Chapter 1 The Nature of Science
advertisement

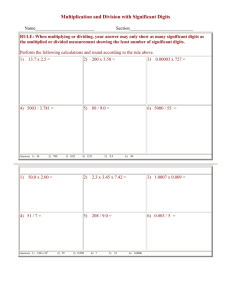
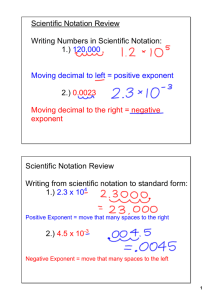
6th Please be in your seat ready to go when the bell rings We will start the quiz after a short review Chapter 1 The Nature of Science Chapter 1 Vocabulary Science Volume Technology Weight Scientific theory Scientific Notation Variable Precision Mass Accuracy What is the purpose of science? •To investigate questions •To support or refute a theory •To gain knowledge Science is a system of knowledge based on facts or principles Technology is the application of science to meet human needs Theories & Laws Theory A tested, possible explanation of a natural event. Law a summary of an observed natural event (a repeated observation about nature) *A theory must pass 3 tests: 1.A theory must explain observations simply & clearly 2. A theory must be repeatable 3. Scientists must be able to predict from a theory Qualitative vs. Quantitative Qualitative Quantitative Describes data using Describes data with words Quality numbers Quantity Ex. There are many Ex. There are 14 cars red cars in the parking lot in the parking lot The Scientific Method What is it used for? Who can use it? State the Question Form A Hypothesis Test the Hypothesis Observe/Collect Data Draw a Conclusion Experiments How many variables are in a typical experiment? How many variables can be tested at one time? The main parts of an experiment Independent Variable Dependent Variable (result) Control Determine the variables in the experiment A botanist is studying the affect of fertilizer on pea plants. She test 5 plants. She adds 6 oz of fertilizer to plant 1, 7 oz of fertilizer to plant 2, 8 oz to plant 3, 9 oz to plant 4 and no fertilizer to plant 5. She waters each of the plants with 200mL of water everyday for 2 weeks and places them in the sun for 3 hours each day. The Metric System The International System of Measurement (SI units) Metric Conversions K H D B D C M Practice Problems 550 mm = ________m 1.6 kg = ________g 2800mmol =________mol Organizing Data There are 3 main types of graphs: Bar Line Pie Scientific Notation A value written as a simple number multiplied by a power of 10. Shortcut: If you move the decimal right the exponent is negative If you move it to the left the exponent is positive Practice 800 000 000 m 0.0015 kg 60 200 L Using Scientific Notation When you multiply, you add the exponents When you divide, you subtract the exponents Significant Digits (Figures) The digits in a measurement that are known for certainty. 1.638 1638 1.6










![Questions for (3.3.3) Externalities in agriculture [True or False?] The](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009995147_1-f1de64b535b6f4b8fe06925685d00ca4-300x300.png)





