to only communicating parties. PUBLIC KEYS 1)Two keys are used, one for Encryption and another is used for decryption. 2)Public key pair is only generated, not shared. 3)One is publicly exposed & other is kept secret. A cryptographic algorithm, plus all possible keys and all the protocols that make it work comprise a cryptosystem. PGP is a cryptosystem. PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) What is PGP? PGP is an open source freely available software package for e-mail security. How PGP works PGP combines some of the best features of both conventional and public key cryptography. PGP is a hybrid cryptosystem. When a user encrypts plaintext with PGP, PGP first compresses the plaintext. Then creates a session key, which is a onetime-only secret key. This key is a random number generated from the random movements of your mouse and the keystrokes you type. This session key works with a very secure, fast conventional encryption algorithm to encrypt the plaintext; the result is cipher text. Once the data is encrypted, the session key is then encrypted to the recipient's public key. This public key-encrypted session key is transmitted along with the cipher text to the recipient. Decryption works in the reverse. The recipient's copy of PGP uses his or her private key to recover the temporary session key, which PGP then uses to decrypt the conventionally-encrypted cipher text. "There are two kinds of cryptography in this world: cryptography that will stop your kid sister from reading your files, and cryptography that will stop major governments from reading your files.” Cryptographic strength is measured in the time and resources it would require to recover the plaintext. The result of strong cryptography is cipher text that is very difficult to decipher without possession of the appropriate decoding tool. One would think, then, that strong cryptography would hold up rather well against even an extremely determined cryptanalyst. Who's really to say? No one has proven that the strongest encryption obtainable today will hold up under tomorrow's computing power. E-business dimensions are expanding day by day Its only cryptography which can provide immunity to those transactions which are likely to toll hundreds of billions of dollars per year. Thank You