Ray Model of Light
advertisement
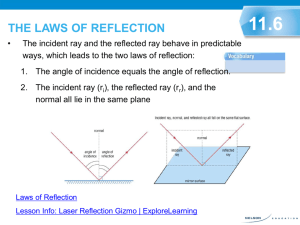
RAY MODEL OF LIGHT RAY MODEL Light tends to travel in straight lines. Light’s straight lines are represented by rays which show the direction that light travels after it leaves its source. Each ray ends with an arrow to indicate the direction of travel. If more rays reach your eye the brighter the object appears. Opaque Translucent Transparent Rays leaving the source and travelling toward an object, travel parallel to one another. The science of how light reflects and bends is called Geometric Optics RAY DIAGRAM RULES – PLANE MIRRORS 1. Plane Mirrors – any mirror that has a flat reflective surface 2. Ray diagrams MUST be drawn with a sharp pencil 3. Normal: dashed line drawn perpendicular to the mirror at the point of reflection. 4. Incident ray: light coming towards the mirror. 5. Reflected ray: light coming out from the mirror. incident ray (i) normal reflected ray (r) RAY DIAGRAM RULES – PLANE MIRRORS 6. Angle of Incidence ( i ) : the angle between the incidence ray and the normal. 7. Angle of Reflection: ( r ) : the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. incident ray (i) reflected ray (r) 8. Angle of incidence and angle of reflection are measured from the normal NOT from the mirror surface. 9. To find the image, extend the reflected rays behind the mirror using dashed lines PLANE MIRROR IMAGES Images are formed in the location where the reflected light rays cross. Therefore, when your eyes detect reflected light from a plane mirror your brain projects these light rays backwards in a straight line. Your brain thinks that there is a light source behind the mirror and that this is where the light rays originate. But the mirror is opaque so there is NOT a light source behind the mirror. This type of image is called a virtual image A virtual image is an image formed by light coming from an apparent light source behind the mirror. The reflected light rays from a plane mirror will never cross in front of the mirror. However if the reflected light rays are extended behind the mirror, the rays will appear to cross and the image is found here. WHERE THE IMAGE IS FORMED http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nrOg85VPQgw CHARACTERISTICS OF IMAGES (L.A.S.T/L.O.S.T.) Use the acronym LAST or LOST to describe the characteristics of all images found during the geometric optics unit. Location of Image •point where reflected rays actually cross or appear to cross object image Attitude of Image •image orientation compared to object: upright or inverted upright inverted Size of Image •comparison to the object – smaller, same, larger smaller same larger Type of Image Real - reflected rays cross in front [solid lines] Virtual - reflected rays appear to cross behind [dashed lines] real virtual Why do you see the light shining through the window? How is this effect created by light?