Human Body Unit 2: Integumentary System and Circulatory System
advertisement

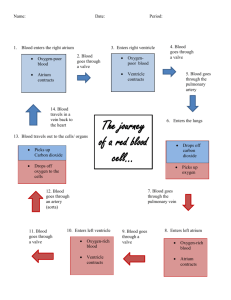
Human Body Unit 2: Integumentary System and Circulatory System Study Guide Name:________________________________________________________ Period:____ Date:_________ 1. What percentage of your body weight is made up of skin? 2. Name two key functions of the integumentary system. 3. Differentiate between the subcutaneous tissue, dermis, and epidermis. 4. What is the name of the protein that makes skin tough and gives it the ability to be waterproof? 5. What are most of your individual hairs made up of? 6. What produces individual hairs? 7. What’s the name of the pigment that ranges in color and primarily determines your hair color. 8. What is the main function of your nails? 9. Explain what causes acne. 10. What is sebum? 11. What causes skin cancer? 12. What are the two main systems within the circulatory system? 13. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 14. What is the function of the lymphatic system? 15. What are the key functions of the circulatory system? 16. What is the difference between a vein and an artery? 17. What is the name of the tiny blood vessels that allow the exchange of gases, nutrients, hormones, and other molecules in the blood? 18. Why are blood vessels necessary for the circulatory system? 19. What is the name of the liquid portion of the blood? 20. Which type of cell in your blood is responsible for helping your body fight disease? 21. What is the name of the protein inside of red blood cells that binds oxygen in the lungs, allowing red blood cells to carry oxygen and transport it to the tissues of the body? 22. What role do platelets play in your body? 23. Which organ provides the pumping action that is needed in order to exert pressure to move blood throughout the body? 24. What is gas exchange and where does it take place in your body? 25. Does the right atrium receive oxygenated or deoxygenated blood returning to the heart? 26. Does the left atrium receive oxygenated or deoxygenated blood returning to the heart? 27. Where does the left ventricle pump blood to? 28. Where does the left ventricle pump blood to? 29. Define blood pressure. 30. What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure? Which number goes on the top of the fraction? What about the bottom? 31. What is the more common name for hypertension? 32. Name a few reasons why hypertension is dangerous. 33. What does a person’s pulse indicate? 34. Which artery did we take our pulse at? 35. What’s the difference between a stroke and a heart attack? 36. Why do heart attacks occur? Directions: In the pictures below, label the following terms: hair follicle, pore, lunula, hair papilla, nail bed, dermis, free edge of nail, melanocyte, sebaceous gland, body of nail, hair root, subcutaneous adipose tissue (label this twice in two separate images), lunula, epidermis, hair root, eponychium, root of nail. Directions: Read over the names and definitions of the parts of the heart that you are required to know for the test below. Write the letter that proceeds each term in the corresponding blank in the picture. Not all blanks will be used. A. Right atrium - the right upper chamber of the heart. It receives oxygen-poor blood from the body through the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava. B. Right ventricle - the right lower chamber of the heart. It pumps the blood into the pulmonary artery. C. Septum - the muscular wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart. D. Superior vena cava - a large vein that carries oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium from the upper parts of the body. E. Aorta - the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body. F. Inferior vena cava - a large vein (a blood vessel carrying blood to the heart) that carries oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium from the lower half of the body. G. Left atrium - the left upper chamber of the heart. It receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein. H. Left ventricle - the left lower chamber of the heart. It pumps the blood through the aortic valve into the aorta. I. Pulmonary artery - the blood vessel that carries oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. J. Pulmonary vein - the blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.