DC Motors Key
advertisement

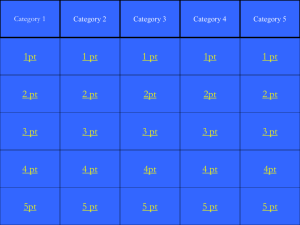
DC Motors – Summary Questions Group: __________ Names:______________________ 1. 2. (0.5pt) Motors are devices that convert _electrical_ energy into _mechanical_ energy. (0.5pt) The basic principle behind the simple DC motor is that wires that carry _current__ experience _forces (torques)_ when placed in regions of space that have _magnetic fields_ 3. (1pt) Only sections of wire that carry current in a direction _perpendicular_ to a magnetic field experience forces. 4. (2 pts) The speed at which the rotor of a motor spins depends on how many different factors (what are the factors and why/how do they affect the speed?) Current, magnetic field strenght and length of wire 5. (1pt) Which of the following chnages to a motor might decrease the speed at which it spins? C a. Using two magnets instead of one b. Using two batteries instead of one c. Using a rotor with only six loops instead of twelve 6. (1pt) Consider the motor built in class. Assume the magnetic field is oriented vertically so that it is directed into the magnet (towards the table). The current runs through the loop in a clockwise manner. What will be the direction of the force on the bottom section of the rotor? B a. Into the plane of the paper b. Out of the plan of the paper c. No force is experienced by the bottom 7. (1pt) Consider the motor in the previous question. What will happen to the direction that the motor spins if the bar magnet is flipped so that the direction of the magnetic field is reversed AND the battery leads are switched os that the direction of the current is reversed and why? The rotor will continue to spin in its initial direction 8. (1 pt) Two students build a DC motor during class one day. When stripping the wire, they don’t follow the directions exactly and strip both straight sections completely (top, bottom and sides). What will happen when they try to run their motor? Oscillates rather than spins 9. (2pts) Engineers often find that while increasing the value of a variable may be beneficial to a desired outcome, a critical point is often reached where increasing the value of that variable any further actually works against them. With the simple DC motor, the number of loops int eh rotor acts as such a variable. a. Explain why increasing the number of loops is initially beneficial. More effective L b. Explain why there is a limit to increasing the number of loops. In other words, why is it that at some point, increasing the number of loops does not increase the speed at which the motor spins? At a certain point the increase in mass (and therefore moment of inertial) will counter the the increase in Lorentz force 10. (2pts) A fellow student suggests making a square rotor instead of a circular one. She proposes that using a similiarly sized square rotor will actually allow the motor to spin faster. Do you agree with her? Why or why not? Square has some perpendicular current and some parallel current components – but will average out similar to a circle – however, the moment of inertia is different for a square. 11. (2pts) The directions for building the motor require one straight section of rotor to be stripped completely and the other straight section to be stripped on the top section only. A fellow student theorizes that in fact, both straight sections need to be stripped on the top only. a. Is the student correct? Would the motor work if stripped as he suggests? If stripped on same side, yes If not, why not? b. If so, why do you suppose the directions require one side to be stripped completely? Ease of lining up 12. (1pt) Explain how one of the other motors we saw on the YouTube videos works. 1