Solving for Absolute Values
advertisement

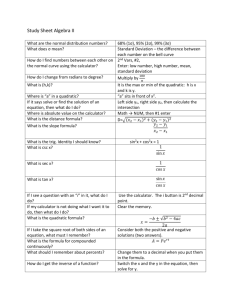
Mr. Visca – Algebra 2 with Trigonometry Finals Class Notes ***FINAL: June _____ @ ___________; Room #: ______________ *** Solving for Absolute Values 1st: Get absolute value by itself; 2nd: drop abs val bars and set equal to both + and – answer; 3rd: solve for each Ex: |2x – 6| + 10 = 22 Inequalities Ex: |2x – 6| + 10 > 22 o Flip sign when negating your one answer Domain and Range Domain = all possible ___________ of equation/graph Range = all possible ____________ of equation/graph Direct/Indirect Variation Direct: Set up 2 _____________ equal to each other, proportions o Ex: Indirect: set up 2 _______________ equal to each other o Ex: Correlation In graph, positive correlation means positive ___________ In graph, negative correlation means negative ___________ Numerically, correlation # should be between -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 IN CALCULATOR: stat edit; stat calc LinReg(ax+b); vars stat EQ r; Trig Functions: Sin Csc (inverse of Sin) = 1/sin Cos Sec (inverse of Cos) = 1/cos Tan = sin/cos Cot (inverse of Tan) = 1/tan OR cos/sin Unit Circle For any point on the unit circle, (x,y), x = __________, and y = ______________ Radians vs Degrees Conversion Radians to Degrees – multiply by Degrees to Radians – multiply by 180 𝜋 𝜋 , then add the o symbol , (careful if π is in radians to start or 180 not!!!) o Simply fraction IN CALCULATOR – math enter enter Graphing Functions: Amplitude – half the distance from the bottom to the top OR from the middle to the top OR from the middle to the bottom Frequency – number of cycles in __________________ Period – distance (in degrees or radians) of __________ o y = a sin bx o a = _____________ ; b = _______________ ; 360/b = __________ Sine, Cos, Tan curves/graphs Moving graphs… Quadratic Regression Just like Linear Regression IN CALCULATOR but use “QuadReg” instead of LinReg; o IN CALCULATOR: stat edit; stat calc QuadReg(ax+b); Completing the Square: Steps: 1) get your x’s alone on one side 2) divide by number in front of x2 if you 3) take number in front of x (not x2), divide it by 2 then square it 4) take the number from step 3 and add it to both sides, not proceed to solve Ex) 3x2 + 12x + 6 = 0 The Quadratic Formula: x= Ex. x2 + 9x + 20 = 0 The imaginery # a negative under the radial o √−16 √−50 i0 = _______ i1 = _______ i2 = _______ i3 = _______ Binomial Theorem Expand: (2a + b)4 Radicals Simplifying exponents under radical, even numbers, divide by 2 o √16𝑥 4 √18𝑥 7 𝑦 5 Simplify fractions w radical in bottom (composite) o Rational Exponents o 𝑥 3 4 Multiple Functions (f○g)(5) f(x) = 2x + 1 g(x) = x – 2 Inverse functions: just switch x and y and solve for y Logs: Natural logs (Ln) – brings exponent down o 32 = 2 𝑥 3 Logs: 52 = 25 is equivalent to log525 = 2 Properties: simplify: Trig Identities: The expression (sec2Ө) (cot2Ө)(sinӨ) is equivalent to: Remember to check your reference sheet on the exam; it will contain a lot of your trig identities! Area of Triangle, Law of Sines and Law of Cosines are all on reference sheet 1 o Area∆ = 𝑎𝑏𝑆𝑖𝑛𝐶 2 o Law of sines: 𝑎 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝐴 = o Law of cosines: 𝑐 = 𝑏 = 𝑐 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝐵 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝐶 √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 − 2𝑎𝑏𝐶𝑜𝑠𝐶 Probability Permutations – order matters, no repetition 𝑛! o nPr = (𝑛−𝑟)! Combinations – order doesn’t matter o nCr = 𝑛! 𝑟!(𝑛−𝑟)! Permutation and Combinations in calculators: math, PRB Binomial Probability: o nCrprq(n-r) + nC(r+1)pr+1q(n-r+1) + nC(r+2)pr+2q(n-r+2) + ... o p = percent, q = percent to not happen (1 – p) Standard Deviation / Normal Bell Curve enter info in calculator… o enter data in stat, edit o stat, calc, 1-var stats, calculate Sx – is standard deviation for SAMPLE DATA σx – is standard deviation for POPULATION DATA o to get sample or population variance, just square the Sx or σx Standard Bell Curve should be on reference sheet Series and Sequence Series – a number pattern o Arithmetic – common difference that is constant between all numbers o Geometric – common ratio, numbers are separated by some ratio or multiple Can just count or use calculator o Set mode to “SEQ” o “y=”, nMin = 1, u(n) is your equation to your number pattern o Look at the table to see all your numbers in that pattern Series o The sum of a sequence o You SHOULD use calculator Math, then option “0”