Kin 304 Writing Assignment
advertisement

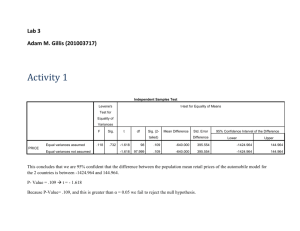
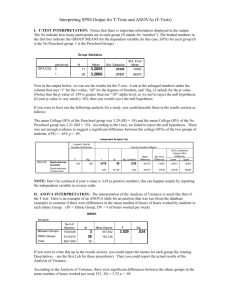
Kin 304 Writing Assignment: Writing the results section of a refereed journal paper Assignment In lab this week we will carry out all the analysis necessary for the assignment. You must take these results and write them up in the form of the Results section of a refereed journal article. Requirements: – – – Title page – Title, Name, Student number Text of the results section Tables and Figures each on separate pages after text (not inline with text) with captions (in bold font - tables at top, figures at bottom). Components of the Results Section Report the results without discussion. It is not enough just to include figures, you must describe the results. No need to justify form of analysis – this was done in the Methods section. Use tables and/or charts to illustrate the results. Do not repeat the same information in both a chart and a table – Space is at a premium. Do not repeat all of a table in the text. Components of the Results Section Always start with a table describing the sample. Include Means, Standard Deviations and sample sizes (Standard Errors of Means not necessary). Statistical analysis can often be indicated on this table. Then follow with tables or figures to illustrate the hypothesis testing Tables Tables should be able to stand alone. Table captions must give enough detail to stand alone. Not just: – Sample Descriptives If variable name abbreviations are used, the full name must be in a table footnote, or the table caption. Tables It is unnecessary and distracting to report digits if they have little scientific relevance. Your device can measure blood pressure to within 0.01 mmHg and your sample mean is 115.73 mmHg. How do you report the sample mean? – – As 115.73, as 115.7, or as 116 mmHg? Does a resolution smaller than 1 mmHg really matter? In contrast, a resolution to 0.001 units is essential for variables like pH or body density. Density converted to % Body Fat using Siri Equation % Body Fat = ((4.95/Density)-4.5)*100 Density gm/ml 1.030 1.035 1.040 1.045 1.050 1.055 1.060 1.065 1.070 1.075 1.080 1.085 %Body Fat 30.58252427 28.26086957 25.96153846 23.68421053 21.42857143 19.1943128 16.98113208 14.78873239 12.61682243 10.46511628 8.333333333 6.221198157 %Body Fat 30.6 28.3 26.0 23.7 21.4 19.2 17.0 14.8 12.6 10.5 8.3 6.2 Reporting the results of a t-test Group Statistics SAFAGR GRIPR SEX 1.0 2.0 1.0 2.0 N 20 23 20 23 Mean 25.801 21.355 52.310 35.304 Std. Deviation 1.9882 1.4569 7.8432 6.8536 Std. Error Mean .4446 .3038 1.7538 1.4291 Independent Samples Test Levene's Tes t for Equality of Variances F SAFAGR GRIPR Equal variances ass umed Equal variances not as sumed Equal variances ass umed Equal variances not as sumed 1.713 .525 Sig. .198 .473 t-tes t for Equality of Means t df Sig. (2-tailed) Mean Difference Std. Error Difference 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower Upper 8.437 41 .000 4.446 .5270 3.3816 5.5101 8.257 34.408 .000 4.446 .5385 3.3521 5.5397 7.589 41 .000 17.006 2.2407 12.4804 21.5309 7.517 38.101 .000 17.006 2.2623 12.4263 21.5850 Men are significantly (p<0.05) bigger than women in skinfold-adjusted forearm girth and grip strength Means and Standard Deviations of Skinfold-adjusted Arm Girth and Maximum Right Hand Grip Strength in Male (N=20) and Female (N=23) University Students Sex Skinfold-adjusted Arm Girth Maximum Right Hand Grip Strength Mean S.D. Sig Male 25.8 2.0 * Female 21.4 1.5 Male 52.3 7.8 Female 35.3 6.9 * * sig. diff. between male and female means, independent t-test d.f.=41, p<0.05 Tests of Between-Subjects Effects Dependent Variable: VO2MAX Between-Subjects Factors N AGE SEX 17.00 18.00 19.00 1.00 2.00 344 286 273 473 430 Source Corrected Model Intercept AGE SEX AGE * SEX Error Total Corrected Total Type III Sum of Squares 424.295 a 16946.730 3.032 403.923 .715 337.122 18407.560 761.417 df 5 1 2 1 2 897 903 902 Mean Square F 84.859 225.789 16946.730 45091.176 1.516 4.034 403.923 1074.742 .358 .952 .376 Sig. .000 .000 .018 .000 .386 a. R Squared = .557 (Adjusted R Squared = .555) Often no need to report statistical results in a table, just include description in the text: – In a two-way Analysis of Variance with VO2max as the dependent variable, both Age Group and Sex were found to be statistically significant factors (P<0.05) Charts Charts should be able to stand alone. Captions should provide enough detail. Do not refer to abbreviations only found in text. Either provide key in caption or footnote to table. Do not bunch up data in one corner of chart. Use Black and white only. Distinguish different data points for group using different shapes Figure 1: Plot of maximum grip strength versus skinfold-adjusted Forearm girth, showing correlation coefficients between variables for men (♂) and women (♀) separately and men and women combined (♂+ ♀) Figure should be able to stand alone with it’s caption. Must be in black and white. But make sure different symbols can still be distinguished