EEG Academic half-day 2009 part 1 and 2
advertisement

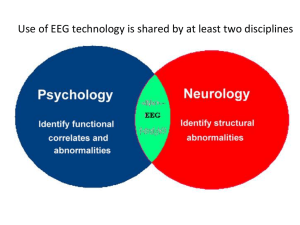
EEG For Neurology Residents 2009 Not exactly EEG, but… …things you need to know. 1. Epilepsy and driving. 2. Epilepsy and pregnancy OUTLINE I. What is an EEG and how is it recorded ? II. How do you read an EEG ? III. The use of EEG IV. Slideshow/Quiz PART I WHAT IS AN EEG AND HOW IS IT RECORDED? Recording procedure 20-30 minutes, relaxed patient Eyes opened/closed Photic stimulation, Hyperventilation +/- sleep +/- pain, noise PART II HOW DO YOU READ AN EEG ? Why do you need to know this? • Exams • Emergencies • To understand the reports An organized approach 1. Orient yourself. 2. Is there normal brain activity present or is it altered ? 3. Is there abnormal activity present ? 4. What is the state ? 5. Is it age – appropriate ? 6. Are there any artifacts present ? 1. ORIENT YOURSELF Montage (bipolar or referential) Time scale Sensitivity (amplitude, positive/negative) Other channels (EKG, EOG) F7, F8 2. Is there normal brain activity or is it altered? • Is the stuff that is supposed to be there actually there ? • Is there evidence of a structural lesion or a toxic/metabolic process that has altered the normal EEG background activity? Normal brain activity • Waves: Delta Theta Alpha Beta 1-3 Hz 4-7 Hz 8-12 Hz > 12 Hz • Posterior dominant alpha rhythm with eye closure. • Alpha rhythm ≠ alpha frequency • Low amplitude, frontal Beta activity. The typical EEG Normal deviations from normal (!) 1. 2. 3. 4. Drowsiness Sleep Age (young and old!) Activation procedures (a) Hyperventilation (b) Photic stimulation Background abnormalities • Slowing (theta or delta) • • • • • Focal or diffuse Bilaterally synchronous or not Rhythmic vs. irregular/polymorphic High vs. low amplitude Intermittent vs. continuous • Can be more subtle • Attenuation of amplitude • Asymmetry of alpha Etc… Focal slowing Generalized slowing Ebersole & Pedley Summary • Focal slowing = rule out structural lesion • Generalized rhythmic slowing = consider deep structural lesion or destructive process • Polymorphic generalized slowing = very nonspecific “Disturbance of the background activity” 3. Abnormal activity Is there any stuff there that should not be there at all ? Not simply alteration of the background Usually, we are asking if there is epileptic activity (interictal or ictal). Focal Inter-ictal activity • • • • • • • Spikes and sharp waves ! Phase reversal Recurrent and consistent With a field Followed by slow wave Asymmetrical Not explained by artifact Focal epileptic activity Focal epileptic activity Terminology “Potentially epileptic abnormality” “Epileptiform abnormality” Phase Reversal Non-epileptic phase reversal (normal background activity) Generalized Inter-ictal Activity Generalized spike and wave Ictal Activity (Seizures) • Electrographic lasts > 10 sec • Seizures not defined by single pattern; spikes, spike and wave, slowing, attenuation etc… • Rhythmic activity that changes with time Partial complex seizure with secondary generalization Neonatal seizure Neonatal seizure cont… 3 Hz spike and wave (from Ebersole and Pedley) Summary • Interictal epileptic activity = spikes and sharp waves • Ictal epileptic activity = evolving rhythmic activity 4. State • 4 Sleep stages, plus REM 1. Lose α, slow EOM, v-waves 2. Spindles, K-complex, v-waves 3. Delta < 50% 4. Delta > 50% REM: -looks normal (i.e. awake), need EOG, EMG etc… • Sleep onset • Most consider stage 1 sleep = drowsiness • But…some define sleep onset as appearance of vwaves, others as sleep spindles. Don’t Forget… 5. Age • Prior to birth, continuous evolution of EEG • Posterior-dominant rhythm by 6-12 months; alpha frequency by 4-8 years 6. Artifacts • EKG or pulse • Eye movement • Electrode • Muscle/movement • Electrical • Weird and wonderful Electrode artifact Eye Movements EKG Artifact Head movement artifact during a pseudoseizure So how do you read an EEG? “Plan and scan” Organized Approach Orient Normal Abnormal Age and State Artifacts Scanning Vertical Horizontal Scanning Focal slowing If all else fails… Describe what you see From Fisch and Spehlmann