Presentation - Austin Community College
advertisement

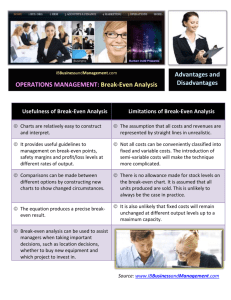
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT With Philip Soward LESSONS 2 AND 3 BUSINESS AND ITS CONTEXT (Material included from Management 8e by Schermerhorn and from Harvard Business Review, 2000 Sept-Oct and February 2004 articles by Kaplan and Norton on Strategy Maps) CHAPTER 6 • The Business Plan • Seizing an Opportunity Study Question 3: How does one start a new venture? Basic items that should be included in a business plan: – – – – – – – – – – – Executive summary Industry analysis Company description Product and services description Market description Marketing strategy Operations description Staffing description Financial projection Capital needs Milestones Study Question 3: How does one start a new venture? Questions that keep a new venture focused on its customers … – Who is your customer? – How will you reach key customer market segments? – What determines customer choices to buy or not buy your product/service? – Why is your product/service a compelling choice for the customer? – How will you price your product/service for the customer? – How much does it cost to make and deliver your product/service? – How much does it cost to attract a customer? – How much does it cost to support and retain a customer? THE BALANCED SCORECARD STRATEGY MAP • BY ROBERT S. KAPLAN AND DAVID P. NORTON • A WAY TO TIE TOGETHER ALL THE ASPECTS OF A COMPANY INTO A COHERENT FRAMEWORK BSC Strategy Map (adapted) & our Chapters Customer New Markets Perspective Ch 4 Customer Intimacy Product Leadership Operational Excellence, Ch 8 Financial Objectives: Ch 8 Revenue from new markets Customer Profitability: Product Profitability: Productivity Strategy: lower costs, high asset turnover: Example Company: Cases Coca Cola, all IBM Consulting Apple UPS, Dell, Walmart Key Internal Processes Marketing, Sales Marketing, Sales Innovation, R&D Supply Chain, Operations Human Capital: International Ch 12, Key Skills knowledge Marketing, Sales Engineering, Marketing Operations Information Capital: Ch 7 IT Laptop, mobile CRM CAD ERP Organization Capital: Ch 4 Culture World travellers Customer knowledge Scientists Efficiency Image of Company: Ch 3 Relationship with Society/Community and Public Relations with external Stakeholders Learning and Growth Perspective: CHAPTER 4 • COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE – 3 STANDARD STRATEGIES: • Operational Excellence • Customer Intimacy • Product Innovation – IN EACH CASE: • Can expand to New Markets • Must protect Company’s Image • BEING CUSTOMER-DRIVEN – Customer Relationship Management • ORGANIZATION CULTURE – To strengthen commitment to company’s strategy Study Question 1: What is the external environment of organizations? Competitive advantage is a core competency that clearly sets an organization apart from competitors and gives it an advantage over them in the marketplace. Study Question 2: What is a customerdriven organization? Customer relationship management establishes and maintains high standards of customer service in order to strategically build lasting relationships with and add value to customers. Supply chain management is the strategic management of all operations relating to an organization’s resource suppliers. Study Question 2: What is a customerdriven organization? Customers want: – High quality. – Low price. – On-time delivery. Key customer service lessons: – Protect reputation for quality products. – Treat customers right. Study Question 4: What is organizational culture? Organizational culture is the system of shared beliefs and values that develops within an organization and guides the behavior of its members. CHAPTER 3: THE COMPANY IN SOCIETY • • • • STAKE HOLDERS CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY THE COMPANY’S IMAGE GOVERNMENT INTERVENTION Study Question 4: What is corporate social responsibility? Organizational stakeholders – Those persons, groups, and other organizations directly affected by the behavior of the organization and holding a stake in its performance. Typical organizational stakeholders – – – – – – – Employees Customers Suppliers Owners Competitors Regulators Interest groups Study Question 4: What is corporate social responsibility? Beliefs that guide socially responsible business practices: – People do their best with a balance of work and – – – – family life. Organizations perform best in healthy communities. Organizations gain by respecting the natural environment. Organizations must be managed and led for longterm success. Organizations must protect their reputations. Study Question 5: How do organizations and governments work together in society? How government influences organizations: – Common areas of government regulation of business affairs: • Occupational safety and health • Fair labor practices • Consumer protection • Environmental protection CHAPTER 12: HUMAN CAPITAL • VALUING HUMAN CAPITAL • DEVELOPING STAFF SKILL – Emphasis needed depends on chosen strategy CHAPTER 7: INFORMATION CAPITAL • HOW IT IS CHANGING: – BUSINESS, – ORGANIZATIONS, – AND THE OFFICE. • AGAIN, WHICH SYSTEMS ARE MOST IMPORTANT WILL DEPEND ON THE CHOSEN STRATEGY, THAT MUST BE SUPPORTED How IT Breaks Barriers People, teams and departments are better connected by IT Suppliers Supply chain management is improved by IT connections Organizations are flatter as IT replaces management levels IT Customers breaks barriers Strategic Partners Customer relationship management is improved by IT connections More things are done by outsourcing and partnerships using IT Study Question 1: How is information technology changing the workplace? Information and knowledge — basic linkages: – Knowledge and knowledge workers provide a decisive competitive factor in today’s economy. – Knowledge worker. • Someone whose value to the organization rests with intellect, not physical capabilities. – Intellectual capital. • Shared knowledge of a workforce that can be used to create wealth. Study Question 1: How is information technology changing the workplace? Implications of IT within organizations: – Facilitation of communication and information sharing. – Operating with fewer middle managers. – Flattening of organizational structures. – Faster decision making. – Increased coordination and control. Study Question 1: How is information technology changing the workplace? Implications of IT for relationships with external environment: – Helps with customer relationship management. – Helps organizations with supply chain management. – Helps in monitoring outsourcing and other business contracts. Study Question 1: How is information technology changing the workplace? How IT is changing the office … – Progressive organizations actively use IT to help achieve high performance in uncertain environments. – IT has dramatically changed nature of offices. – Key developments in networked offices: • Instant messaging. • Peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P). CHAPTER 8: PUTTING IT INTO PRACTICE • • • • PLAN FOR SUCCESS CONTROL: MAKE SURE IT HAPPENS MBO TO SECURE STAFF COMMITMENT HOW EACH STRATEGY WILL AFFECT THE BREAK-EVEN POINT What is “Planning”? Planning is a process of… setting objectives and… determining how to accomplish them. Karnak’s Criteria for a Good Objective • Specific • Measurable • Linked to a timetable • Challenging but attainable Study Question 1: How do managers plan? Planning – The process of setting objectives and determining how to best accomplish them. Objectives – Identify the specific results or desired outcomes that one intends to achieve. Plan – A statement of action steps to be taken in order to accomplish the objectives. Study Question 1: How do managers plan? Benefits of planning: – Improves focus and flexibility. – Improves action orientation. – Improves coordination. – Improves time management. – Improves control. Study Question 4: What is the control process? Steps in the control process: – Step 1 — establish objectives and standards. – Step 2 — measure actual performance. – Step 3 — compare results with objectives and standards. – Step 4 — take corrective action as needed. THIS IS THE REAL MBO • Joint objective setting • Individual works • Supervisor supports • Joint review of results Study Question 5: What are the common organizational controls? Management by Objectives (MBO) – A structured process of regular communication. – Supervisor/team leader and workers jointly set performance objectives. – Supervisor/team leader and workers jointly review results. Study Question 5: What are the common organizational controls? Advantages of MBO – Focuses workers on most important tasks and objectives. – Focuses supervisor’s efforts on important areas of support. – Contributes to relationship building. – Gives workers a structured opportunity to participate in decision making. Study Question 5: What are the common organizational controls? Break-even analysis … – Determination of the point at which sales revenues are sufficient to cover costs. – Break-Even Point = Fixed Costs / (Price – Variable Costs) – Used in evaluating: • New products • New program initiatives Total Sales Revenue Break-even Point Revenues = Costs Dollar Costs & Revenues Total Costs = Fixed+Variable Variable Costs Fixed Costs Unit Sales