Ecosystems
advertisement

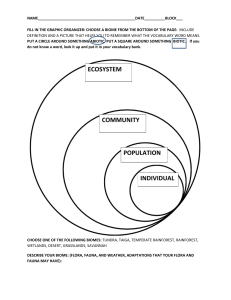
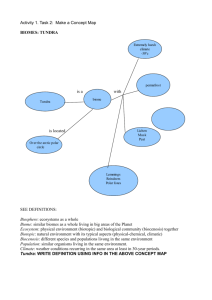
Ecosystems A group of organisms interacting with each other and their environment through a flow of energy and the cycling of matter. • An ecosystem is a natural system consisting of all plants, animals and microorganisms (biotic factors) in an area functioning together with all the non-living physical (abiotic) factors of the environment. Biotic Factors • All living things in an ecosystem. • Examples= • Animals, plants, insects, fish Abiotic • All non-living physical factors of the environment • Examples • Water, Air, Dirt, Rocks Biomes • Large geographic areas that have similar climates and ecosystems. • Seven common types of biomes • 1. Desert, 2. Grassland, 3. Tropical Rainforest, 4. Temperate rainforest, 5. deciduous forest, 6. Taiga, 7. Tundra. Desert • Driest biome • Less than an inch of rain a year • Does not support large plant and animal populations Grassland • Grasslands are characterized as lands dominated by grasses rather than large shrubs or trees. Tropical Rainforest • Tropical forests are characterized by the greatest diversity of species. They occur near the equator. One of the major characteristics of tropical forests is their distinct seasonality: winter is absent, and only two seasons are present (rainy and dry). The length of daylight is 12 hours and varies little. Deciduous Forest • forests occur in eastern North America, northeastern Asia, and western and central Europe. Well-defined seasons with a distinct winter characterize this forest biome. Taiga • Boreal forests, or taiga, represent the largest terrestial biome in the world Tundra • Tundra is the coldest of all the biomes. Tundra comes from the Finnish word tunturi, meaning treeless plain. It is noted for its frost-molded landscapes, extremely low temperatures, little precipitation, poor nutrients, and short growing seasons. Aquatic Ecosystems • Freshwater is defined as having a low salt concentration — usually less than 1%. Plants and animals in freshwater regions are adjusted to the low salt content and would not be able to survive in areas of high salt concentration (i.e., ocean). There are different types of freshwater regions: • Ponds and lakes • Streams and rivers Marine • Marine regions cover about three-fourths of the Earth's surface and include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. Marine algae supply much of the world's oxygen supply and take in a huge amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide. The evaporation of the seawater provides rainwater for the land. • Oceans • Coral reefs • Estuaries Succession • Ecological succession, a fundamental concept in ecology, refers to more-or-less predictable and orderly changes in the composition or structure of an ecological community. Succession may be initiated either by formation of new, unoccupied habitat (e.g., a lava flow or a severe landslide) or by some form of disturbance (e.g. fire, severe windthrow, logging) of an existing community. Ecological Succession